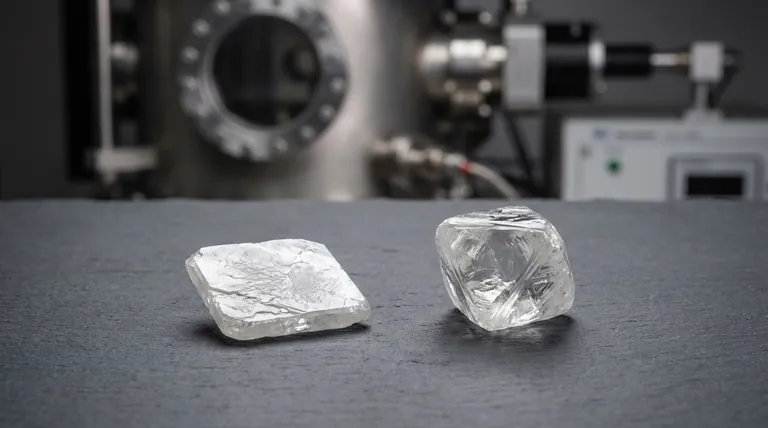
As-grown CVD diamonds typically have a flat, tabular, or somewhat squarish crystal shape. This form is not accidental; it is a direct result of the chemical vapor deposition (CVD) process, which builds the diamond atom by atom in consistent, upward layers on top of a flat seed.
The shape of a raw CVD diamond is an engineered outcome, not a random occurrence. Unlike the varied shapes of mined diamonds, CVD diamonds grow in predictable, flat layers, resulting in a tabular crystal that is fundamentally different from diamonds formed under geological pressure.

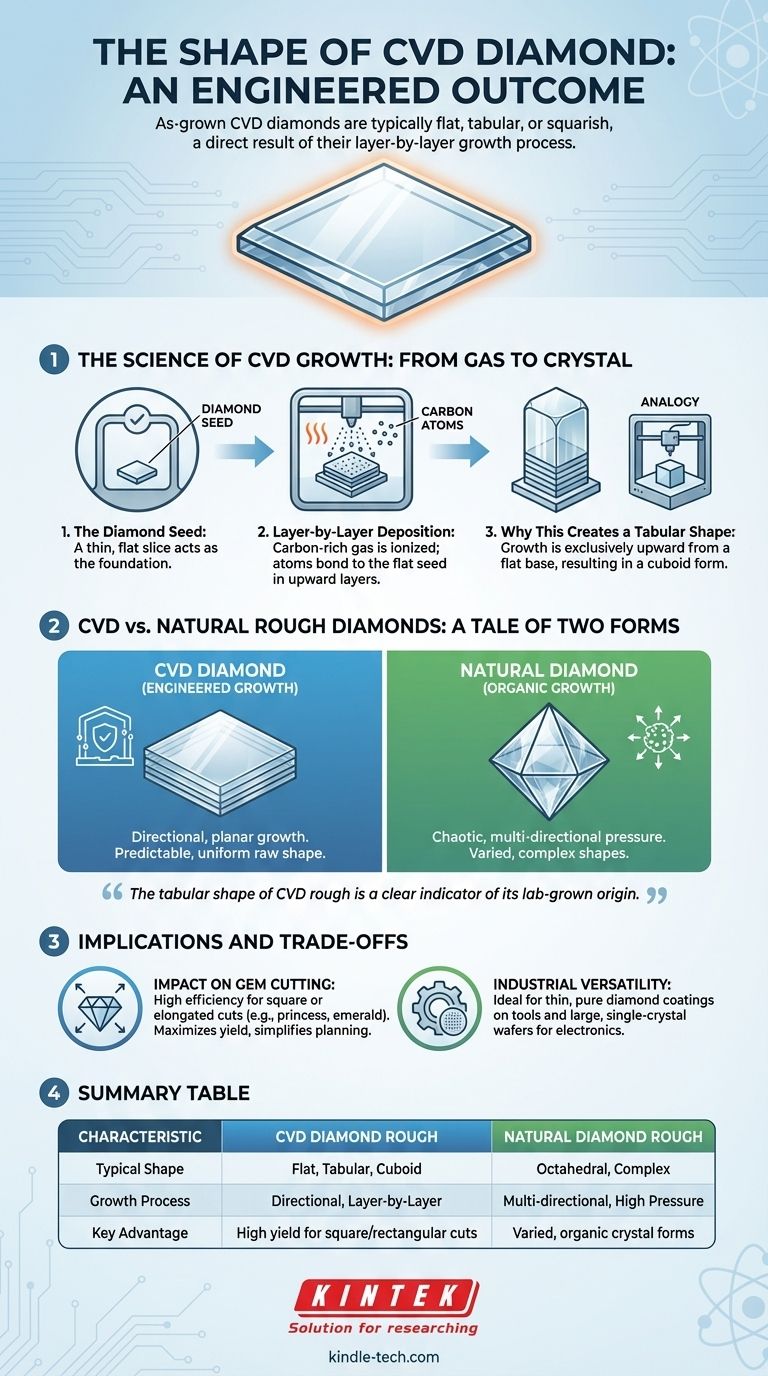
The Science of CVD Growth: From Gas to Crystal
To understand the shape, you must first understand the process. The form of a CVD diamond is a direct consequence of its highly controlled, layer-by-layer creation.
The Diamond Seed: The Foundation of Shape
The process begins by placing a thin, flat slice of a diamond crystal, known as a diamond seed, into a sealed deposition chamber. This seed acts as the template, or foundation, upon which the new diamond will grow.
Layer-by-Layer Deposition
The chamber is heated to around 800°C and filled with a carbon-rich gas. This gas is ionized, breaking the molecules apart and freeing pure carbon atoms. These atoms then rain down and bond to the flat surface of the diamond seed, perfectly aligning with its crystal structure.
This method is analogous to atomic-level 3D printing. Just as a 3D printer builds an object layer by layer from the bottom up, the CVD process builds a diamond crystal layer by layer on top of the seed.
Why This Creates a Tabular Shape
Because the growth is exclusively upward from a flat base, the resulting raw crystal is naturally tabular or cuboid. It expands vertically and outwards from the seed, maintaining a generally flat top and squarish profile dictated by the underlying crystal lattice.
CVD vs. Natural Rough Diamonds: A Tale of Two Forms
The engineered shape of a CVD diamond stands in stark contrast to the forms of diamonds created by nature.
Engineered vs. Organic Growth
Natural diamonds form under immense, multi-directional pressure and heat deep within the Earth's mantle. This chaotic, unconstrained environment allows crystals to grow outwards in multiple directions simultaneously.
The CVD process, however, is a directional and controlled deposition. The growth is planar, not multi-directional, leading to a much more predictable and uniform raw shape.
The Resulting Raw Shapes
This difference in formation leads to distinct rough shapes. Many natural rough diamonds have an octahedral shape (like two pyramids joined at the base). In contrast, CVD rough is almost always tabular. This difference in the raw crystal's form is one of the clearest indicators of its origin.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Implications
The shape of the rough crystal has significant practical consequences for both industrial uses and finished gemstones.
Impact on Gem Cutting
The flat, regular shape of CVD rough is highly efficient for modern gem cutting. It allows cutters to maximize the yield and produce popular square or elongated shapes, such as princess, radiant, and emerald cuts, with minimal waste. The predictable form simplifies the planning process compared to the complex and irregular shapes of many natural rough diamonds.
Versatility for Industrial Applications
The CVD process is not just for creating gems. It is exceptionally well-suited for producing thin, pure diamond coatings on tools and machine parts, enhancing their hardness and durability.
Furthermore, the process can be scaled to create large, single-crystal diamond wafers, some reaching up to four inches in diameter. These are critical components in advanced electronics and high-power optics, where a flat, uniform, and pure material is essential.
How to Apply This Knowledge
Understanding the raw form helps you understand the final product, whether it's an industrial tool or a piece of jewelry.
- If your primary focus is on identifying a diamond's origin: A distinctly flat or tabular rough crystal is a strong characteristic of the CVD growth process.
- If you are comparing lab-grown methods: A rough diamond with a more complex, multi-faceted shape is more typical of the HPHT (High-Pressure, High-Temperature) method, which more closely mimics natural growth conditions.
- If you are purchasing a finished gemstone: Know that the original tabular shape of CVD rough makes it exceptionally well-suited for creating square and rectangular cuts, which can influence market availability and pricing.
Ultimately, the shape of a raw CVD diamond is a clear testament to its origin: a precise, controlled feat of modern engineering.
Summary Table:
| Characteristic | CVD Diamond Rough | Natural Diamond Rough |
|---|---|---|
| Typical Shape | Flat, Tabular, Cuboid | Octahedral, Complex |
| Growth Process | Directional, Layer-by-Layer | Multi-directional, High Pressure |
| Key Advantage | High yield for square/rectangular cuts | Varied, organic crystal forms |
Need high-quality lab equipment for your own material synthesis or analysis? KINTEK specializes in the precise lab equipment and consumables required for advanced processes like CVD. Whether you're scaling up research or optimizing production, our solutions ensure the control and reliability your laboratory demands. Contact our experts today to discuss how we can support your specific application!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom CVD Diamond Coating for Lab Applications
- CVD Diamond Domes for Industrial and Scientific Applications
- Cylindrical Resonator MPCVD Machine System Reactor for Microwave Plasma Chemical Vapor Deposition and Lab Diamond Growth
- CVD Diamond Cutting Tool Blanks for Precision Machining
- CVD Diamond Optical Windows for Lab Applications
People Also Ask
- How are tools coated with diamond? Achieve Superior Hardness and Low Friction for Your Tools
- Is diamond coating permanent? The Truth About Its Long-Lasting Durability
- Is diamond coating worth it? Maximize Component Life and Performance
- What are diamond coated films? Enhance Materials with Super-Hard, Transparent Layers
- How thick is CVD diamond coating? Balancing Durability and Stress for Optimal Performance



















