At its core, the purpose of a rotating disk electrode (RDE) is to create a highly controlled and reproducible flow of solution to a working electrode's surface. This forced flow, or convection, allows researchers to overcome the limitations of passive diffusion and precisely study the fundamental speed (kinetics) and mechanisms of electrochemical reactions.
In a standard, stationary experiment, the speed of your measurement is often limited by how fast reactants can randomly diffuse to the electrode. An RDE eliminates this ambiguity by using rotation to create a constant, predictable supply of reactants, turning mass transport from an uncontrolled variable into a precise experimental knob.

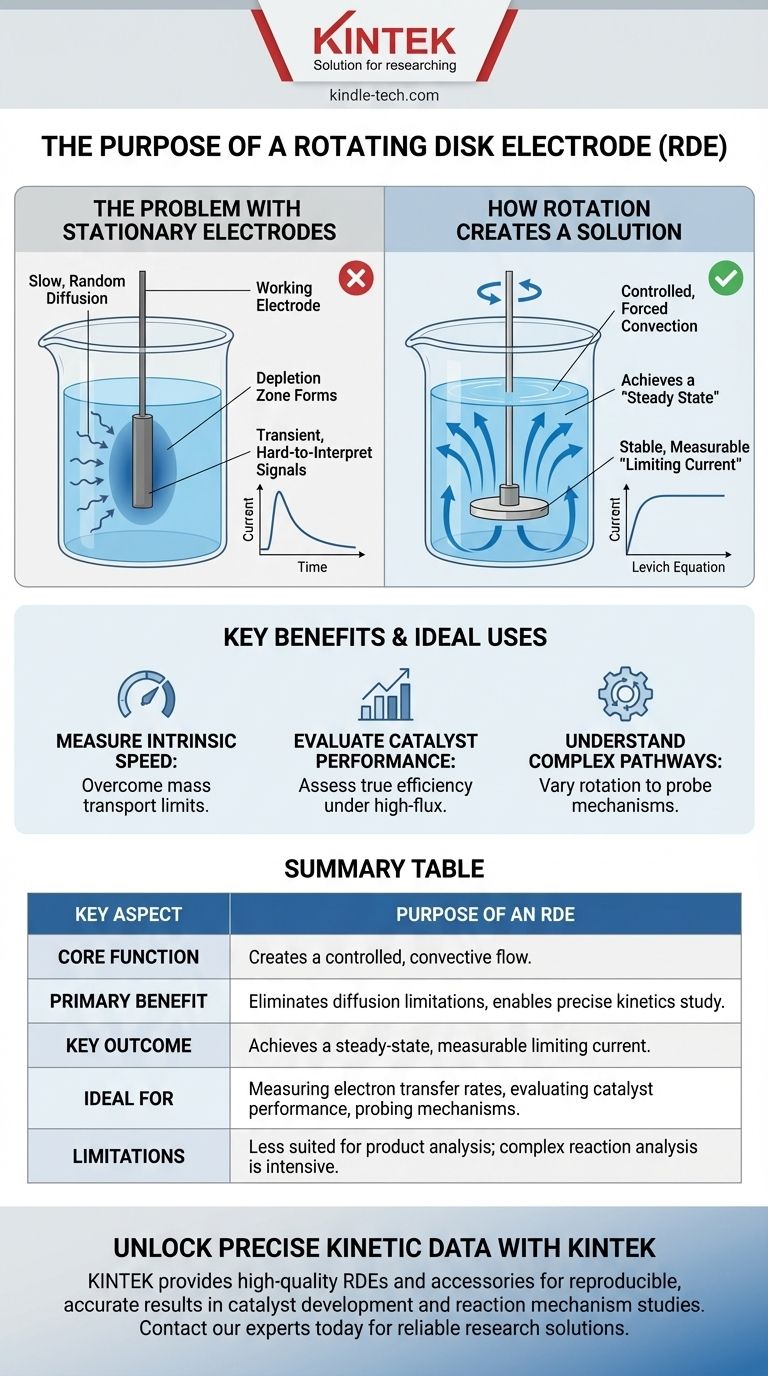
The Problem with Stationary Electrodes
To understand the value of an RDE, you must first appreciate the limitations of a standard, stationary electrode in a quiet solution.
The Dominance of Uncontrolled Diffusion
In a still solution, reactants only reach the electrode surface through diffusion—a slow, random process. This makes the rate at which reactants arrive inconsistent and difficult to quantify.
The Formation of a Depletion Zone
As the reaction consumes reactants near the electrode, a "depletion zone" forms. This zone of lower concentration acts as a bottleneck, further slowing the arrival of new reactants and obscuring the true rate of the reaction itself.
Transient, Hard-to-Interpret Signals
This diffusion-limited process results in the familiar peak-and-decay shape of a standard cyclic voltammogram. The current is constantly changing as the depletion zone grows, making it difficult to extract stable, quantitative data about the reaction's intrinsic speed.
How Rotation Creates a Solution
The RDE systematically solves these problems by introducing controlled, forced convection.
From Diffusion to Convection
The spinning motion of the electrode disk actively pulls fresh solution from the bulk towards its surface and then flings it outwards. This convective flow is far more efficient and powerful than passive diffusion.
Achieving a "Steady State"
This constant, forceful supply of reactants replenishes what is being consumed by the reaction. This effectively prevents the formation of a significant depletion zone and creates a stable equilibrium known as a steady state.
A Stable, Measurable Current
At this steady state, the current stops changing and forms a stable plateau, called the limiting current. This current is directly and predictably related to the analyte concentration and, most importantly, the electrode's rotation rate. This relationship is mathematically described by the Levich equation.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, the RDE is a specialized tool, and its use involves specific considerations.
It Is Not a Universal Tool
The RDE is designed specifically for studying reaction kinetics and mechanisms. For simpler applications, like merely detecting a substance's presence or its bulk concentration, a stationary electrode setup is often more than sufficient.
Product Analysis is Different
Because the rotation continually sweeps reaction products away from the electrode surface, it is less suited for studying the properties of those products or their subsequent reactions compared to cyclic voltammetry on a stationary electrode.
Analysis Can Be Complex
While the concept is elegant, modeling the data for more complicated, multi-step reactions can be mathematically intensive. These scenarios often require numerical simulations to fully interpret the results.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Using an RDE is a deliberate choice to gain specific information about a reaction's fundamental properties.
- If your primary focus is measuring the intrinsic speed of an electron transfer: The RDE is essential, as it allows you to increase the mass transport until it is no longer the rate-limiting step, revealing the true kinetic rate.
- If your primary focus is evaluating a catalyst's performance: The RDE provides the controlled, high-flux conditions needed to push a catalyst to its limit and assess its true turnover frequency and efficiency.
- If your primary focus is understanding a complex reaction pathway: Varying the rotation rate is a powerful method for probing multi-step mechanisms, identifying intermediates, and determining the rate-limiting step of the overall process.
- If your primary focus is simple qualitative or quantitative analysis: A stationary electrode setup is typically simpler, more practical, and provides the necessary information without the added complexity of hydrodynamics.
By transforming mass transport from a messy variable into a precise control, the rotating disk electrode empowers you to look past diffusion and observe the true kinetic behavior of your electrochemical system.
Summary Table:
| Key Aspect | Purpose of a Rotating Disk Electrode (RDE) |
|---|---|
| Core Function | Creates a controlled, convective flow to the electrode surface. |
| Primary Benefit | Eliminates diffusion limitations, enabling precise study of reaction kinetics. |
| Key Outcome | Achieves a steady-state, measurable limiting current. |
| Ideal For | Measuring electron transfer rates, evaluating catalyst performance, probing reaction mechanisms. |
| Limitations | Less suited for product analysis; data interpretation can be complex for multi-step reactions. |
Ready to unlock precise kinetic data for your electrochemical research?
At KINTEK, we specialize in providing high-quality lab equipment, including rotating disk electrodes and accessories, to help you achieve reproducible and accurate results. Whether you are developing new catalysts or studying complex reaction mechanisms, our solutions are designed to meet the demanding needs of your laboratory.
Contact our experts today to discuss how KINTEK can support your research goals with reliable equipment and consumables.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Disc Rotary Mixer for Efficient Sample Mixing and Homogenization
- Electrolytic Electrochemical Cell for Coating Evaluation
- Custom PTFE Teflon Parts Manufacturer for PTFE Mesh F4 Sieve
- Laboratory Vibratory Sieve Shaker Machine Slap Vibrating Sieve
- Ring Press Mold for Lab Applications
People Also Ask
- What function does a high-speed rotor-stator homogenizer perform in biomass processing? Optimize Structural Disruption
- What is grinder in chemistry? A Guide to Precision Sample Preparation
- How does a high-efficiency homogenizing mixer contribute to the preparation of Tobermorite and Xonotlite precursors?
- What is the function of high-shear dispersion equipment in corona-resistant nanocomposites? Elevate Your Insulation
- How does a constant temperature rotary shaker contribute to evaluating iron nanoparticles? Optimize Dye Degradation






