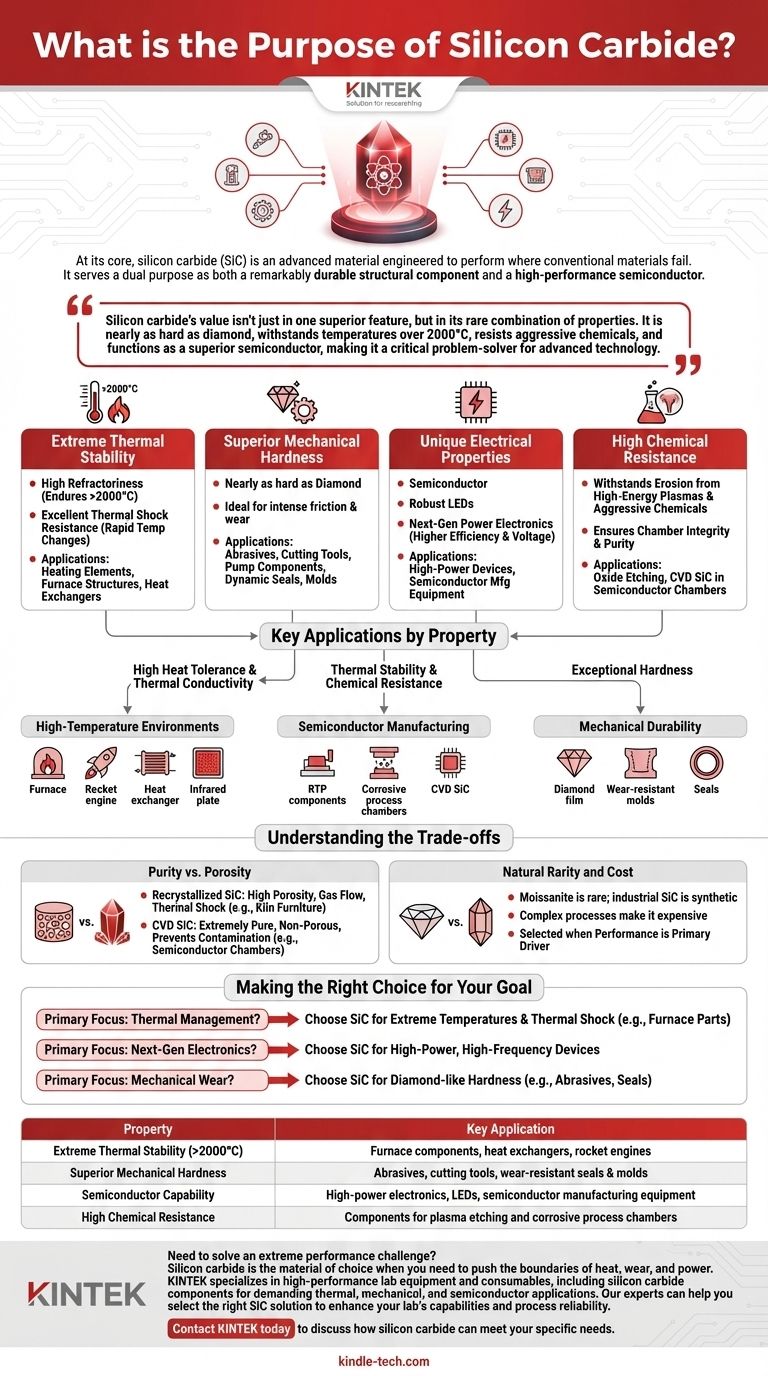
At its core, silicon carbide (SiC) is an advanced material engineered to perform where conventional materials fail. It serves a dual purpose as both a remarkably durable structural component and a high-performance semiconductor. Its primary function is to provide extreme resistance to heat, wear, and chemical attack in demanding environments, from industrial furnaces and rocket engines to the microscopic world of semiconductor fabrication.
Silicon carbide's value isn't just in one superior feature, but in its rare combination of properties. It is nearly as hard as diamond, withstands temperatures over 2000°C, resists aggressive chemicals, and functions as a superior semiconductor, making it a critical problem-solver for advanced technology.
The Foundation: Why is Silicon Carbide So Versatile?
The purpose of silicon carbide becomes clear when you understand its fundamental properties. It isn't used because it's a general-purpose replacement for steel or plastic; it's chosen specifically for its ability to overcome extreme challenges.
Extreme Thermal Stability
Silicon carbide has a very high refractoriness, meaning it maintains its strength and structure at temperatures exceeding 2000°C.
It also possesses excellent thermal shock resistance, allowing it to endure rapid temperature changes without cracking. This is why it's essential for components like heating elements and the internal structures of high-temperature furnaces.
Superior Mechanical Hardness
Historically, the primary use of SiC was in abrasives like sandpaper and cutting tools. This is a direct result of its exceptional hardness, which is surpassed only by a few materials like diamond.
This property makes it ideal for parts that experience intense friction and wear, such as pump components, dynamic seals, and molds.
Unique Electrical Properties
Unlike many other ceramics, silicon carbide is a semiconductor. This single property unlocks its use in modern electronics.
It serves as a substrate for building robust Light-Emitting Diodes (LEDs) and is a key material in creating the next generation of power electronics that are more efficient and can handle higher voltages.
High Chemical Resistance
In semiconductor manufacturing, silicon carbide components are used inside processing chambers for applications like oxide etching.
This is because SiC can withstand erosion from the high-energy plasmas and aggressive chemicals used in these processes, ensuring chamber integrity and process purity.
Key Applications by Property
Different industries leverage specific aspects of SiC's profile. Understanding this helps clarify its role in technology.
For High-Temperature Environments
The combination of high heat tolerance and high thermal conductivity makes SiC a premier material for thermal management.
Applications include furnace muffles, floors, and guide rails, as well as high-efficiency heat exchangers and combustion nozzles. Its high blackness (emissivity) also makes it effective for far-infrared heating plates.
For Semiconductor Manufacturing
Here, both thermal stability and chemical resistance are vital. Chamber components, like those used for Rapid Thermal Processing (RTP), must remain stable at high temperatures while resisting corrosive process chemistries.
The use of CVD (Chemical Vapor Deposition) silicon carbide is common in these applications because the process creates an exceptionally pure and resilient material.
For Mechanical Durability
Beyond simple abrasives, SiC is used in parts designed for longevity under harsh conditions, including rocket engine components.
To further enhance its performance, a diamond film can be deposited on a silicon carbide surface, creating an incredibly wear-resistant component ideal for molds and seals.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, SiC is not a universal solution. Its application is a deliberate engineering choice based on performance requirements.
Purity vs. Porosity
The manufacturing method determines the final properties. Recrystallized silicon carbide, for instance, has high porosity and is excellent for applications like kiln furniture or nozzles where gas flow and thermal shock are key.
In contrast, SiC used in semiconductor chambers is made via processes like CVD to be extremely pure and non-porous, preventing contamination.
Natural Rarity and Cost
Naturally occurring silicon carbide, known as moissanite, is incredibly rare. Therefore, virtually all SiC used in industry is synthetic.
The complex and energy-intensive processes required to produce high-quality SiC make it significantly more expensive than traditional materials. It is selected when performance, not cost, is the primary driver.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To determine if silicon carbide is the right material, you must align its properties with your primary objective.
- If your primary focus is thermal management: SiC is the solution for applications demanding stability at extreme temperatures and resistance to thermal shock, such as furnace components or heat exchangers.
- If your primary focus is next-gen electronics: SiC's semiconductor properties are essential for creating high-power, high-frequency devices and the robust equipment needed to manufacture them.
- If your primary focus is mechanical wear and durability: SiC offers hardness approaching that of a diamond, making it the clear choice for abrasive tools, long-lasting seals, and other components exposed to intense friction.
Ultimately, silicon carbide is the material of choice when you need to push the boundaries of performance in heat, durability, and power.
Summary Table:
| Property | Key Application |
|---|---|
| Extreme Thermal Stability (>2000°C) | Furnace components, heat exchangers, rocket engines |
| Superior Mechanical Hardness | Abrasives, cutting tools, wear-resistant seals & molds |
| Semiconductor Capability | High-power electronics, LEDs, semiconductor manufacturing equipment |
| High Chemical Resistance | Components for plasma etching and corrosive process chambers |
Need to solve an extreme performance challenge?
Silicon carbide is the material of choice when you need to push the boundaries of heat, wear, and power. KINTEK specializes in high-performance lab equipment and consumables, including silicon carbide components for demanding thermal, mechanical, and semiconductor applications.
Our experts can help you select the right SiC solution—whether it's for furnace parts, durable tooling, or specialized chamber components—to enhance your lab's capabilities and process reliability.
Contact KINTEK today to discuss how silicon carbide can meet your specific needs.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Silicon Carbide (SIC) Ceramic Sheet Wear-Resistant Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics
- Precision Machined Silicon Nitride (SiN) Ceramic Sheet for Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics
- Silicon Carbide SiC Thermal Heating Elements for Electric Furnace
- Engineering Advanced Fine Alumina Al2O3 Ceramic Rod Insulated for Industrial Applications
- Precision Machined Zirconia Ceramic Ball for Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics
People Also Ask
- What are the characteristics of SiC? Unlock High-Temp, Hard, and Chemically Inert Performance
- Is silicon carbide heat resistant? Unlock Superior Performance in Extreme Temperatures
- Is silicon carbide better than ceramic? Discover the Superior Technical Ceramic for Your Application
- What is the resistivity of silicon carbide? It's a tunable property from <0.1 ohm-cm to highly resistive.
- What are the properties of SiC? Unlock High-Temperature, High-Frequency Performance



















