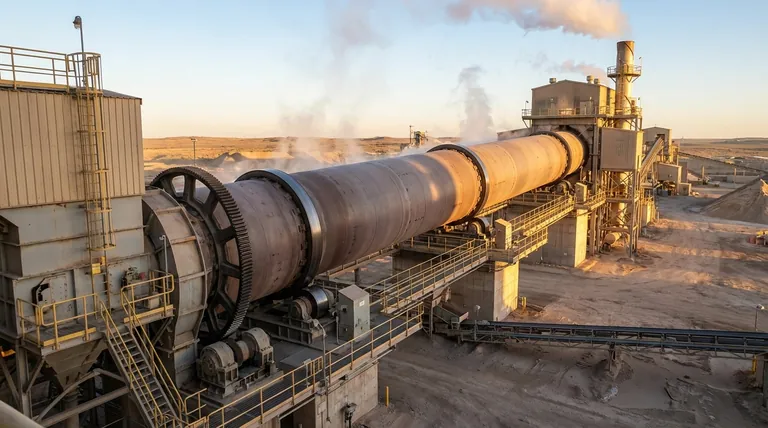
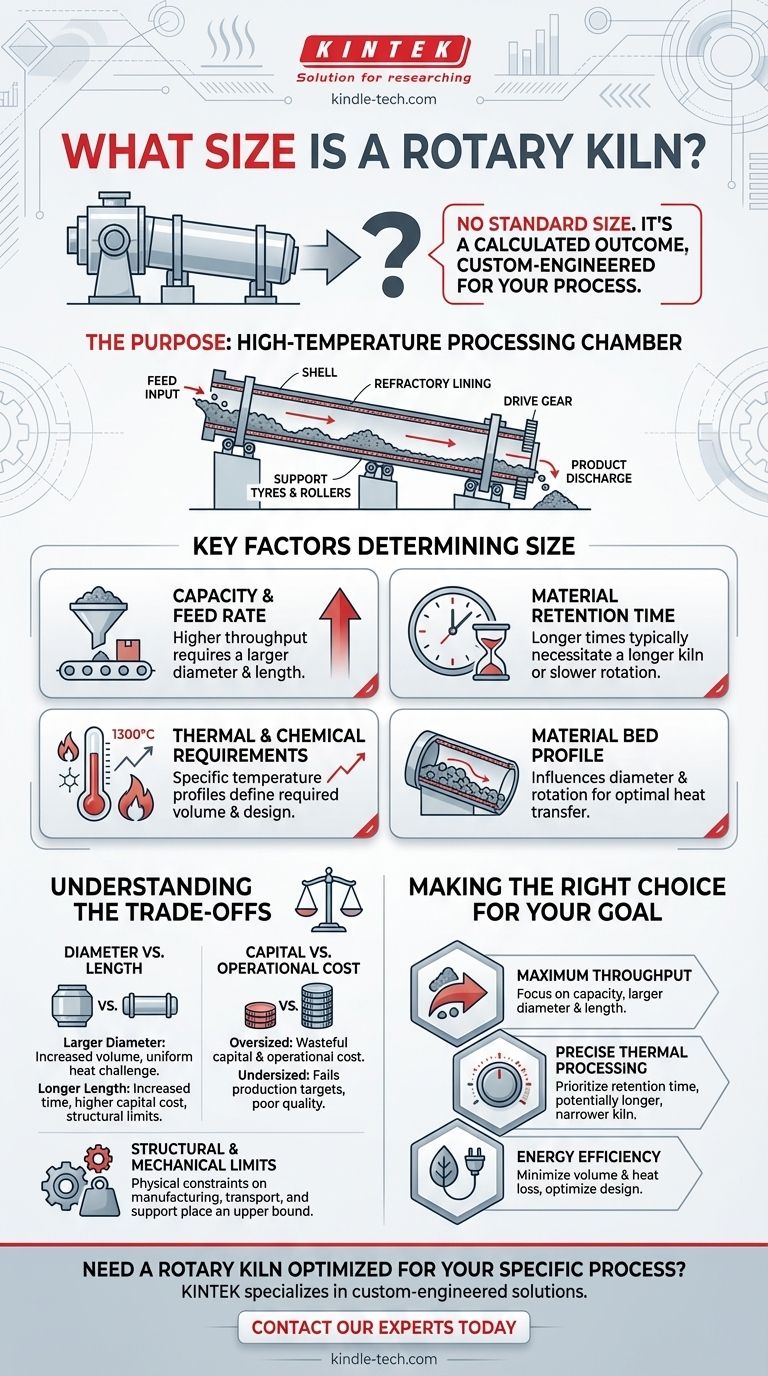
To be clear, a rotary kiln has no standard size. Its dimensions—specifically its length and diameter—are custom-engineered for a specific industrial process, material, and desired output. The final size is a complex calculation based on thermal requirements, material properties, and production capacity goals.
A rotary kiln's size is not a fixed specification you can look up in a catalog. It is a calculated outcome, determined by the precise amount of material you need to process, the temperature it requires, and the exact length of time it must be heated.

The Purpose of the Rotary Kiln
A High-Temperature Processing Chamber
A rotary kiln is essentially a large, rotating cylinder, also known as the shell, that is slightly inclined. It is mounted between stationary feed and outlet housings.
Material is fed into the higher end and moves slowly toward the lower end as the kiln rotates. This design makes it the heart of many industrial processes that require high temperatures for specific chemical or physical reactions.
Key Components Influencing Scale
The main components of any rotary kiln are the shell, an internal refractory lining to withstand heat, support tyres (or riding rings) and rollers that allow it to rotate, and a drive gear. The size of these components scales directly with the overall dimensions of the kiln.
Key Factors That Determine Kiln Size
Sizing a rotary kiln is a balancing act between multiple engineering variables. Each factor directly influences the final diameter and length of the cylindrical shell.
Required Capacity and Feed Rate
The most fundamental factor is capacity, or the quantity of material you need to process per hour. A higher maximum feed rate naturally requires a larger volume, which can be achieved by increasing the kiln's diameter, length, or both.
Material Retention Time
Retention time is the duration a material must spend inside the kiln to undergo the desired reaction. This is dictated by the process chemistry and thermodynamics.
Longer required retention times typically necessitate a longer kiln or a slower rotation speed to ensure the material is processed completely before it exits.
Thermal and Chemical Requirements
The specific temperature profile is critical. For an indirect kiln, furnace tube temperatures can reach 1200-1300 °C to achieve material temperatures under 1150 °C.
The design must account for the heat required to raise the material to this temperature and whether the material's reaction generates or consumes heat. This thermal load calculation is a primary driver of the kiln's required volume and surface area.
Material Bed Profile
The bed profile refers to how the material tumbles and fills the cross-section of the kiln as it rotates. This behavior affects how efficiently heat is transferred into the material.
The kiln's diameter and rotational speed are adjusted to optimize this tumbling action, ensuring every particle is exposed to the correct temperature for the required amount of time.
Understanding the Trade-offs
The statement that sizing requires "experience" points to the critical trade-offs involved. A bigger kiln is not always a better or more efficient solution.
Diameter vs. Length
A larger diameter increases the kiln's volume and capacity, but it can make it harder to achieve uniform heat transfer to the center of the material bed.
A longer length increases retention time but also raises the capital cost, requires a larger physical footprint, and presents greater structural engineering challenges. The final ratio of length-to-diameter is a carefully optimized compromise.
Capital Cost vs. Operational Efficiency
An oversized kiln represents a significant waste. It costs more to build (capital cost) and consumes more fuel to heat its excess volume and surface area (operational cost).
Conversely, an undersized kiln will fail to meet production targets or may not provide adequate retention time, leading to poor quality product. The goal is to design the smallest, most efficient kiln that reliably meets all process requirements.
Structural and Mechanical Limits
There are physical limits to how large a rotary kiln can be manufactured, transported, and supported. The immense weight of the steel shell, refractory lining, and the material inside must be safely managed by the support rollers and drive system. These mechanical constraints place a practical upper bound on kiln size.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The optimal size and shape of a rotary kiln are always tied to its primary processing objective.
- If your primary focus is maximum throughput: The design will be driven by capacity calculations, likely resulting in a larger diameter and length to handle high feed rates.
- If your primary focus is precise thermal processing: The design will prioritize retention time and temperature control, which may favor a longer, narrower kiln to ensure a specific heating profile.
- If your primary focus is energy efficiency: The design will be meticulously calculated to minimize volume and heat loss, ensuring the kiln is no larger than absolutely necessary to meet the required capacity and retention time.
Ultimately, determining the correct rotary kiln size is an engineering discipline focused on aligning physical dimensions with specific process outcomes.
Summary Table:
| Key Factor | Impact on Kiln Size |
|---|---|
| Capacity / Feed Rate | Higher throughput requires a larger diameter and/or length. |
| Material Retention Time | Longer processing times typically necessitate a longer kiln. |
| Thermal Requirements | High temperatures and heat loads drive the required volume and design. |
| Material Bed Profile | Influences diameter and rotation speed for optimal heat transfer. |
Need a Rotary Kiln Optimized for Your Specific Process?
Determining the correct size is critical for your project's success, balancing throughput, quality, and efficiency. KINTEK specializes in custom-engineered lab equipment and industrial solutions, including rotary kilns tailored to your exact material, capacity, and thermal requirements.
Contact our experts today to discuss your application. We'll help you design the most efficient and cost-effective kiln for your laboratory or production needs.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Pyrolysis Furnace Plant Machine Calciner Small Rotary Kiln Rotating Furnace
- Electric Rotary Kiln Continuous Working Small Rotary Furnace Heating Pyrolysis Plant
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace for Activated Carbon Regeneration
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Three-dimensional electromagnetic sieving instrument
People Also Ask
- How is cement prepared by rotary kiln method? A Step-by-Step Guide to Clinker Production
- How does a rotary calciner work? Achieve Uniform Thermal Processing for Bulk Solids
- What are the end products of plastic pyrolysis? Unlocking Fuel, Gas, and Char from Waste
- What is the composition of wood pyrolysis gas? A Guide to Syngas Production & Control
- What are the advantages of catalytic pyrolysis? Produce High-Value Biofuels from Biomass
- How are rotary kilns heated? Direct vs. Indirect Heating Methods Explained
- What is the temperature maintained in calcination zone of rotary kiln? It's All About Your Material
- Is pyrolysis just burning? Unlocking the Key Differences in Thermal Processes



















