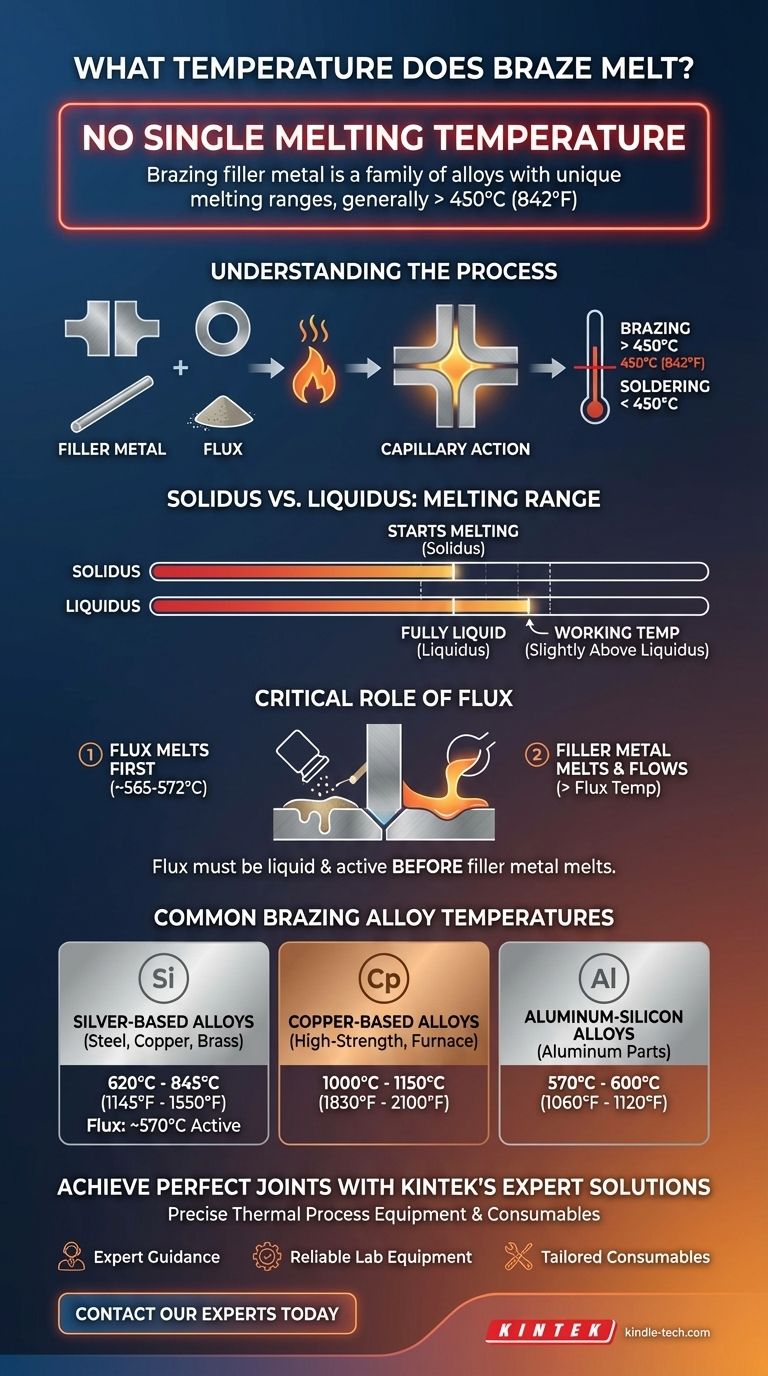
There is no single melting temperature for "braze." Brazing filler metal is a family of alloys, each with a unique melting range designed for specific applications. These temperatures generally start above 450°C (842°F) and can exceed 1100°C (2012°F), depending on the alloy's composition.
The most critical concept to understand is that brazing involves two different materials with two different melting points: the flux and the filler metal. For a successful joint, the flux must become active and liquid at a temperature below the melting point of the filler metal.
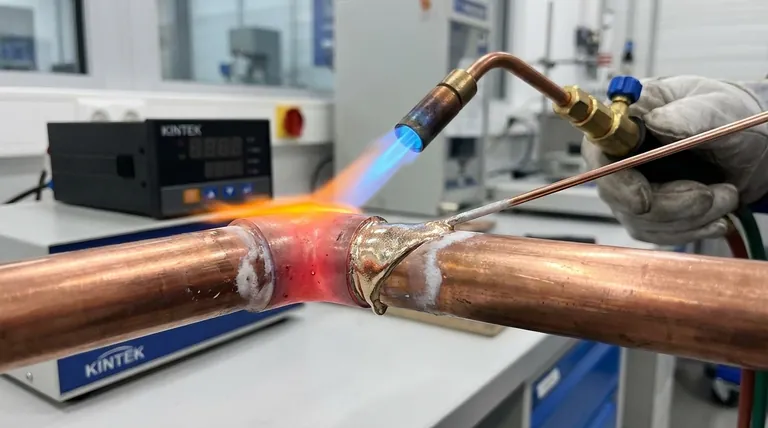

Understanding the Brazing Process
To select the correct temperature, you must first distinguish between the materials and the process itself. The term "braze" is often used loosely, leading to confusion.
The Defining Temperature of Brazing
Brazing is a metal-joining process where a filler metal is heated above its melting point and distributed between two or more close-fitting parts by capillary action. The international standard that separates brazing from its lower-temperature cousin, soldering, is a process temperature of 450°C (842°F).
Any process using a filler metal that melts below this threshold is considered soldering.
Brazing Filler Metal: An Alloy, Not a Pure Metal
The material used to create the joint is a brazing filler metal. These are rarely pure metals but are instead alloys—a mixture of two or more metallic elements.
This is why there is no single answer to "what temperature does braze melt?" A silver-copper-zinc alloy will melt at a very different temperature than a copper-phosphorus alloy.
Solidus vs. Liquidus: The Melting Range
Because filler metals are alloys, they don't melt at a single, precise point. They melt across a temperature range.
- Solidus: The temperature at which the alloy begins to melt.
- Liquidus: The temperature at which the alloy becomes fully liquid.
The working temperature for brazing is typically slightly above the liquidus temperature to ensure the alloy is fluid enough to flow via capillary action.
The Critical Role of Flux
The reference to a melting range of 565-572°C (1049-1062°F) is for a common type of brazing flux, not the filler metal itself. Understanding flux is key to understanding the entire process.
What is Brazing Flux?
Flux is a chemical compound applied to the joint before heating. Its primary jobs are to clean any oxides from the base metals and the filler metal, and to shield the joint from oxidation during heating.
Without effective fluxing, the molten filler metal cannot "wet" or bond with the base metals, resulting in a failed joint.
Why Flux Must Melt First
The flux must be liquid and chemically active before the filler metal begins to melt. This allows it to perform its cleaning function, preparing a pristine surface for the molten filler metal to flow onto.
If you are using a flux that melts around 570°C, your chosen filler metal must melt at a higher temperature, typically above 620°C (1145°F).
Common Brazing Alloy Temperatures
Different base metals and application requirements call for different filler metal alloys and their corresponding temperatures.
Silver-Based Alloys (Silver Solder)
These are extremely common for joining dissimilar metals like steel, copper, and brass. Their melting ranges are typically between 620°C and 845°C (1145°F and 1550°F). A flux active around 570°C is perfectly suited for these alloys.
Copper-Based Alloys
Used for brazing steel, nickel, and copper alloys, often in furnace brazing. These have much higher melting points, often in the range of 1000°C to 1150°C (1830°F to 2100°F). They require high-temperature fluxes.
Aluminum-Silicon Alloys
Specifically designed for brazing aluminum alloys. These have a very low melting range, often 570°C to 600°C (1060°F to 1120°F), which is just below the melting point of the aluminum base metals being joined.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Pitfalls
Achieving a strong brazed joint requires a precise thermal management strategy. Errors in temperature control are a primary cause of failure.
Mismatching Filler and Flux
This is the most common mistake. If the filler metal melts before the flux is active, the joint will be dirty and the bond will fail. If the flux's active range is too far below the filler's melting point, the flux may burn out and lose its effectiveness before the filler metal can flow.
Overheating the Joint
Applying too much heat can damage the base metals by changing their metallurgical properties (e.g., annealing or weakening them). It can also vaporize or "burn" the flux, leaving the joint unprotected from oxidation at the critical moment.
Insufficient Heat
The base metals must be heated to the filler metal's working temperature. If only the filler metal is melted (a common mistake with a torch), it will not flow into the joint. The heat stored in the surrounding base metals is what allows for proper capillary action.
Making the Right Choice for Your Project
Your goal determines the right combination of filler metal, flux, and temperature.
- If your primary focus is general-purpose repair or fabrication (steel, copper, brass): Choose a silver-based brazing alloy and a matching flux, aiming for a process temperature between 650°C and 800°C (1200°F - 1475°F).
- If your primary focus is joining aluminum parts: You must use a specialized aluminum-silicon filler and a corresponding low-temperature flux, working in a very narrow window around 580°C (1075°F).
- If your primary focus is high-strength joints on steel in a controlled atmosphere: Consider a copper-based filler metal in a furnace brazing operation, with process temperatures exceeding 1100°C (2012°F).
Ultimately, successful brazing depends on matching the active range of your flux to the melting range of your filler metal.
Summary Table:
| Brazing Filler Metal Type | Typical Melting Range (°C) | Typical Melting Range (°F) | Common Applications |
|---|---|---|---|
| Silver-Based Alloys | 620°C - 845°C | 1145°F - 1550°F | Steel, copper, brass joints |
| Copper-Based Alloys | 1000°C - 1150°C | 1830°F - 2100°F | High-strength steel, furnace brazing |
| Aluminum-Silicon Alloys | 570°C - 600°C | 1060°F - 1120°F | Aluminum parts joining |
| Brazing Flux (Activation) | ~565°C - 572°C | ~1049°F - 1062°F | Must melt before filler metal |
Achieve Perfect Brazing Joints with KINTEK's Expert Solutions
Selecting the right brazing filler metal and flux is critical for joint strength and durability. KINTEK specializes in providing high-quality lab equipment and consumables for precise thermal processes, including brazing applications. Our team can help you identify the ideal materials and temperature parameters for your specific base metals and project requirements.
We provide:
- Expert guidance on filler metal and flux selection
- Reliable lab equipment for precise temperature control
- Consumables tailored to your brazing applications
Let us help you optimize your brazing process – Contact our experts today for personalized support and solutions that ensure strong, reliable joints every time.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- High Shear Homogenizer for Pharmaceutical and Cosmetic Applications
- Vacuum Cold Trap Chiller Indirect Cold Trap Chiller
- Automatic Laboratory Heat Press Machine
- Vacuum Cold Trap Direct Cold Trap Chiller
- Versatile PTFE Solutions for Semiconductor and Medical Wafer Processing
People Also Ask
- Why are high-shear mixing or ultrasonic homogenizers necessary for MMT nanocomposites? Unlock True Nano-Reinforcement
- What functions do laboratory centrifuges and high-shear homogenizers perform? Optimize Your Nano-Modified Composites
- What role does a high-shear homogenizer play in ODC catalyst suspensions? Unlock Superior Electrochemical Efficiency
- What are the advantages of using a high-shear homogenizer for BED/GMA coatings? Achieve Superior Nano-Dispersion
- What function do magnetic stirrers and high-shear homogenizers serve? Optimize Core-Shell PCM Synthesis







