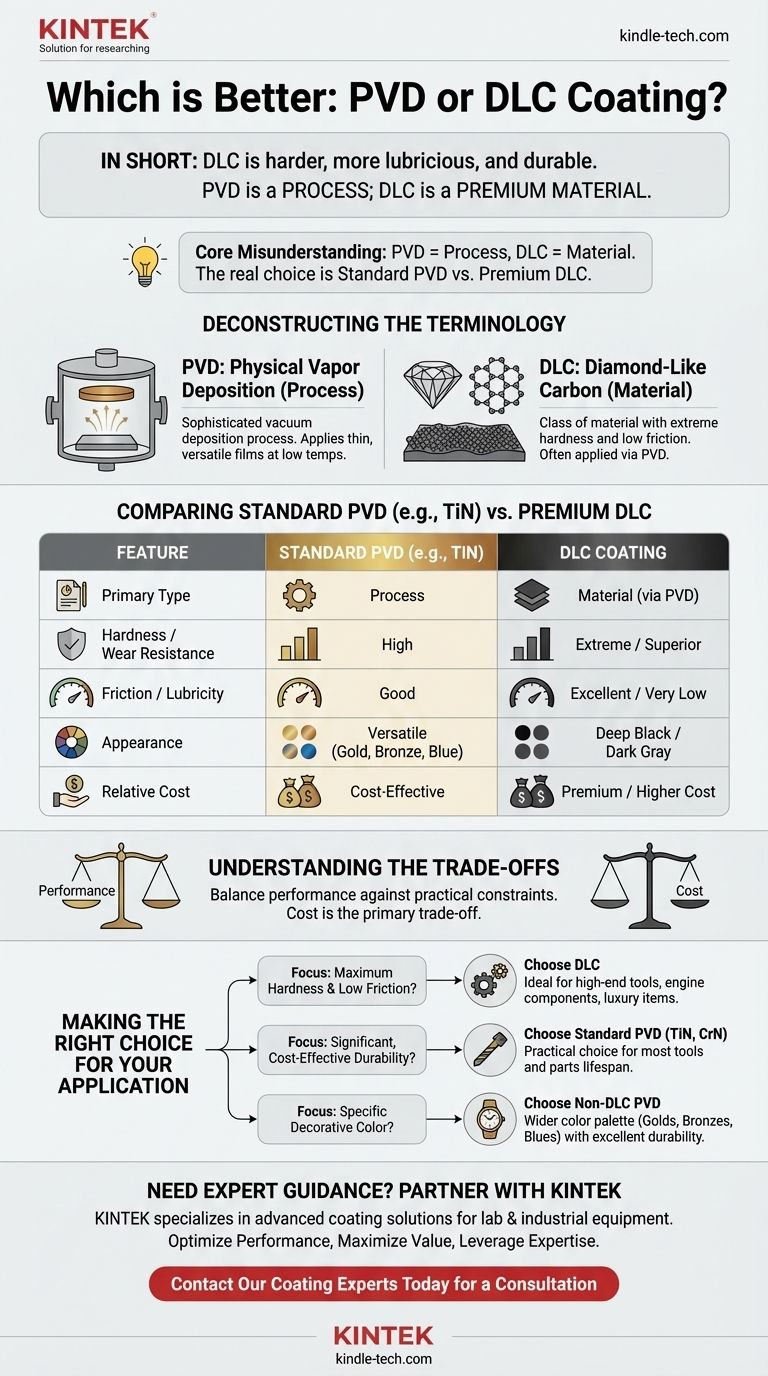
In short, a Diamond-Like Carbon (DLC) coating is generally harder, more durable, and more lubricious than a standard Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD) coating. While both provide a significant improvement in surface performance, DLC is a premium, high-performance variant often applied using the PVD process itself.
The core misunderstanding is in pitting "PVD vs. DLC." PVD is the process used to apply a coating, while DLC is the material being applied. The real choice is between a standard, cost-effective PVD coating (like Titanium Nitride) and a premium DLC coating for maximum performance.

Deconstructing the Terminology: Process vs. Material
To make an informed decision, it's critical to understand what these terms actually mean. The confusion often comes from marketing language that uses them interchangeably.
What is PVD (Physical Vapor Deposition)?
PVD is a sophisticated vacuum deposition process. In simple terms, a solid material (like titanium nitride or carbon) is vaporized in a vacuum chamber and then deposited as a thin, high-performance film onto a substrate.
This process is valued for its versatility. It can be used to apply dozens of different types of coatings, each with unique properties.
PVD coatings are applied at relatively low temperatures, which prevents warping or damage to the underlying part. This makes it ideal for components with tight tolerances, like cutting tools or watch cases.
What is DLC (Diamond-Like Carbon)?
DLC is a specific class of material with a molecular structure that has properties of both natural diamond and graphite. It is not pure diamond but an amorphous carbon film.
The defining characteristics of DLC are its extreme hardness and exceptionally low friction, creating a slick, durable surface. As one of the references notes, it is made similarly to synthetic diamonds and is "significantly harder and more resistant" than other common coatings.
Crucially, DLC is most often applied to a surface using the PVD process. So, DLC is not an alternative to PVD; it is a high-end type of PVD coating.
Comparing Standard PVD Coatings vs. DLC
When people ask "PVD vs. DLC," they are typically comparing a common PVD coating like Titanium Nitride (TiN) against the more advanced DLC.
Performance: Hardness and Wear Resistance
Standard PVD coatings like TiN dramatically increase the hardness and wear resistance of a surface. They provide excellent protection against scratches, abrasion, and corrosion.
DLC takes this a step further. Its diamond-like carbon structure provides a level of hardness and scratch resistance that is superior to almost any other PVD coating. For applications involving extreme wear, DLC is the clear performance leader.
Performance: Friction and Lubricity
While all PVD coatings reduce friction compared to an uncoated surface, DLC is in another league. It creates an intensely slick, or "lubricious," surface.
This makes DLC the premier choice for high-performance moving parts, such as internal engine components, firearm bolts, or elite watch movements, where minimizing friction is paramount.
Appearance and Aesthetics
Standard PVD processes can produce a wide spectrum of stable, decorative colors, including various shades of gold, bronze, blue, and black. This makes it a versatile choice for consumer products.
DLC coatings are almost always a shade of dark gray or deep, rich black. While this look is highly desirable for tactical and luxury goods, it lacks the color versatility of other PVD types.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing a coating is always a matter of balancing performance against other practical constraints. There is no single "best" option for every scenario.
The Deciding Factor: Cost
The primary trade-off is cost. The process for depositing a high-quality DLC film is more complex and time-consuming than for a standard TiN coating.
Consequently, DLC is a significantly more expensive, premium finish. Its cost is only justifiable when its unique performance characteristics are a genuine requirement.
Application Suitability
Standard PVD coatings are the workhorse of the industry. They provide a massive, cost-effective performance boost for countless applications, from drill bits and cutting tools to door hardware and faucets.
DLC is often reserved for applications where failure is not an option or where peak performance provides a competitive advantage. It can be considered "overkill" for a standard tool but essential for a high-frequency racing engine part.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Your goal should guide your decision. The question is not which coating is better, but which is the right tool for your specific job.
- If your primary focus is maximum hardness and low-friction performance: Choose DLC. It is the superior option for extreme wear resistance and lubricity, ideal for high-end tools, internal components, and luxury items.
- If your primary focus is a significant, cost-effective durability upgrade: Choose a standard PVD coating like TiN or CrN. This is the most practical and economical choice for improving the lifespan of most tools and parts.
- If your primary focus is achieving a specific decorative color: Choose a non-DLC PVD coating. You will have a much wider palette of options, including golds, bronzes, and blues, while still gaining excellent durability.
Ultimately, selecting the right surface treatment requires aligning the material's properties with your application's demands and budget.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Standard PVD Coating (e.g., TiN) | DLC Coating |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Type | Process (can apply many materials) | Material (often applied via PVD) |
| Hardness / Wear Resistance | High | Extreme / Superior |
| Friction / Lubricity | Good | Excellent / Very Low |
| Appearance | Versatile (Golds, Bronzes, Blues) | Deep Black / Dark Gray |
| Relative Cost | Cost-Effective | Premium / Higher Cost |
| Best For | General durability, decorative colors | Extreme wear, low friction, peak performance |
Need Expert Guidance on the Ideal Coating for Your Components?
Choosing between a standard PVD coating and a premium DLC finish is critical for your product's performance, durability, and cost. The right choice depends entirely on your specific application requirements.
KINTEK specializes in advanced coating solutions for laboratory and industrial equipment. We can help you navigate these complex material decisions to ensure your components meet the highest standards.
Partner with KINTEK to:
- Optimize Performance: Select the coating that delivers the exact hardness, lubricity, and corrosion resistance your project demands.
- Maximize Value: Balance superior performance with budget constraints, avoiding over-engineering or under-specifying.
- Leverage Expertise: Benefit from our deep knowledge of PVD processes and materials, including high-end DLC applications.
Let's discuss your project's needs. Contact our coating experts today for a personalized consultation and discover how KINTEK's solutions can enhance your lab equipment and consumables.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition RF PECVD
- Hemispherical Bottom Tungsten Molybdenum Evaporation Boat
- Aluminized Ceramic Evaporation Boat for Thin Film Deposition
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine for Lamination and Heating
- Ceramic Evaporation Boat Set Alumina Crucible for Laboratory Use
People Also Ask
- What are the advantages of PECVD? Enable Low-Temperature, High-Quality Thin-Film Deposition
- What are the benefits of PECVD? Achieve Superior Low-Temperature Thin Film Deposition
- Why does PECVD commonly use RF power input? For Precise Low-Temperature Thin Film Deposition
- How are PECVD and CVD different? A Guide to Choosing the Right Thin-Film Deposition Process
- What is the principle of plasma enhanced chemical vapor deposition? Achieve Low-Temperature Thin Film Deposition



















