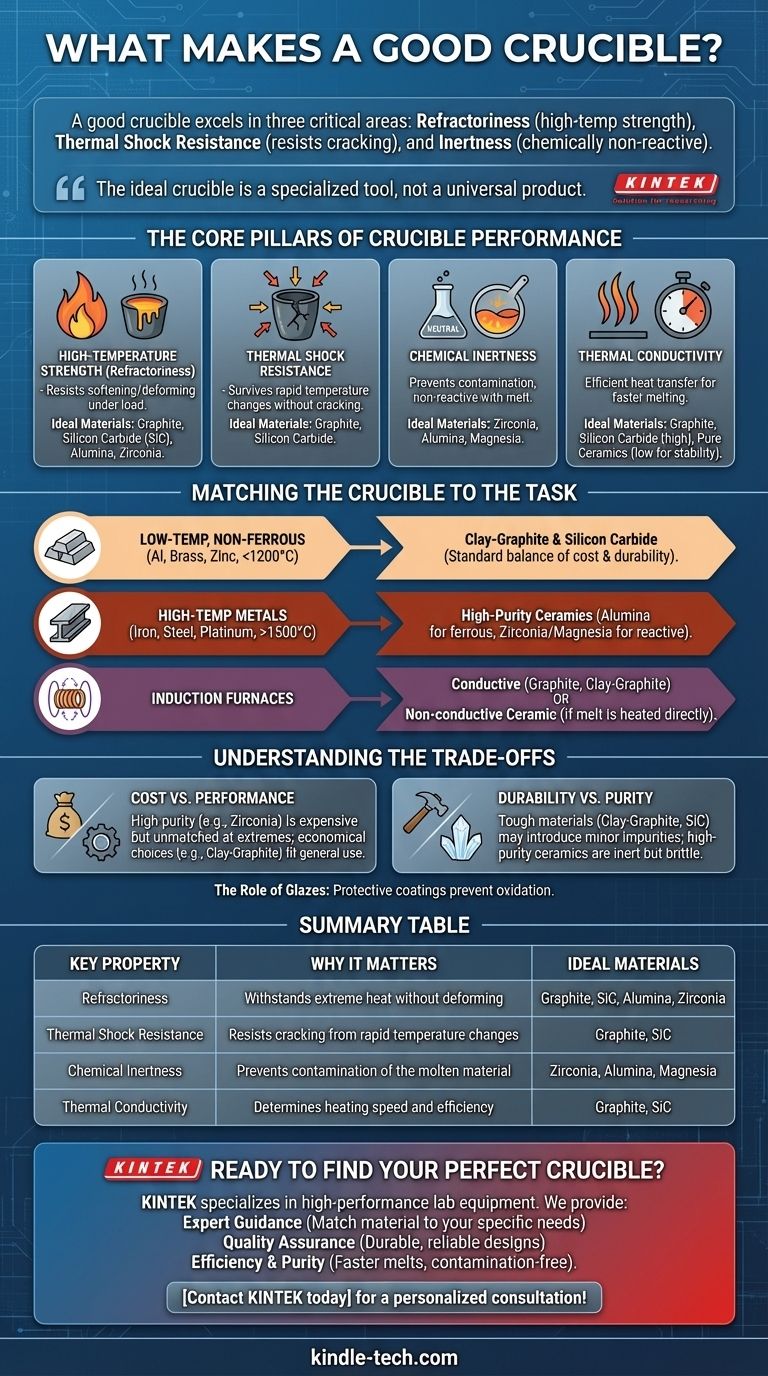
In short, a good crucible excels in three critical areas. It must be able to withstand extreme temperatures without failing (refractoriness), resist cracking from rapid heating and cooling (thermal shock resistance), and remain chemically non-reactive with the molten material it holds (inertness).
The search for a single "best" crucible is misguided. The ideal crucible is not a universal product, but rather a specialized tool whose material properties—from thermal conductivity to chemical stability—are precisely matched to the metal being melted, the temperatures reached, and the type of furnace used.

The Core Pillars of Crucible Performance
To select the right crucible, you must understand the fundamental properties that dictate its success or failure in a high-temperature environment. These are the non-negotiable performance characteristics to evaluate.
High-Temperature Strength (Refractoriness)
A crucible's primary job is to hold its shape and strength at extreme temperatures. This property, known as refractoriness, is more than just a high melting point.
The material must resist softening, deforming, or sagging under the weight of the molten charge. Materials like graphite, silicon carbide (SiC), and ceramics like alumina and zirconia are chosen specifically for this capability.
Thermal Shock Resistance
Crucibles are subjected to immense stress from rapid temperature changes. The ability to survive this without cracking is called thermal shock resistance.
When a crucible is heated, it expands; when cooled, it contracts. If this happens too quickly or unevenly, internal stresses can cause catastrophic failure. Materials with high thermal conductivity and low thermal expansion, like graphite and silicon carbide, are exceptional in this regard.
Chemical Inertness
A crucible should be a neutral container. It must not react with, dissolve into, or otherwise contaminate the molten material inside it.
For example, melting highly reactive metals requires extremely stable ceramic crucibles like zirconia. Using a carbon-based (graphite) crucible to melt low-carbon steel would be a mistake, as the crucible itself would introduce carbon into the alloy, altering its properties.
Thermal Conductivity
This property dictates how quickly and efficiently heat is transferred from the furnace to the material inside.
High thermal conductivity, found in graphite and SiC crucibles, allows for faster melt times and greater energy efficiency. Low thermal conductivity, a characteristic of some pure ceramics, is better for maintaining a stable temperature once the material is molten.
Matching the Crucible to the Task
The right crucible is entirely dependent on the application. A durable workhorse for an aluminum foundry is a poor choice for a lab melting platinum.
For Low-Temp, Non-Ferrous Metals (Aluminum, Brass, Zinc)
For these common applications (under 1200°C / 2200°F), clay-graphite and silicon carbide crucibles are the industry standard. They offer an excellent combination of high thermal conductivity, superb thermal shock resistance, and mechanical durability at a reasonable cost.
For High-Temp Metals (Iron, Steel, Platinum Group)
As temperatures climb above 1500°C (2730°F), material selection becomes far more critical. Pure graphite can be used in oxygen-free environments, but high-purity ceramics are often required.
Alumina (Al₂O₃) is excellent for many ferrous alloys, while zirconia (ZrO₂) and magnesia (MgO) offer superior stability for even higher temperatures and more reactive melts.
For Induction Furnaces
Induction heating requires a crucible material that can interact with the furnace's electromagnetic fields.
Conductive materials like graphite and clay-graphite are heated directly by the induction currents, which in turn melts the charge. Alternatively, a non-conductive ceramic crucible can be used if the metal charge itself is heated directly by the furnace field.
Understanding the Trade-offs
There is no perfect, one-size-fits-all crucible. Every choice involves a compromise between performance, lifespan, and cost.
Cost vs. Performance
A high-purity zirconia crucible can cost ten times more than a standard clay-graphite one. While its performance at extreme temperatures is unmatched, it would be financially impractical for melting aluminum. The goal is to select the most economical crucible that safely meets the requirements of the task.
Durability vs. Purity
Clay-graphite and SiC crucibles are tough, forgiving, and resistant to mechanical damage. However, they are composed of materials that can introduce minor impurities (carbon, silicon) into a melt. High-purity ceramic crucibles offer superior chemical inertness but are often more brittle and less resistant to thermal shock.
The Role of Glazes
Many crucibles, particularly clay-graphite and SiC, are coated with a protective glaze. This layer is crucial for preventing the underlying material from oxidizing at high temperatures, which would severely shorten the crucible's service life.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your final decision must be guided by your specific objective.
- If your primary focus is general-purpose melting of non-ferrous metals like aluminum or brass: A clay-graphite or silicon carbide crucible provides the best balance of durability, performance, and cost.
- If your primary focus is high-purity melts or very high-temperature metals like steel or platinum: You must invest in a high-purity ceramic crucible such as alumina or zirconia, ensuring it is chemically compatible with your melt.
- If your primary focus is speed and efficiency in a fuel-fired or induction furnace: The high thermal conductivity of a silicon carbide or graphite crucible is your ideal choice.
Ultimately, a "good" crucible is one that safely and cleanly contains your material under specific heating conditions, making the right choice an exercise in matching the tool to the task.
Summary Table:
| Key Property | Why It Matters | Ideal Materials |
|---|---|---|
| Refractoriness | Withstands extreme heat without deforming | Graphite, Silicon Carbide (SiC), Alumina, Zirconia |
| Thermal Shock Resistance | Resists cracking from rapid temperature changes | Graphite, Silicon Carbide (SiC) |
| Chemical Inertness | Prevents contamination of the molten material | Zirconia, Alumina, Magnesia |
| Thermal Conductivity | Determines heating speed and efficiency | Graphite, Silicon Carbide (SiC) |
Ready to Find Your Perfect Crucible?
Choosing the right crucible is critical for the success and safety of your melting process. KINTEK specializes in high-performance lab equipment and consumables, including a comprehensive range of crucibles for every application—from aluminum foundries to high-purity research labs.
We provide:
- Expert Guidance: Our specialists will help you match the perfect crucible material (graphite, SiC, alumina, zirconia, and more) to your specific metal, temperature, and furnace type.
- Quality Assurance: Durable, reliable crucibles designed for superior performance and longevity.
- Efficiency & Purity: Achieve faster melt times, better temperature control, and contamination-free results.
Don't compromise on your melt. Let our experts help you select the ideal crucible for your needs.
Contact KINTEL today for a personalized consultation!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Alumina Al2O3 Ceramic Crucible Semicircle Boat with Lid for Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics
- Arc-Shaped Alumina Ceramic Crucible High Temperature Resistant for Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics
- Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics Alumina Al2O3 Crucible With Lid Cylindrical Laboratory Crucible
- Engineering Advanced Fine Alumina Al2O3 Ceramic Crucible for Laboratory Muffle Furnace
- Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics Alumina Crucibles (Al2O3) for Thermal Analysis TGA DTA
People Also Ask
- What is a crucible furnace used for melting of? Melt Non-Ferrous Metals from Aluminum to Gold
- What role does a nickel crucible play during the alkali fusion? Ensure Safe & Efficient Zeolite Synthesis
- What is the temperature range of a crucible? Match Material to Your Lab's Heat Needs
- How do MgO crucibles and sacrificial powders help LATP sintering? Ensure Purity and Prevent Adhesion
- What role does a graphite crucible with a tight-fitting lid play in smelting? Master the Reductive Micro-Environment
- What is the temperature range of graphite crucible? Choose the Right Crucible for Your High-Temp Application
- What role does a ceramic boat play in the carbonization of aluminum-based metal-organic frameworks? Ensure High Purity
- Why are graphite crucibles selected as melting vessels for AlMgZn cross-over alloys? Essential Benefits & Purity Tips



















