An inert atmosphere is created by displacing the ambient air in a space with a non-reactive gas. The most common gases used for this purpose are nitrogen (N2), argon (Ar), and carbon dioxide (CO2). Each gas is chosen based on its specific properties and the requirements of the application.
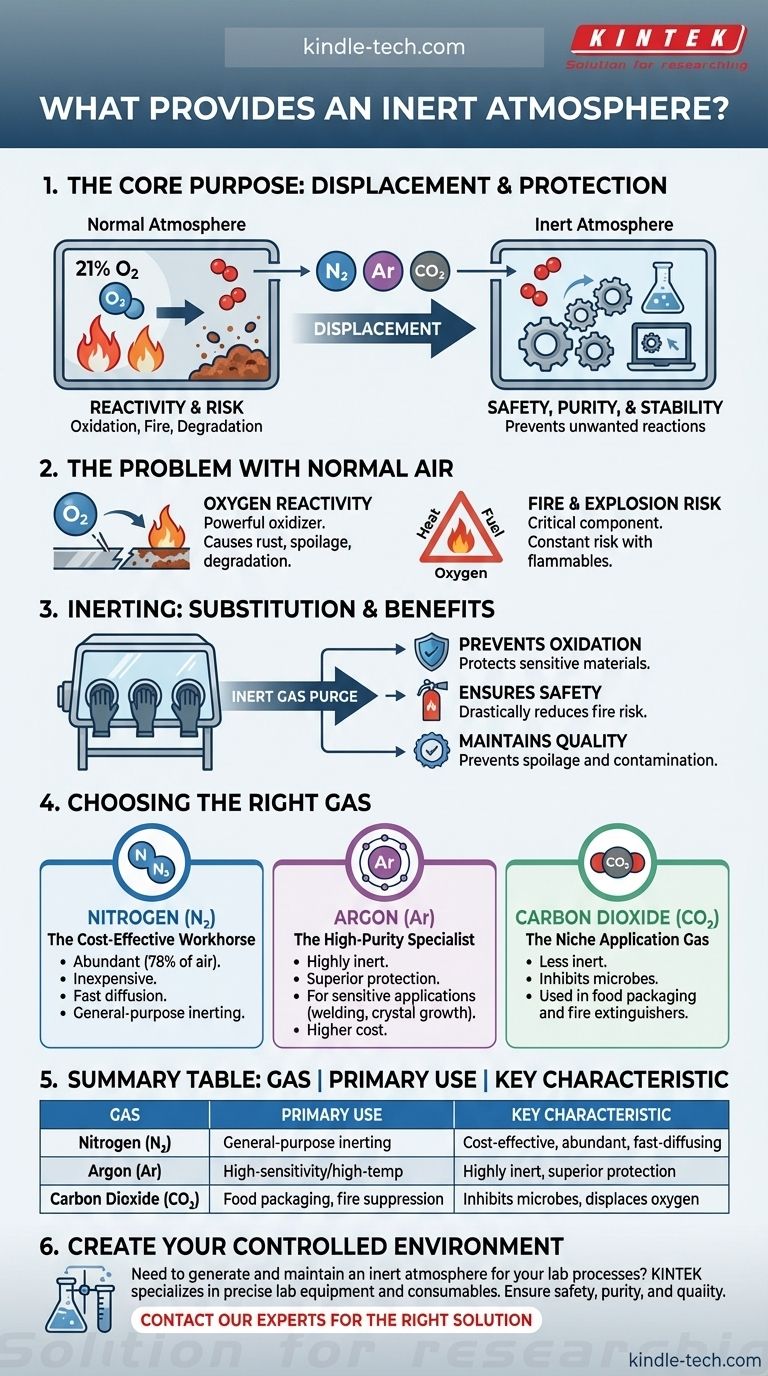
The core purpose of an inert atmosphere is not simply to fill a space, but to strategically remove reactive gases—primarily oxygen—to prevent unwanted chemical reactions like oxidation, degradation, or combustion.

Why a Normal Atmosphere is Often the Problem
A standard atmosphere is a highly reactive environment. Understanding why it needs to be replaced is the key to understanding inerting.
The Reactivity of Oxygen
The air we breathe is approximately 21% oxygen. While essential for life, oxygen is a powerful oxidizing agent.
This means it readily reacts with other substances, causing chemical changes. These changes are often undesirable, leading to rust on metals, spoilage in food, and degradation of sensitive chemicals.
The Fire and Explosion Risk
Oxygen is also a critical component of the fire triangle (heat, fuel, and oxygen).
In environments with flammable materials, the presence of atmospheric oxygen creates a constant risk of fire or explosion. Removing the oxygen effectively breaks the fire triangle and mitigates this hazard.
How an Inert Atmosphere Solves the Problem
Inerting is a process of substitution. By flooding an enclosed space with a non-reactive gas, you physically push out, or purge, the reactive oxygen.
The Principle of Displacement
Inert gases are chosen because they are chemically stable and do not readily participate in chemical reactions under most conditions.
When introduced into a container, glovebox, or processing vessel, the inert gas lowers the oxygen concentration to a level where reactions like oxidation or combustion cannot occur.
Key Benefits of Inerting
This process provides several critical advantages across various industries:
- Prevents Oxidation and Degradation: Protects sensitive electronics, pharmaceuticals, and chemicals from damage.
- Ensures Safety: Drastically reduces the risk of fire and explosion in chemical processing and storage.
- Maintains Purity and Quality: Prevents spoilage in food and beverage packaging and avoids contamination in high-tech manufacturing.
Understanding the Trade-offs When Choosing a Gas
While several gases can be used, the choice is not arbitrary. It involves balancing performance, cost, and the specific needs of the application.
Nitrogen: The Cost-Effective Workhorse
Nitrogen is by far the most common inerting gas. It is abundant (making up ~78% of our atmosphere), relatively inexpensive to produce, and effective for most applications. Its high diffusion rate allows it to quickly and evenly fill a space.
Argon: The High-Purity Specialist
Argon is more inert than nitrogen and is used for highly sensitive applications. At very high temperatures, nitrogen can still react with certain metals.
For processes like specialized welding or crystal growth, argon provides a superior level of non-reactivity. This performance, however, comes at a higher cost.
Carbon Dioxide: The Niche Application Gas
Carbon dioxide is less inert than nitrogen or argon but is used in specific scenarios. In food packaging, it not only displaces oxygen but also helps inhibit the growth of some microbes. It is also commonly used in fire extinguishers.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the correct gas is a matter of aligning its properties with your primary objective.
- If your primary focus is general-purpose inerting and cost-effectiveness: Nitrogen (N2) is the standard and most practical choice for the vast majority of applications.
- If your primary focus is protecting highly sensitive materials or high-temperature processes: Argon (Ar) offers the highest degree of non-reactivity, justifying its higher cost.
- If your primary focus is food preservation or specific types of fire suppression: Carbon dioxide (CO2) can provide unique benefits beyond simple inerting.
Ultimately, creating an inert atmosphere is a fundamental strategy for controlling a chemical environment to ensure safety, quality, and stability.
Summary Table:
| Gas | Primary Use Case | Key Characteristic |
|---|---|---|
| Nitrogen (N₂) | General-purpose inerting | Cost-effective, abundant, fast-diffusing |
| Argon (Ar) | High-sensitivity/high-temperature processes | Highly inert, superior protection |
| Carbon Dioxide (CO₂) | Food packaging, fire suppression | Inhibits microbes, displaces oxygen |
Need to create a controlled, inert environment for your lab processes? KINTEK specializes in providing the precise lab equipment and consumables needed to generate and maintain inert atmospheres for applications ranging from sensitive material handling to chemical synthesis. Ensure the safety, purity, and quality of your work—contact our experts today to find the right solution for your laboratory's needs.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1200℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Nitrogen Inert Atmosphere Furnace
- 1700℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Nitrogen Inert Atmosphere Furnace
- 1400℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace with Nitrogen and Inert Atmosphere
- Controlled Nitrogen Inert Hydrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What is an inert condition? A Guide to Preventing Fires and Explosions
- Why nitrogen is used in furnace? A Cost-Effective Shield for High-Temperature Processes
- How do you make an inert atmosphere? Master Safe, Pure Processes with Inerting
- Can nitrogen be used for brazing? Key Conditions and Applications Explained
- How we can develop inert atmosphere for a chemical reaction? Master Precise Atmospheric Control for Your Lab



















