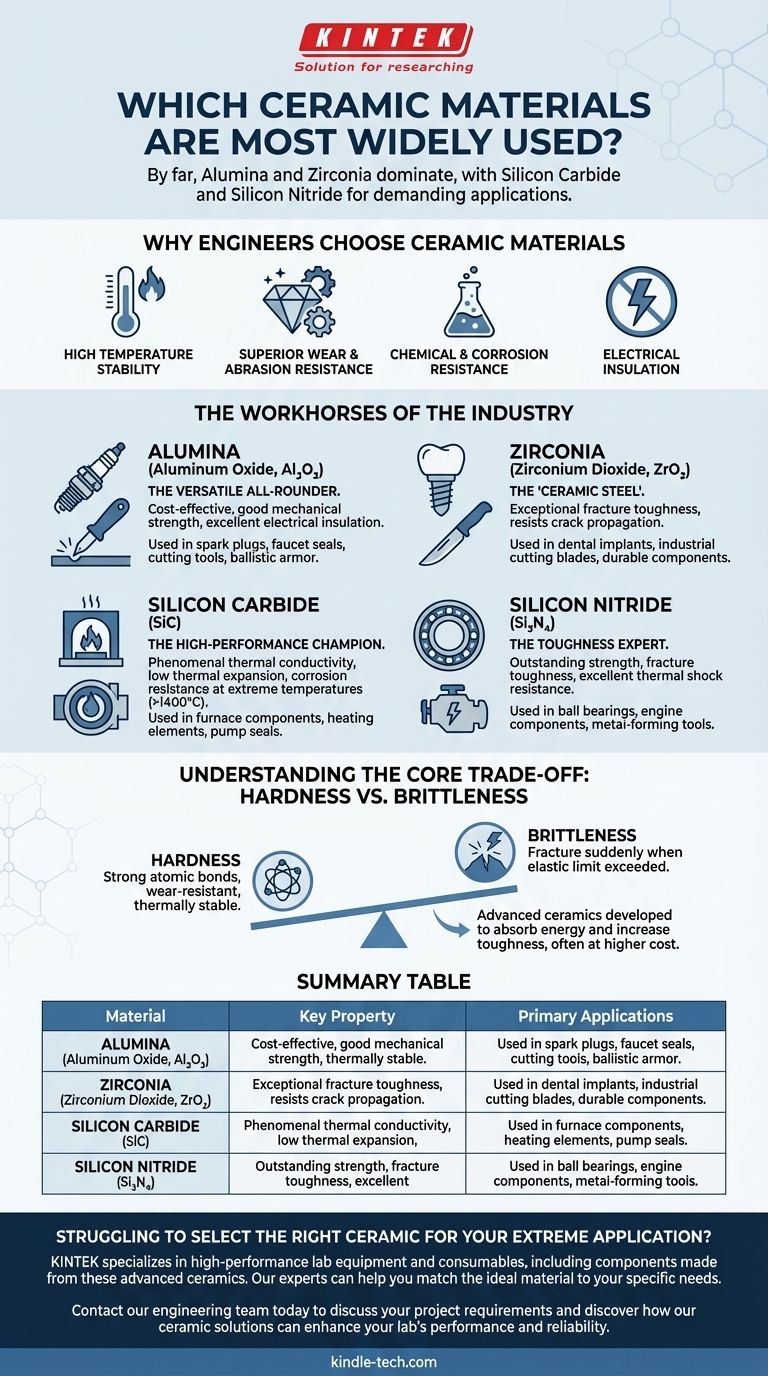
By far, the most widely used technical ceramics are Alumina and Zirconia, with Silicon Carbide and Silicon Nitride also holding significant roles in more demanding applications. These materials form the backbone of the advanced ceramics industry due to their exceptional properties and relative cost-effectiveness, making them indispensable in fields ranging from electronics and medicine to aerospace and manufacturing.
The selection of a ceramic material is never about finding a single "best" option. It is a precise engineering decision that involves matching a specific material’s unique profile of hardness, temperature stability, and toughness to the non-negotiable demands of an application.
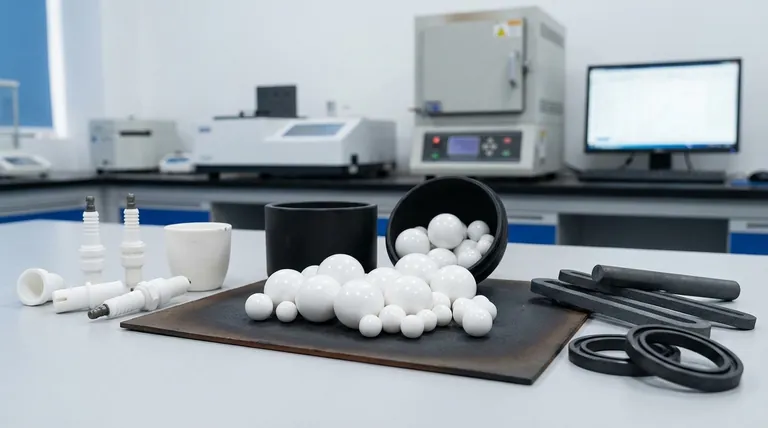

Why Engineers Choose Ceramic Materials
Engineers turn to technical ceramics when polymers and metals fail to meet performance requirements. The unique atomic bonds in ceramics give them a distinct set of characteristics that make them ideal for extreme environments.
High Temperature Stability
Ceramics maintain their strength and structural integrity at temperatures where metals would soften or melt. This is due to their strong covalent and ionic bonds, which require a great deal of thermal energy to break.
Superior Wear and Abrasion Resistance
Technical ceramics are exceptionally hard, often approaching the hardness of diamond. This makes them highly resistant to scratching, friction, and erosive wear, leading to a longer service life in abrasive conditions.
Chemical and Corrosion Resistance
Ceramics are largely inert and do not react with most acids, alkalis, or other corrosive agents. This quality is critical for components used in chemical processing, medical implants, and harsh industrial environments.
Electrical Insulation
Most technical ceramics are excellent electrical insulators, meaning they do not conduct electricity. This property makes them essential for manufacturing electronic components, circuit carriers, and high-voltage insulators.
The Workhorses of the Industry
While thousands of ceramic compositions exist, a few materials dominate industrial use due to their balanced properties, reliability, and established manufacturing processes.
Alumina (Aluminum Oxide, Al₂O₃): The Versatile All-Rounder
Alumina is the most common and cost-effective technical ceramic. Its combination of good mechanical strength, high hardness, and excellent electrical insulation makes it a go-to material for a vast range of applications.
You will find it in everything from spark plug insulators and faucet seals to cutting tools and ballistic armor.
Zirconia (Zirconium Dioxide, ZrO₂): The "Ceramic Steel"
Zirconia is renowned for its exceptional fracture toughness, a property that sets it apart from all other ceramics. By adding stabilizing agents, it can be engineered to resist crack propagation.
This makes it the material of choice for dental implants, industrial cutting blades, and components that require the hardness of a ceramic but with enhanced durability and resistance to catastrophic failure.
Silicon Carbide (SiC): The High-Performance Champion
Silicon Carbide is prized for its phenomenal thermal conductivity, low thermal expansion, and resistance to chemical corrosion at extreme temperatures. It maintains its strength at temperatures above 1,400°C.
Its primary uses are in high-temperature applications like furnace components, carborundum heating elements, and seals for high-performance chemical pumps.
Silicon Nitride (Si₃N₄): The Toughness Expert
Silicon Nitride offers an outstanding combination of high strength, fracture toughness, and excellent thermal shock resistance. It can withstand rapid and repeated temperature changes without cracking.
This unique profile makes it ideal for high-load, high-temperature applications like ball bearings in jet engines, automotive engine components, and metal-forming tools.
Understanding the Core Trade-off: Hardness vs. Brittleness
The primary challenge when working with ceramic materials is managing their inherent trade-off between hardness and toughness.
The Problem of Brittleness
The same strong atomic bonds that make ceramics hard, wear-resistant, and thermally stable also make them brittle. Unlike metals, which can bend or deform under stress, ceramics tend to fracture suddenly when their elastic limit is exceeded.
Engineering Around Brittleness
Material scientists have developed advanced ceramics like Zirconia and Silicon Nitride specifically to address this issue. These materials have microstructures that can absorb energy and stop a crack from spreading, significantly increasing their toughness.
However, this enhanced performance often comes at a higher manufacturing cost, representing a key decision point for any engineering project.
Matching the Material to Your Application
Choosing the right ceramic requires a clear understanding of your project's primary performance driver.
- If your primary focus is cost-effective wear resistance and electrical insulation: Alumina is almost always the correct starting point.
- If your primary focus is maximum fracture toughness and crack resistance: Zirconia is the leading candidate, especially for structural or medical components.
- If your primary focus is performance at extreme temperatures or in corrosive chemical environments: Silicon Carbide is likely the only viable option.
- If your primary focus is reliability under severe thermal shock and high mechanical load: Silicon Nitride offers a specialized and highly effective solution.
Ultimately, understanding the specific strengths and weaknesses of these core materials empowers you to make an informed and effective engineering choice.
Summary Table:
| Material | Key Property | Primary Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Alumina (Al₂O₃) | Cost-effective, excellent electrical insulation | Spark plugs, seals, cutting tools, electronic substrates |
| Zirconia (ZrO₂) | Exceptional fracture toughness | Dental implants, cutting blades, wear parts |
| Silicon Carbide (SiC) | Extreme temperature & corrosion resistance | Furnace components, heating elements, pump seals |
| Silicon Nitride (Si₃N₄) | High strength & thermal shock resistance | Engine bearings, automotive components, metal-forming tools |
Struggling to select the right ceramic for your extreme application? KINTEK specializes in high-performance lab equipment and consumables, including components made from these advanced ceramics. Our experts can help you match the ideal material—whether it's Alumina, Zirconia, SiC, or Si3N4—to your specific needs for temperature, wear, or corrosion resistance.
Contact our engineering team today to discuss your project requirements and discover how our ceramic solutions can enhance your lab's performance and reliability.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Precision Machined Zirconia Ceramic Ball for Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics
- Advanced Engineering Fine Ceramics Low Temperature Alumina Granulation Powder
- Advanced Engineering Fine Ceramics Boron Nitride (BN) Ceramic Parts
- Conductive Boron Nitride BN Ceramics Composite for Advanced Applications
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What are the applications of zirconia ceramics? Unlock High-Performance Solutions for Extreme Environments
- What are the advantages of using zirconia milling jars for sulfide electrolytes? Enhance Purity and Conductivity
- Why are ZrO2 grinding jars and balls required for sulfide solid electrolytes? Ensure Purity & Performance
- Why are 3mm zirconia grinding balls selected for Na3FePO4CO3 synthesis? Optimize Energy and Purity
- Why are zirconia grinding balls recommended for sulfide solid electrolytes? Essential Tips for High Purity Milling



















