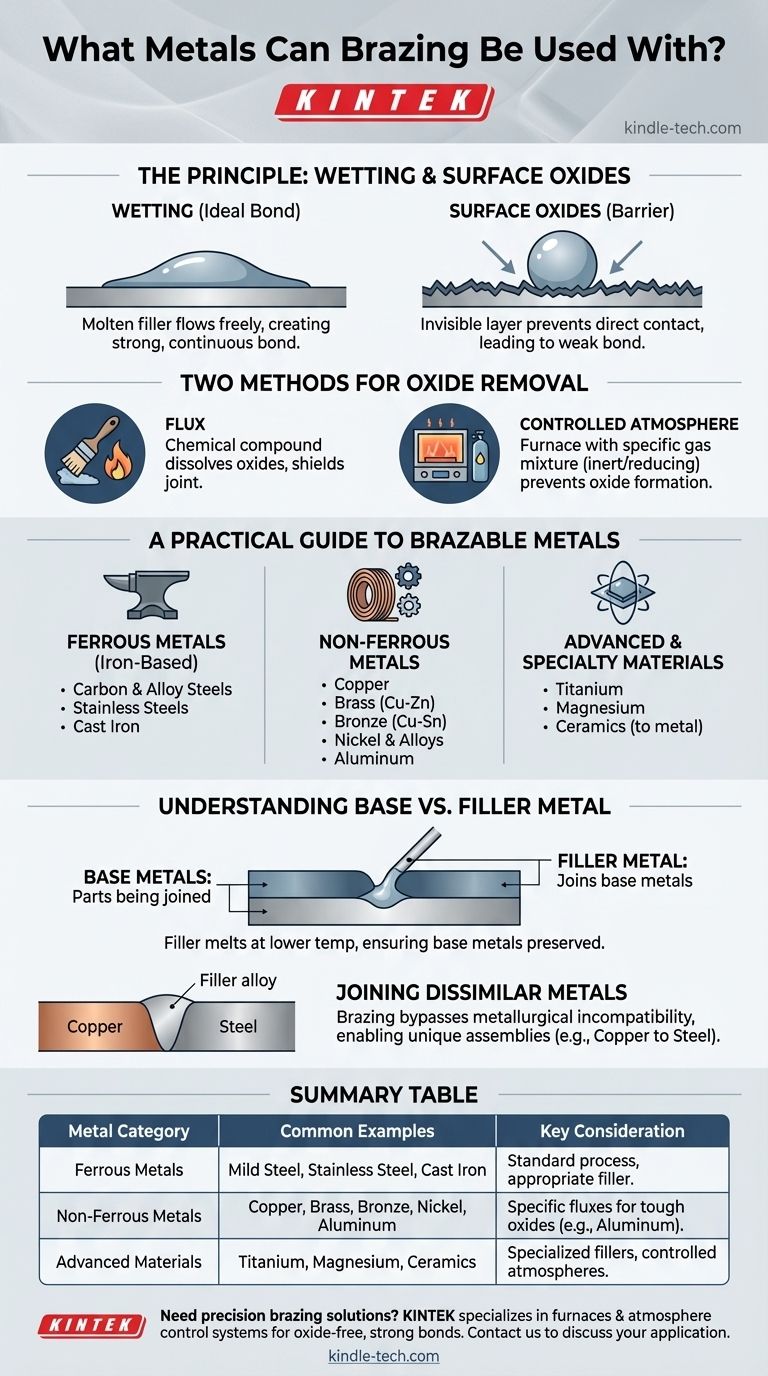
In principle, brazing can be used to join almost any metal. The extensive list of compatible materials includes common ferrous metals like mild steel, stainless steel, and cast iron, as well as non-ferrous metals like copper, brass, bronze, nickel, aluminum, titanium, and magnesium. The process is even effective for joining metals to ceramics.
The success of brazing is less about the specific metal you choose and more about ensuring the correct scientific conditions are met. The key is creating a surface that allows the filler metal to "wet" and bond to the base materials, a process that requires the complete removal of surface oxides.
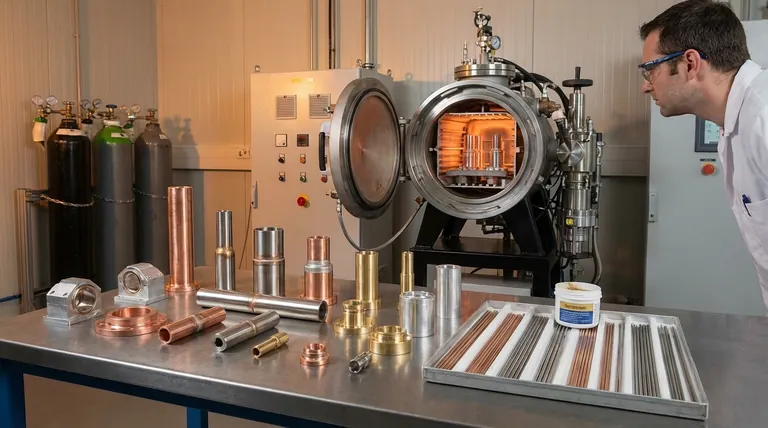

The Fundamental Principle: Achieving a 'Wetted' Surface
Brazing works by drawing a molten filler metal into a joint through capillary action. For this to happen, the filler must be able to flow freely over the surfaces of the parts being joined, a phenomenon known as wetting.
What is Wetting?
Think of wetting like water spreading across a perfectly clean pane of glass. The liquid flows evenly and adheres to the entire surface. In brazing, the molten filler alloy must behave this way, creating a continuous, strong bond as it cools.
The Enemy of Brazing: Surface Oxides
Nearly all metals react with air to form a thin, invisible layer of oxide on their surface. This oxide layer acts as a barrier, preventing the filler metal from making direct contact with the pure base metal and completely inhibiting wetting. It's like trying to apply glue to a dusty surface; the bond will be weak and unreliable.
Two Methods for Removing Oxides
To ensure a strong braze, this oxide layer must be removed and prevented from reforming during the heating process. This is achieved in one of two ways:
-
Flux: A chemical compound applied to the joint before heating. The flux melts, dissolves the oxides, and shields the joint from the air, allowing the filler metal to wet the clean surfaces.
-
Controlled Atmosphere: In furnace brazing, the parts are heated in a chamber where the air has been replaced with a specific gas mixture. This atmosphere either chemically reduces the oxides or is inert, preventing them from forming in the first place.
A Practical Guide to Brazable Metals
With the right process control, the versatility of brazing is remarkable. The compatible materials can be grouped into several key categories.
Ferrous Metals (Iron-Based)
These are among the most commonly brazed materials. The list includes:
- Carbon and alloy steels
- Stainless steels
- Cast iron
Non-Ferrous Metals
Brazing is highly effective for a wide range of non-ferrous metals and their alloys:
- Copper
- Brass (copper-zinc alloy)
- Bronze (copper-tin alloy)
- Nickel and nickel-based alloys
- Aluminum
Advanced and Specialty Materials
The precision of brazing also allows it to be used for more challenging or specialized materials:
- Titanium
- Magnesium
- Ceramics (when brazing to a metal)
Understanding the Trade-offs: Base vs. Filler Metal
A common point of confusion is the distinction between the metals being joined (base metals) and the alloy used to join them (filler metal). Your choice of filler is just as critical as the base metal itself.
The Role of the Filler Metal
The filler metal is designed to melt at a temperature lower than the base metals. Common filler alloys include combinations of silver, copper, zinc, nickel, and palladium. This ensures the parts being joined are never melted, preserving their original shape and strength.
Matching Filler to Base Metal
You cannot use just any filler for any job. Filler metals are engineered for compatibility with specific base metals. For instance, some fillers are designed to work with the resilient oxides on stainless steel, while others are formulated for joining copper alloys.
The Advantage of Joining Dissimilar Metals
One of brazing's greatest strengths is its ability to join different types of metals, such as copper to steel or stainless steel to brass. Because the base metals are not melted, issues of metallurgical incompatibility are often bypassed, enabling unique and complex assemblies.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To apply this knowledge, consider the specific materials you intend to join.
- If your primary focus is joining common steels or copper alloys: These are straightforward applications where a standard flux and a silver or copper-based filler metal will produce excellent results.
- If your primary focus is joining aluminum or stainless steel: You must select a specialized flux designed for these materials' tough oxide layers, or consider controlled atmosphere brazing for the highest quality.
- If your primary focus is joining dissimilar or specialty metals: Brazing is an ideal candidate, but success requires careful research to select a filler metal that is chemically compatible with all base materials involved.
Ultimately, the question is not if a metal can be brazed, but how to prepare it for a successful bond.
Summary Table:
| Metal Category | Common Examples | Key Consideration |
|---|---|---|
| Ferrous Metals | Mild Steel, Stainless Steel, Cast Iron | Standard process with appropriate filler metal. |
| Non-Ferrous Metals | Copper, Brass, Bronze, Nickel, Aluminum | Requires specific fluxes for tough oxides (e.g., on aluminum). |
| Advanced Materials | Titanium, Magnesium, Ceramics | Often requires specialized filler metals and controlled atmospheres. |
Need to join dissimilar metals or tackle a challenging material? The right equipment is crucial for successful brazing. KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables, serving laboratory needs with precision brazing furnaces and atmosphere control systems that ensure oxide-free, strong bonds. Let our experts help you achieve flawless results. Contact us today to discuss your specific application!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Small Vacuum Heat Treat and Tungsten Wire Sintering Furnace
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Vacuum Dental Porcelain Sintering Furnace
People Also Ask
- How does a magnetron sputtering work? A Guide to High-Quality Thin Film Deposition
- What is a vacuum furnace? The Ultimate Guide to Contamination-Free Thermal Processing
- What is a sputtering machine? A Guide to High-Quality Thin Film Deposition
- What is magnetron sputtering machine? Precision Thin-Film Deposition for Advanced Materials
- What is the role of the hydraulic system in hot pressing? Achieve Maximum Material Density and Strength



















