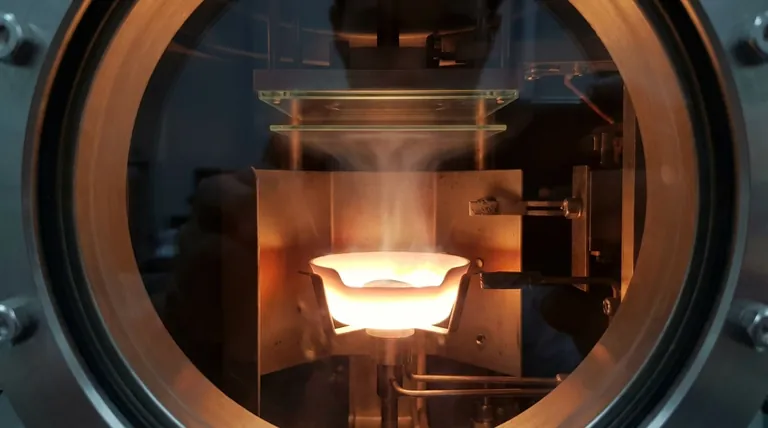
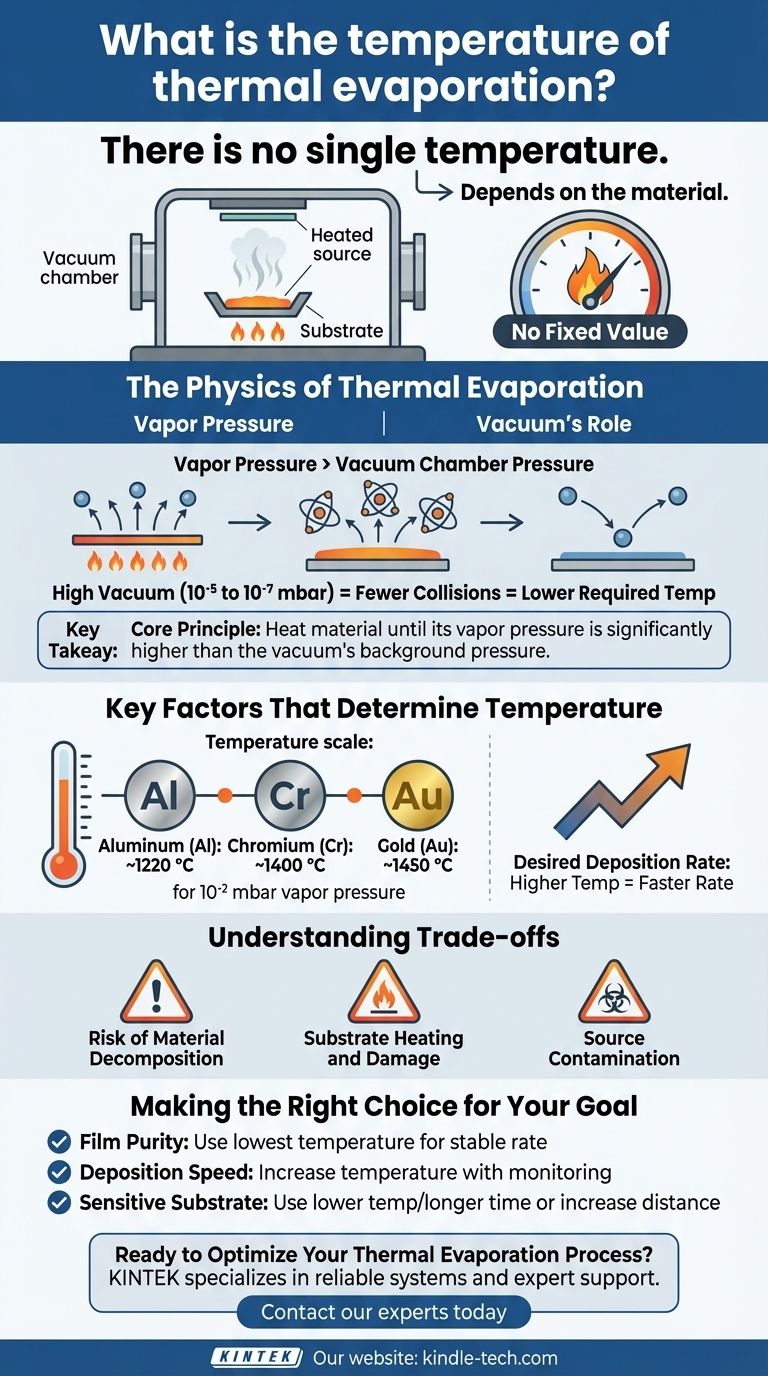
There is no single temperature for thermal evaporation. The required temperature is entirely dependent on the specific material being deposited. For example, evaporating aluminum requires a different temperature than evaporating gold, as each element has a unique point at which it generates sufficient vapor in a vacuum.
The core principle is not about reaching a fixed temperature, but about heating a material until its vapor pressure is significantly higher than the pressure of the surrounding vacuum chamber. This temperature-driven pressure difference is what allows atoms to leave the source and coat your substrate.

The Physics of Thermal Evaporation
To truly understand the process, we must look beyond a simple temperature value and focus on the interplay between the material, heat, and the vacuum environment.
What is Vapor Pressure?
Vapor pressure is the natural pressure exerted by the vapor of a substance in a closed system. All materials, even solids like metals, have a vapor pressure.
This pressure increases dramatically with temperature. As you heat a material, you give its atoms more energy, making it easier for them to escape the surface.
How Temperature Drives Deposition
In thermal evaporation, the goal is to create a stream of vapor flowing from the source material to the substrate.
This is achieved by heating the source material until its vapor pressure is much higher than the chamber's background pressure. This pressure differential creates the necessary flow of atoms for deposition.
The Critical Role of Vacuum
A high-vacuum environment (typically 10⁻⁵ to 10⁻⁷ mbar) is essential for two reasons.
First, it removes air and other gas particles that would collide with the evaporated atoms, preventing them from reaching the substrate. This ensures a "mean free path" long enough for a clean deposition.
Second, by drastically lowering the ambient pressure, you make it possible to achieve the required vapor pressure at a much lower, more manageable temperature than you would need at atmospheric pressure.
Key Factors That Determine Evaporation Temperature
The specific temperature you need is a variable that depends on several critical process parameters.
The Source Material
This is the most significant factor. Materials with higher melting points and stronger atomic bonds generally require higher temperatures to generate sufficient vapor pressure.
For example, a common target is to achieve a vapor pressure of about 10⁻² mbar.
- Aluminum (Al): Reaches this pressure around 1220 °C.
- Chromium (Cr): Reaches this pressure around 1400 °C.
- Gold (Au): Reaches this pressure around 1450 °C.
The Desired Deposition Rate
If you need to deposit a film more quickly, you must increase the evaporation rate.
This is done by raising the source temperature further, which increases the material's vapor pressure and, consequently, the flow of atoms toward the substrate.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Simply increasing the temperature is not always the best solution, as it introduces potential complications.
Risk of Material Decomposition
Some complex compounds or alloys can decompose or break apart if heated too aggressively. The material might break down into its constituent elements rather than evaporating as a uniform molecule, ruining the film's properties.
Substrate Heating and Damage
The hot evaporation source radiates significant heat. This can damage sensitive substrates, such as plastics or organic electronics, that cannot withstand high temperatures.
Source Contamination
At very high temperatures, the heated boat or crucible holding the source material can begin to react with or evaporate itself. This can introduce impurities from the holder (e.g., tungsten, molybdenum) into your deposited thin film.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The optimal temperature is a carefully balanced process parameter, not a fixed number. Your specific goal determines how you should approach it.
- If your primary focus is film purity: Use the lowest temperature that provides a stable and acceptable deposition rate to minimize the risk of source contamination.
- If your primary focus is deposition speed: Carefully increase the temperature while monitoring film quality and potential substrate damage.
- If your primary focus is coating a sensitive substrate: Use a lower source temperature for a longer time, or increase the distance between the source and the substrate to reduce radiative heating.
Ultimately, temperature is the primary control variable used to achieve the desired outcome in any thermal evaporation process.
Summary Table:
| Material | Approx. Temperature for 10⁻² mbar Vapor Pressure |
|---|---|
| Aluminum (Al) | ~1220 °C |
| Chromium (Cr) | ~1400 °C |
| Gold (Au) | ~1450 °C |
Ready to Optimize Your Thermal Evaporation Process?
Choosing the right temperature is critical for achieving high-purity, uniform thin films. KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables, providing the reliable thermal evaporation systems and expert support you need to master your deposition parameters.
Contact our experts today to discuss your specific material and application requirements. Let us help you achieve superior coating results, whether your priority is film purity, deposition speed, or protecting sensitive substrates.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition RF PECVD
- Molybdenum Tungsten Tantalum Evaporation Boat for High Temperature Applications
- Evaporation Boat for Organic Matter
- Hemispherical Bottom Tungsten Molybdenum Evaporation Boat
- Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment System Chamber Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
People Also Ask
- Why is an alumina boat selected for catalyst precursors? Ensure Sample Purity at 1000 °C
- What is the function of electron coating? Boost Your Device's Electrical & Optical Performance
- How do you thin film deposition? Choosing the Right Method for Your Material's Performance
- What are two common ways to heat the source material in evaporation? Resistive vs. E-Beam Methods
- What is thermal vapour deposition? A Simple Guide to PVD Coating Technology
- What precautions should be taken during evaporation process? Ensure High-Quality Film Deposition
- What is the difference between thermal evaporation and e beam evaporation? Choose the Right Method for Your Thin Film
- What is an example of thermal evaporation? Creating Reflective Headlight Coatings and More



















