In thermal evaporation, an exceptionally wide range of materials can be used, spanning pure metals, alloys, semiconductors, and a variety of inorganic compounds. Common examples include metals like aluminum, gold, and chromium, as well as materials like oxides and fluorides. The essential characteristic is that the material must be able to sublimate or evaporate when heated in a high-vacuum environment without chemically decomposing.
The versatility of thermal evaporation comes from a simple principle: if a material can be heated until it turns into a vapor within a vacuum, it can likely be deposited as a thin film. This makes the technique suitable for everything from simple metallic coatings to complex optical layers.

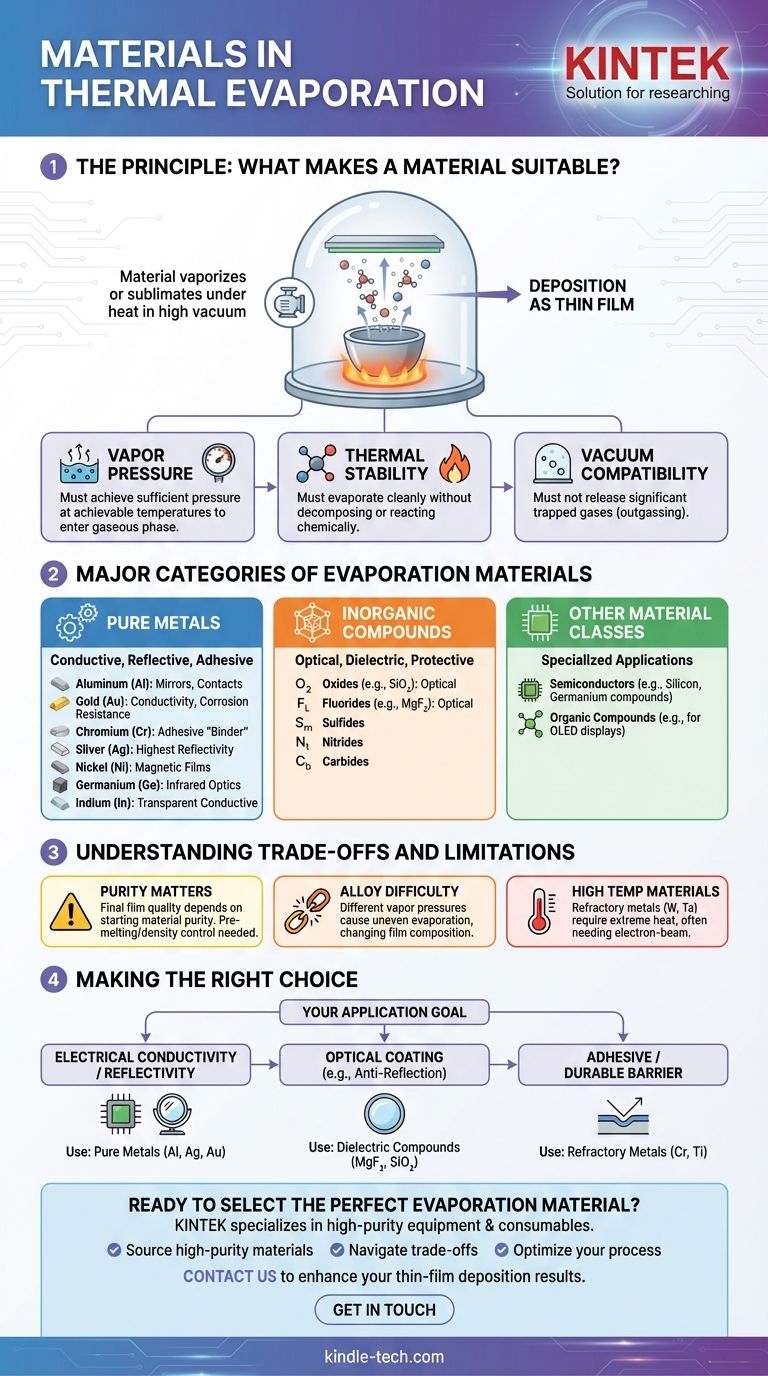
The Principle: What Makes a Material Suitable?
Before listing materials, it's crucial to understand the properties that make them compatible with thermal evaporation. The success of the process hinges on the material's behavior under heat and vacuum.
Vapor Pressure
A material must be able to achieve a sufficiently high vapor pressure at a temperature that is practically achievable in a vacuum chamber. This is the point where atoms or molecules leave the solid or liquid surface and enter the gaseous phase, allowing them to travel to the substrate.
Thermal Stability
The material must evaporate or sublimate cleanly. If it decomposes or reacts chemically when heated, the resulting film will be impure and its properties will be unpredictable.
Vacuum Compatibility
The source material must be compatible with a high-vacuum environment. Materials that release large amounts of trapped gasses (a process called outgassing) can contaminate the vacuum and compromise the purity of the deposited film.
Major Categories of Evaporation Materials
Materials used for thermal evaporation are typically grouped by their chemical nature and application.
Pure Metals
This is the most common and straightforward category. Metals are widely used for creating conductive layers for electronics, reflective surfaces for optics, and adhesive layers for other coatings.
Common examples include:
- Aluminum (Al): Widely used for mirror coatings and electrical contacts.
- Gold (Au): Valued for its conductivity and resistance to corrosion.
- Chromium (Cr): Often used as a durable, adhesive "binder" layer.
- Silver (Ag): Offers the highest reflectivity and excellent conductivity.
- Nickel (Ni): Used in magnetic films and as a barrier layer.
- Germanium (Ge): A semiconductor used in infrared optics.
- Indium (In): Used for transparent conductive coatings.
Inorganic Compounds
This diverse group of materials is critical for producing optical coatings, dielectric layers, and protective films. They are chosen for specific properties like refractive index or hardness.
These include categories such as:
- Oxides (e.g., Silicon Dioxide)
- Fluorides (e.g., Magnesium Fluoride)
- Sulfides
- Nitrides
- Carbides
Other Material Classes
While less common or requiring more specialized setups, thermal evaporation can also be used for other material types.
- Semiconductors: Materials like germanium and silicon compounds fall into this category.
- Organic Compounds: Some organic materials can be evaporated for applications like OLED displays, though this often requires carefully controlled, low-temperature sources.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
While the list of potential materials is long, practical considerations often narrow the choice.
Purity and Form Matter
The quality of the final film is directly dependent on the starting material. Evaporation materials often undergo special processing like pre-melting or density control to ensure they evaporate evenly and produce high-purity films.
Evaporating Alloys is Difficult
Depositing a true alloy can be challenging. If the constituent metals have different vapor pressures, the one that evaporates more easily will dominate the vapor stream first. This results in a film whose composition changes through its thickness and does not match the source material.
Very High Temperature Materials
Some materials, particularly refractory metals like tungsten or tantalum, have extremely high melting points. Reaching their evaporation temperature can be difficult or impossible with standard thermal (resistive) evaporation, often requiring the higher energy of an electron-beam evaporator.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Your choice of material is dictated entirely by the desired properties of the final thin film.
- If your primary focus is electrical conductivity or reflectivity: Pure metals like aluminum (Al), silver (Ag), and gold (Au) are the industry standard.
- If your primary focus is creating an optical coating (e.g., anti-reflection): Dielectric compounds such as magnesium fluoride (MgF₂) or silicon dioxide (SiO₂) are the most common choices.
- If your primary focus is an adhesive or durable barrier layer: Refractory metals like chromium (Cr) or titanium (Ti) provide excellent adhesion to a wide variety of substrates.
Ultimately, successful thin-film deposition depends on matching the material's physical properties to both your process capabilities and the final application's requirements.
Summary Table:
| Material Category | Common Examples | Primary Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Pure Metals | Aluminum (Al), Gold (Au), Silver (Ag), Chromium (Cr) | Conductive layers, reflective coatings, adhesive layers |
| Inorganic Compounds | Silicon Dioxide (SiO₂), Magnesium Fluoride (MgF₂) | Optical coatings, dielectric layers, protective films |
| Other Materials | Germanium (Ge), Indium (In), some Organic Compounds | Semiconductors, infrared optics, OLED displays |
Ready to Select the Perfect Evaporation Material for Your Project?
Choosing the right material is critical for achieving the desired electrical, optical, or mechanical properties in your thin film. KINTEK specializes in providing high-purity lab equipment and consumables for thermal evaporation, serving research and industrial laboratories.
We can help you:
- Source high-purity metals and compounds for consistent, reliable deposition.
- Navigate the trade-offs between different materials for your specific application.
- Ensure your process is optimized for the material you choose.
Contact us today using the form below to discuss your project requirements and discover how our expertise can enhance your thin-film deposition results.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Aluminized Ceramic Evaporation Boat for Thin Film Deposition
- Vacuum Cold Trap Direct Cold Trap Chiller
- Laboratory Rapid Thermal Processing (RTP) Quartz Tube Furnace
- High-Purity Titanium Foil and Sheet for Industrial Applications
- Lab Plastic PVC Calender Stretch Film Casting Machine for Film Testing
People Also Ask
- What is the difference between PPF and coating? Armor vs. Slick Shell for Your Car
- How is deposition time calculated? Mastering the Clock for Strategic Legal Advantage
- How does a molybdenum evaporation source function in H2S for MoS2 synthesis? Master Reactive Film Deposition
- How thick is the sputter coating for SEM? Achieve Optimal Imaging & Analysis
- What is evaporation material? The Key to Precision Thin-Film Deposition



















