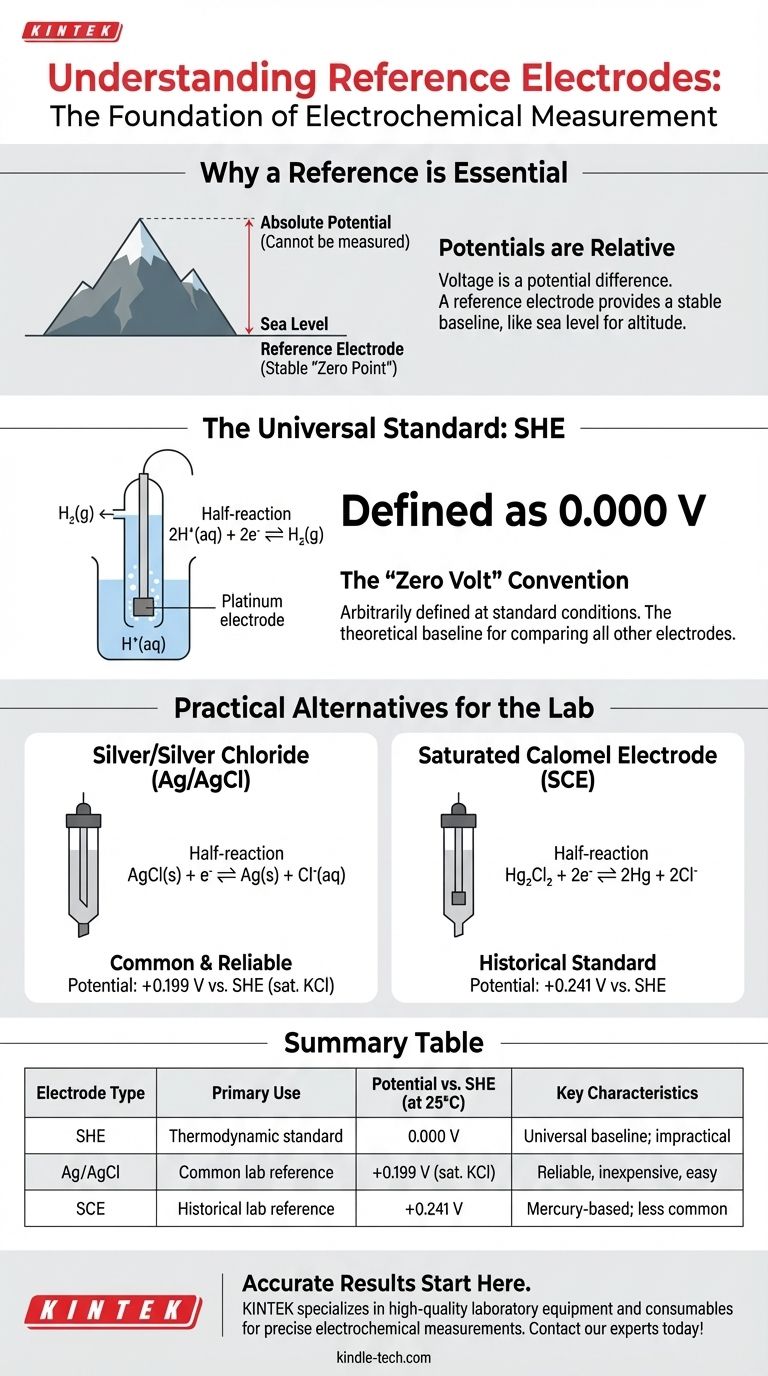
In electrochemistry, all potentials are measured relatively. The universal reference standard for measuring and reporting half-cell potentials is the Standard Hydrogen Electrode (SHE). By international convention, the SHE is arbitrarily assigned a potential of exactly 0.000 volts under standard conditions, creating a definitive baseline against which all other electrode potentials are compared.
You cannot measure the absolute potential of a single electrode in isolation. Voltage is a potential difference, so you must always measure it between two points. A reference electrode provides a stable, known potential, acting as a reliable "zero point" for measuring the unknown potential of another half-cell.

Why a Reference Electrode is Essential
The Problem of Absolute Potential
Think of measuring the height of a mountain. You can only describe its height relative to a common reference point, like sea level. You cannot assign it an "absolute" height in empty space.
An electrochemical half-cell is like that mountain peak. Its potential can only be determined by measuring the voltage difference between it and a stable reference point.
The Role of the Reference
The reference electrode provides that electrochemical "sea level." It is a half-cell designed to maintain a constant and reproducible potential, unaffected by the composition of the solution it is measuring.
When you connect your test electrode and the reference electrode into a circuit, a voltmeter measures the potential difference (E_cell) between them. Since you know the potential of the reference (E_ref), you can easily calculate the potential of your test electrode (E_test).
The Universal Standard: The SHE
Defining the Baseline
The Standard Hydrogen Electrode (SHE) is the primary reference electrode used for all thermodynamic calculations and tabulations of standard electrode potentials.
The half-reaction for the SHE is: 2H⁺(aq) + 2e⁻ ⇌ H₂(g).
The "Zero Volt" Convention
By international agreement, the potential of the SHE is defined as exactly 0.000 V at standard conditions: 25°C, a hydrogen ion concentration of 1 M, and a hydrogen gas pressure of 1 atm.
This value is not measured; it is an arbitrary definition that establishes a universal scale for comparing all other electrode systems.
Practical Alternatives: Secondary Reference Electrodes
The Need for Convenience
While the SHE is the fundamental standard, it is extremely impractical for routine laboratory work. It requires a continuous supply of flammable hydrogen gas and is difficult to prepare and maintain.
Because of this, chemists use more convenient and robust secondary reference electrodes. These are calibrated against the SHE, so their potential on the hydrogen scale is precisely known.
The Silver/Silver Chloride (Ag/AgCl) Electrode
The Ag/AgCl electrode is one of the most common secondary reference electrodes. It is reliable, inexpensive, and simple to use.
Its half-reaction is: AgCl(s) + e⁻ ⇌ Ag(s) + Cl⁻(aq).
The potential of an Ag/AgCl electrode is determined by the concentration of the chloride solution it contains. For example, one filled with saturated KCl solution has a potential of +0.199 V versus the SHE at 25°C.
The Saturated Calomel Electrode (SCE)
Another historically common secondary electrode is the Saturated Calomel Electrode (SCE). It is based on a mercury/mercurous chloride reaction and has a potential of +0.241 V versus the SHE at 25°C.
Understanding the Trade-offs
SHE: The Standard vs. The Tool
The SHE is the perfect theoretical standard, providing the zero point for our entire electrochemical scale. However, it is a poor practical tool due to its complexity and safety requirements.
Ag/AgCl: The Practical Workhorse
The Ag/AgCl electrode is the go-to for most applications due to its stability and ease of use. Its main limitation is that its potential is temperature-dependent and it can become contaminated by solutions containing proteins or sulfides that react with silver ions.
The Importance of Reporting
When you measure a potential using a secondary reference, it is critical to report which electrode was used (e.g., "+0.50 V vs. Ag/AgCl"). This allows any researcher to convert the measured value back to the universal SHE scale, ensuring results can be compared accurately across different labs and experiments.
Making Sense of Potential Values
To properly interpret electrochemical data, it is crucial to know which reference was used.
- If your primary focus is fundamental theory: Understand that the Standard Hydrogen Electrode (SHE) is the zero point against which all standard electrode potentials in textbooks are defined.
- If your primary focus is practical lab work: You will most likely use a secondary electrode like Ag/AgCl, and you must know its potential relative to the SHE to accurately calculate your unknown cell's potential.
- If your primary focus is comparing data from different sources: Always convert all reported potentials to the universal SHE scale to ensure you are making a valid, apples-to-apples comparison.
Mastering the concept of the reference electrode is the key to moving from theoretical electrochemistry to accurate, real-world measurement.
Summary Table:
| Electrode Type | Primary Use | Potential vs. SHE (at 25°C) | Key Characteristics |
|---|---|---|---|
| Standard Hydrogen Electrode (SHE) | Thermodynamic standard, defining zero point | 0.000 V | Universal baseline; impractical for routine use |
| Silver/Silver Chloride (Ag/AgCl) | Common laboratory reference | +0.199 V (saturated KCl) | Reliable, inexpensive, easy to use |
| Saturated Calomel Electrode (SCE) | Historical laboratory reference | +0.241 V | Mercury-based; less common today |
Need precise electrochemical measurements in your lab? KINTEK specializes in high-quality laboratory equipment and consumables, including reliable reference electrodes and electrochemical cells. Our products ensure accurate, reproducible results for researchers and technicians. Let us help you select the right tools for your specific application. Contact our experts today to discuss your laboratory needs!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Reference Electrode Calomel Silver Chloride Mercury Sulfate for Laboratory Use
- Rotating Platinum Disk Electrode for Electrochemical Applications
- Graphite Disc Rod and Sheet Electrode Electrochemical Graphite Electrode
- H-Type Double-Layer Optical Electrolytic Electrochemical Cell with Water Bath
- Platinum Sheet Electrode for Laboratory and Industrial Applications
People Also Ask
- Why is a Saturated Calomel Electrode (SCE) used as a reference electrode in microbial fuel cell research?
- Why is the calomel electrode used as a secondary reference electrode? A Practical Guide to Stable Measurements
- What is the reference electrode for mercury mercury chloride? Discover the Saturated Calomel Electrode (SCE)
- Which electrode is used as a reference? A Guide to Accurate Electrochemical Measurements
- What are the characteristics of a saturated calomel electrode for neutral solutions? Understanding its stability and limitations.



















