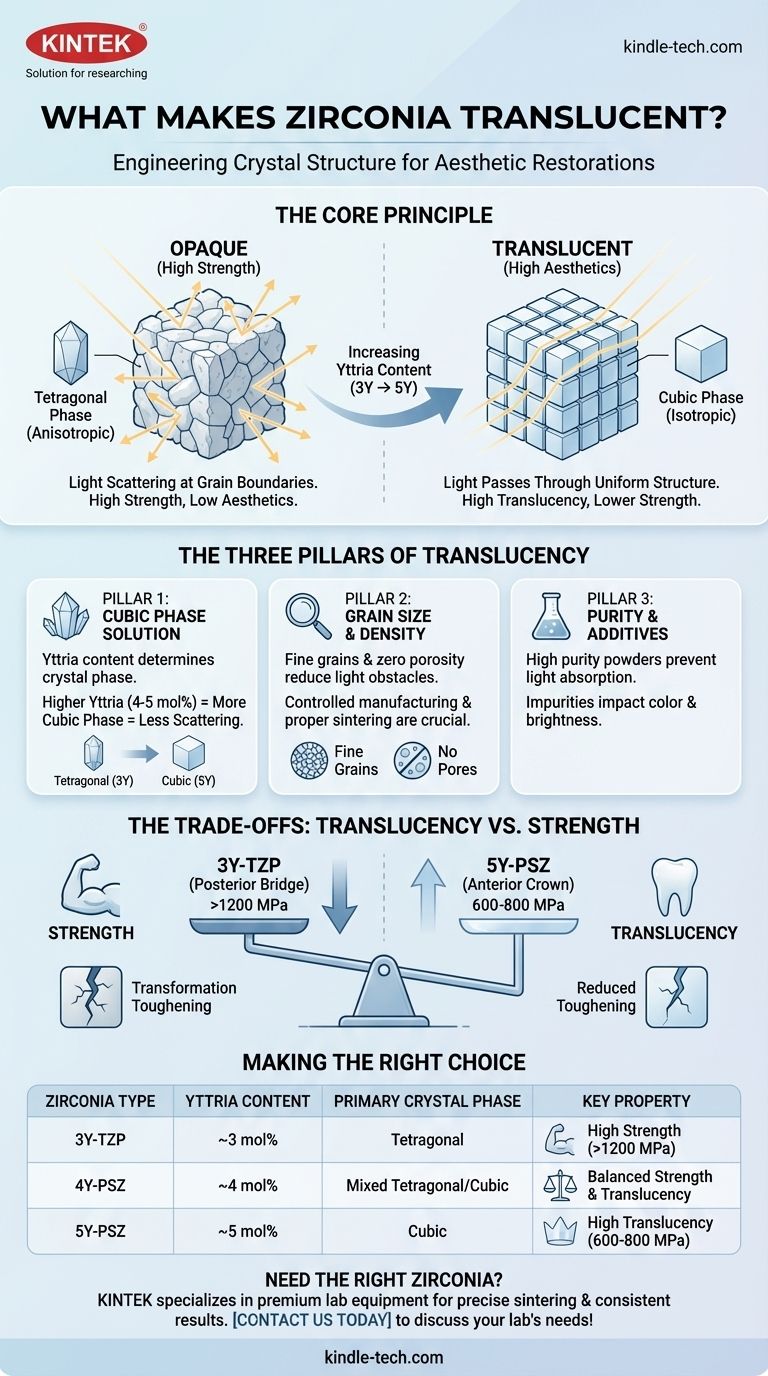
At its core, the translucency of modern dental zirconia is achieved by deliberately engineering its internal crystal structure. By increasing the percentage of a highly symmetrical, light-friendly crystal form called the cubic phase, manufacturers can dramatically reduce the amount of light that scatters when passing through the material, allowing it to mimic the appearance of a natural tooth.
The central challenge in zirconia development is a fundamental trade-off: the chemical and structural changes that increase translucency and improve aesthetics also inherently reduce the material's flexural strength and fracture toughness. Understanding this balance is key to selecting the right material for the right clinical application.

The Journey of Light Through Zirconia
To understand translucency, we must first understand what makes a material opaque. For a polycrystalline ceramic like zirconia, opacity is primarily caused by light scattering.
From Opaque to Translucent
Early dental zirconia was extremely strong but also chalky and opaque. This is because it was composed almost entirely of a crystal structure that was very effective at scattering light, making it suitable only for non-visible frameworks that would be covered with porcelain.
The goal of modern zirconia is to allow light to pass through with minimal disruption, creating the translucency needed for aesthetic, monolithic (full-contour) restorations.
The Enemy of Clarity: Light Scattering
Zirconia is not a single, uniform crystal like glass. It is a polycrystalline material, meaning it is composed of millions of microscopic crystal grains fused together.
Light scatters primarily at the grain boundaries—the interfaces where these individual crystals meet. This scattering is caused by a property mismatch between adjacent crystals, which deflects light in random directions instead of letting it pass straight through.
The Three Pillars of Zirconia Translucency
Achieving high translucency is a sophisticated process that relies on controlling the material's chemistry and microstructure at a microscopic level.
Pillar 1: The Cubic Phase Solution
The most critical factor for translucency is controlling the crystalline phase of the zirconia. Zirconia is stabilized with yttrium oxide ("yttria") to control its structure at room temperature.
-
High-Strength Zirconia (3Y-TZP): Traditional zirconia contains about 3 mol% yttria. This creates a predominantly tetragonal phase crystal structure. These crystals are anisotropic (asymmetrical), causing significant light scattering at grain boundaries, resulting in high opacity but also very high strength.
-
High-Translucency Zirconia (4Y & 5Y-PSZ): Modern aesthetic zirconia contains more yttria (4-5 mol%). This higher yttria content encourages the formation of the cubic phase. Cubic crystals are isotropic (symmetrical in all directions). This symmetry means light is much less likely to scatter at the grain boundaries, allowing it to pass through and creating high translucency.
Pillar 2: Grain Size and Density
Reducing the number of obstacles in the light's path is also key. This is achieved in two ways during the manufacturing and sintering (firing) process.
First, manufacturers aim for a very fine grain size. When the crystal grains are smaller than the wavelength of visible light, light is less likely to be scattered by them.
Second, proper sintering is crucial to eliminate porosity. Any microscopic pores or voids left in the material act as powerful scattering centers, dramatically reducing translucency. Modern zirconia is sintered to near-full density.
Pillar 3: Purity and Additives
The base purity of the zirconium oxide powder and the absence of contaminants are essential. Any impurities or secondary elements can absorb specific wavelengths of light, negatively impacting the material's color and overall brightness.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Translucency vs. Strength
The decision to use a more translucent zirconia is not without consequence. The very mechanism that provides its beauty is also the source of its primary limitation.
The Inherent Compromise
There is an inverse relationship between translucency and strength in zirconia. As the yttria content increases to create more of the translucent cubic phase, the material's flexural strength and fracture toughness decrease.
A highly aesthetic 5Y cubic zirconia may have a flexural strength of 600-800 MPa, while a high-strength 3Y tetragonal zirconia can exceed 1200 MPa.
Why Strength Decreases
The exceptional strength of 3Y tetragonal zirconia comes from a mechanism called transformation toughening. When a crack begins to form, the stress at the crack tip causes the tetragonal crystals to instantly transform into a different (monoclinic) phase.
This transformation involves a slight volume expansion, which effectively creates a zone of compression that squeezes the crack shut and stops it from propagating.
In 5Y cubic zirconia, the crystals are already in a more stable state. This valuable transformation toughening mechanism is significantly reduced or eliminated, making the material less resistant to fracture.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
This knowledge empowers you to move beyond marketing terms and select materials based on engineering principles and clinical demands.
- If your primary focus is aesthetics (e.g., an anterior crown or veneer): Choose a high-translucency zirconia (like 5Y) that prioritizes cubic phase content to best mimic natural enamel.
- If your primary focus is maximum strength (e.g., a long-span posterior bridge): Choose a high-strength zirconia (like 3Y) that prioritizes the tetragonal phase and its transformation toughening capability.
- If you need a balance of both: Consider a multi-layered or gradient zirconia disc, which strategically combines a stronger, more opaque cervical layer with a highly translucent incisal layer in a single restoration.
By understanding the interplay between crystal phase, light transmission, and mechanical properties, you can make an informed material selection that ensures both beautiful and durable clinical outcomes.
Summary Table:
| Zirconia Type | Yttria Content | Primary Crystal Phase | Key Property |
|---|---|---|---|
| 3Y-TZP | ~3 mol% | Tetragonal | High Strength (>1200 MPa) |
| 4Y-PSZ | ~4 mol% | Mixed Tetragonal/Cubic | Balanced Strength & Translucency |
| 5Y-PSZ | ~5 mol% | Cubic | High Translucency (600-800 MPa) |
Need the right zirconia for your dental lab? Selecting the optimal material is critical for balancing aesthetics and strength in your restorations. KINTEK specializes in premium lab equipment and consumables for dental technicians, ensuring you have the tools for precise sintering and consistent results. Let our experts help you choose the perfect zirconia solution for your specific applications. Contact us today to discuss your lab's needs!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Dental Porcelain Zirconia Sintering Ceramic Vacuum Press Furnace
- Dental Porcelain Zirconia Sintering Ceramic Furnace Chairside with Transformer
- Vacuum Dental Porcelain Sintering Furnace
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- How do electronic controllers function in a furnace for sintering dental materials? The Key to Precision Sintering
- What are the materials used in dental ceramics? Choosing the Right Material for Strength & Aesthetics
- What is the strongest type of zirconia? A Guide to Choosing the Right Dental Zirconia
- What is sintering dental materials? The Key to Durable, High-Strength Dental Restorations
- Do dentists still use porcelain? Discover the High-Tech Ceramics Transforming Modern Dentistry
- Do ceramic crowns look natural? Achieve a Seamless, Natural-Looking Smile
- What can all-ceramic restorations be used for? Complete Guide to Modern Dental Solutions
- What are the different types of temperature calibration systems used in porcelain furnaces? Ensure Precision for Every Ceramic Type



















