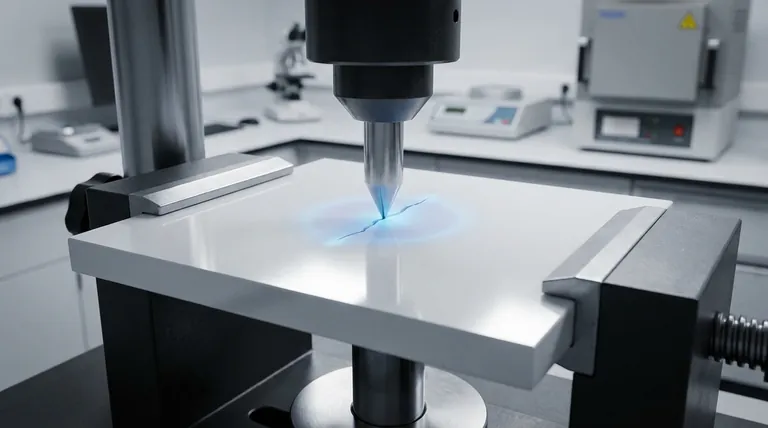
In material science, the strongest and toughest phase of zirconia is the tetragonal phase, specifically when it is stabilized in a polycrystalline form (TZP). Its exceptional performance isn't due to inherent static strength alone, but rather a dynamic, stress-activated mechanism called transformation toughening. This unique property allows the material to actively resist crack propagation, making it incredibly durable for high-stress applications.
The core reason for tetragonal zirconia's strength is its ability to change its crystal structure under stress. This transformation absorbs energy and creates localized compressive forces that literally squeeze a forming crack shut, halting its growth.
The Three Phases of Zirconia: A Primer
Zirconium dioxide (ZrO2), or zirconia, is an allotropic material, meaning it can exist in different crystal structures, known as phases, depending on temperature and pressure. Understanding these three primary phases is essential to understanding its properties.
Monoclinic (M)
The monoclinic phase is the most stable form of zirconia at room temperature and up to approximately 1170°C. Pure zirconia exists in this phase naturally. While stable, it is significantly more brittle and lacks the high mechanical strength of the other phases.
Tetragonal (T)
The tetragonal phase is the high-strength, metastable phase. It is naturally stable only at high temperatures (between 1170°C and 2370°C). To be useful in engineering applications, it must be "trapped" in this state at room temperature by adding stabilizing oxides like yttria (Y₂O₃). This is the key to materials like Yttria-stabilized Tetragonal Zirconia Polycrystal (Y-TZP).
Cubic (C)
The cubic phase is stable at even higher temperatures (above 2370°C). Like the tetragonal phase, it can be stabilized at room temperature with sufficient additives. Cubic zirconia is less strong and hard than tetragonal zirconia but offers superior optical clarity and ionic conductivity, which is why it is used for gemstones (cubic zirconia) and in applications like oxygen sensors.
The Mechanism Behind Tetragonal Zirconia's Strength
The remarkable properties of Y-TZP are not just about the tetragonal phase itself, but about its potential to transform.
What is Transformation Toughening?
This is the central phenomenon behind zirconia's toughness. In stabilized tetragonal zirconia, the grains are held in a metastable state—like a compressed spring, ready to release energy.
When a microscopic crack begins to form and propagate through the material, the intense stress concentrated at the crack's tip provides the energy needed to trigger a phase change.
Volume Expansion: The Crack-Stopping Force
The triggered phase change is a transformation from the tetragonal structure to the more stable monoclinic structure. Crucially, the monoclinic phase has a volume that is 3-5% larger than the tetragonal phase.
This localized volume expansion creates a powerful compressive stress field directly around the crack tip. This compressive force works against the tensile stress that is pulling the crack open, effectively squeezing the crack shut and blunting it. This process absorbs a significant amount of the fracture energy, dramatically increasing the material's resistance to catastrophic failure.
The Role of Stabilizers (Yttria)
Without a stabilizer, the tetragonal phase would immediately revert to the monoclinic phase as it cools from its sintering temperature. The resulting uncontrolled volume change would cause the material to shatter.
Stabilizers like yttria precisely control this process, allowing the tetragonal phase to be retained at room temperature in its high-energy, metastable state, ready to transform only when needed at the tip of a crack.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
While incredibly strong, tetragonal zirconia is not a perfect material. Its properties come with critical trade-offs that dictate its use.
Strength vs. Translucency
There is a direct trade-off between fracture toughness and optical properties. The fine-grained, dense structure of Y-TZP that enables transformation toughening also scatters light, making it relatively opaque.
Materials with a higher concentration of the cubic phase (like 5Y-TZP, often called "translucent zirconia") are more aesthetic but have significantly lower strength and fracture toughness because there are fewer tetragonal grains available to halt cracks.
The Risk of Low-Temperature Degradation (LTD)
Over time, especially in the presence of water or humidity, the metastable tetragonal phase can slowly and spontaneously transform into the monoclinic phase on the material's surface. This phenomenon, also known as aging, can create surface micro-cracking and degrade the material's strength.
The composition and manufacturing process must be carefully controlled to minimize susceptibility to this long-term degradation, which is a major concern for permanent medical implants.
Selecting the Right Zirconia for Your Application
The choice of zirconia phase is not about finding the "best" one, but the most appropriate one for a specific engineering goal.
- If your primary focus is maximum fracture toughness and mechanical strength: A 3Y-TZP formulation with a high concentration of metastable tetragonal grains is the clear choice for load-bearing structural components or dental frameworks.
- If your primary focus is aesthetics and translucency: A zirconia with more cubic phase stabilizers, such as 5Y-TZP, is the ideal selection for applications like monolithic anterior dental crowns where appearance is paramount.
- If your primary focus is balancing strength and appearance: A hybrid formulation, such as 4Y-TZP, provides a compromise, offering better translucency than 3Y-TZP while retaining higher strength than 5Y-TZP.
Understanding the interplay between these crystalline phases is the key to successfully harnessing the full potential of this advanced ceramic.
Summary Table:
| Zirconia Phase | Stability Temperature | Key Characteristics | Common Applications |
|---|---|---|---|
| Monoclinic (M) | Room temp to ~1170°C | Brittle, stable at room temp | Limited engineering use |
| Tetragonal (T) | 1170°C to 2370°C | High strength, toughness (via transformation toughening) | Dental implants, cutting tools, industrial components |
| Cubic (C) | Above 2370°C | High optical clarity, ionic conductivity | Gemstones, oxygen sensors |
Need the right zirconia material for your application?
At KINTEK, we specialize in providing high-performance lab equipment and consumables, including advanced ceramic materials like yttria-stabilized tetragonal zirconia (Y-TZP). Whether you're developing dental implants, industrial components, or research prototypes, our expertise ensures you get the optimal material for maximum strength, toughness, and reliability.
Let us help you select the perfect zirconia grade for your needs. Contact our experts today for a consultation!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom-Made Alumina Zirconia Special-Shaped Ceramic Plates for Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics Processing
- Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics Head Tweezers with Pointed Elbow Zirconia Ceramic Tip
- Precision Machined Zirconia Ceramic Ball for Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics
- Precision Machined Yttria Stabilized Zirconia Ceramic Plate for Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics
- Zirconia Ceramic Gasket Insulating Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics
People Also Ask
- What are the strengths of brazing? Achieve Strong, Clean, and Precise Metal Joining
- What are the three types of coating? A Guide to Architectural, Industrial, and Special Purpose
- How many types of hardening techniques are there? A Multi-Layered Security Strategy Explained
- What is the main difference between soldering and brazing? Choose the Right Metal Joining Method
- What function do alumina ceramic plates serve as supports in the preparation of molecular sieve membranes?



















