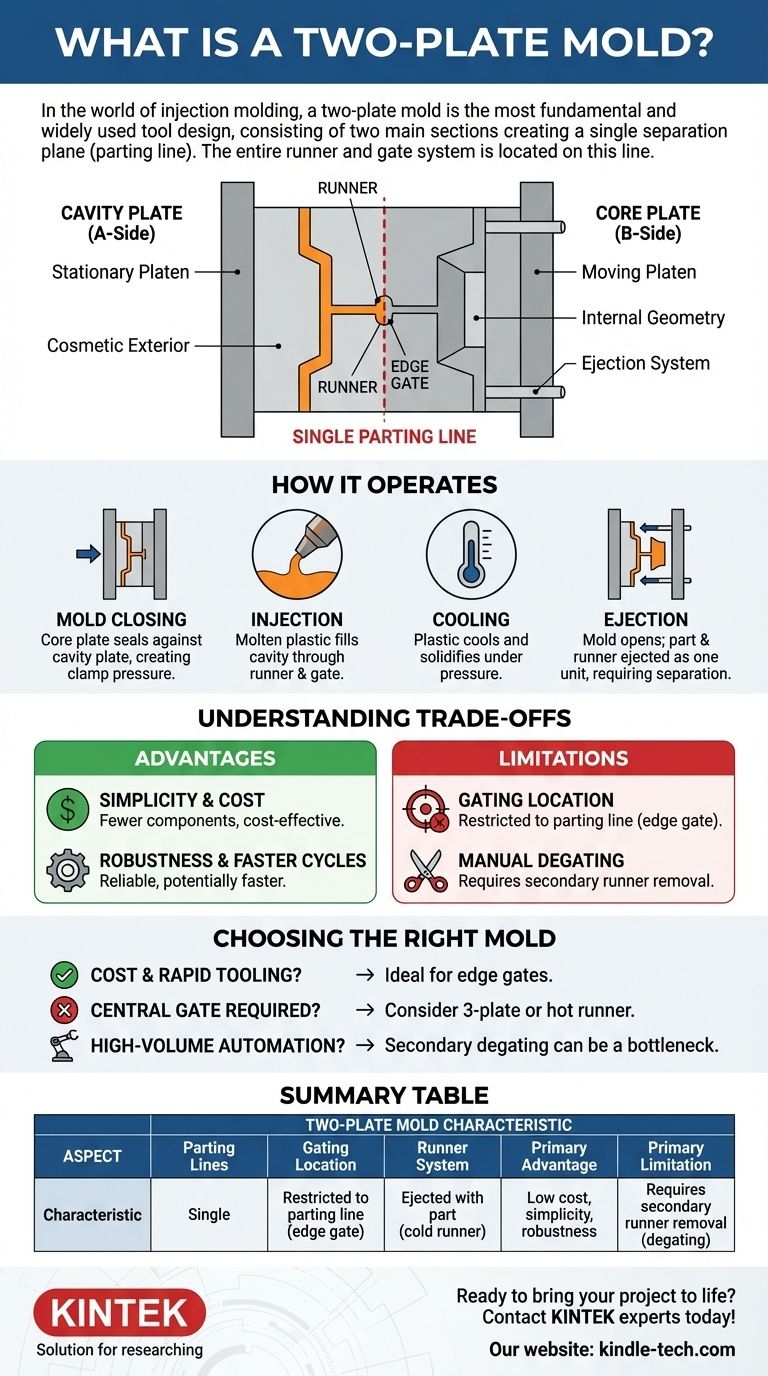
In the world of injection molding, a two-plate mold is the most fundamental and widely used tool design. It consists of two main sections, a cavity side (A-side) and a core side (B-side), which meet to form a single separation plane, known as the parting line. The entire system for delivering plastic—the runner and gate—is located on this parting line, meaning the part and its attached runner are ejected together.
The core principle of a two-plate mold is its simplicity. By having only one parting plane, the design is straightforward and cost-effective, but this simplicity also restricts where the plastic can be injected and often requires manual removal of the runner system.

The Anatomy of a Two-Plate Mold
To understand its function, you must first understand its core components. The design is elegant in its simplicity, with every part serving a direct purpose.
The Core and Cavity Plates
A two-plate mold is constructed from two primary halves. The cavity plate, or "A-side," typically forms the cosmetic exterior of the part and is mounted on the stationary platen of the injection molding machine.
The core plate, or "B-side," forms the internal geometry of the part and contains the ejection system. This half is mounted on the moving platen.
The Single Parting Line
This is the defining characteristic of a two-plate mold. The parting line is the single surface where the core and cavity plates meet. When the molding cycle is complete, the mold separates only along this plane.
The Runner and Gate System
The runner is a channel machined into the surface of the parting line that guides molten plastic from the machine's nozzle to the part.
The gate is the small, localized opening where the runner meets the part cavity. In a two-plate mold, the gate must be located directly on the parting line, typically on the edge of the part. This is often called an "edge gate."
The Ejection System
Housed within the core (B-side) of the mold, the ejection system consists of pins or other mechanisms. After the part has cooled and the mold opens, these pins push forward to eject the finished part and its attached runner system.
How a Two-Plate Mold Operates
The operational cycle is direct and efficient, broken down into four clear stages.
Stage 1: Mold Closing
The moving platen pushes the core plate forward until it seals tightly against the stationary cavity plate, creating a high-pressure clamp along the parting line.
Stage 2: Injection
Molten plastic is injected under high pressure. It travels through the runner system and enters the cavity through the gate until the part is fully formed.
Stage 3: Cooling
The plastic is held under pressure and allowed to cool and solidify within the mold, taking on the shape of the cavity.
Stage 4: Ejection
The moving platen retracts, separating the mold at the parting line. The part and its attached runner stick to the core side until the ejection system activates, pushing them out as a single unit. The runner must then be manually or robotically separated from the part.
Understanding the Trade-offs
The simplicity that makes the two-plate mold so common also introduces specific limitations. Understanding these trade-offs is critical for making sound design and manufacturing decisions.
Advantage: Simplicity and Cost
With fewer components and a simpler mechanical action, two-plate molds are the most cost-effective to design, manufacture, and maintain. Their reliability is a direct result of this simplicity.
Advantage: Robustness and Faster Cycles
Fewer moving parts mean fewer potential points of failure. The simple open-and-close action can also lead to faster cycle times compared to more complex mold designs.
Limitation: Gating Location
Because the gate must be on the parting line, you are restricted to placing it on the perimeter of the component. This leaves a small but visible mark (vestige) where the gate is trimmed, which may be unacceptable for highly cosmetic surfaces.
Limitation: Manual or Secondary Degating
The part is ejected with the runner still attached, much like a part in a model airplane kit. This requires a secondary operation—either manual labor or a robotic process—to separate the runner from the finished part, adding to cycle time and labor costs.
Choosing the Right Mold for Your Part
The decision to use a two-plate mold hinges on balancing cost, part design, and production requirements.
- If your primary focus is cost-effectiveness and rapid tooling: A two-plate mold is almost always the correct choice, especially for parts where a small gate mark on the edge is acceptable.
- If your part requires a central gate for structural integrity or flow dynamics: A two-plate design is unsuitable, and you should explore a three-plate or hot runner mold.
- If your primary focus is fully automated, high-volume production: The need for secondary degating can be a bottleneck, making more complex molds with automatic runner separation a better long-term investment.
Understanding the fundamental trade-offs of this foundational design empowers you to make an informed decision that aligns with your project's technical and financial goals.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Two-Plate Mold Characteristic |
|---|---|
| Parting Lines | Single parting line |
| Gating Location | Restricted to the parting line (edge gate) |
| Runner System | Ejected with the part (cold runner) |
| Primary Advantage | Low cost, simplicity, and robustness |
| Primary Limitation | Requires secondary runner removal (degating) |
Ready to bring your injection molding project to life? Choosing the right mold design is critical for balancing cost, quality, and production efficiency. At KINTEK, we specialize in providing the lab equipment and consumables needed to support your R&D and production processes. Our expertise can help you select the optimal tooling strategy for your specific part design and volume requirements. Contact our experts today to discuss how we can support your laboratory and manufacturing goals!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Isostatic Molding Pressing Molds for Lab
- Cylindrical Press Mold for Lab Applications
- Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Heated Plates for Vacuum Box Laboratory Hot Press
- Custom PTFE Wafer Holders for Lab and Semiconductor Processing
- Lab Internal Rubber Mixer Rubber Kneader Machine for Mixing and Kneading
People Also Ask
- What is the function of a graphite mold during the vacuum hot pressing sintering process? Optimize Composite Performance
- What are the factors affecting molding? Master the 4 Keys to Perfect Plastic Parts
- What is a three-up mold? Boost Production Efficiency with Multi-Cavity Tooling
- What are the different types of compression molding? BMC vs. SMC and Mold Design Explained
- Why Use a Copper Mold for NiCoFeCr Alloys? Key to Achieving Uniform Microstructure in HEAs
- What are the disadvantages of three plate mould? Higher Costs, Complexity & Maintenance
- What are the functions of high-purity graphite molds in SPS? Essential Roles in Spark Plasma Sintering
- What are the advantages of a three plate mold? Achieve Superior Gating and Part Quality












