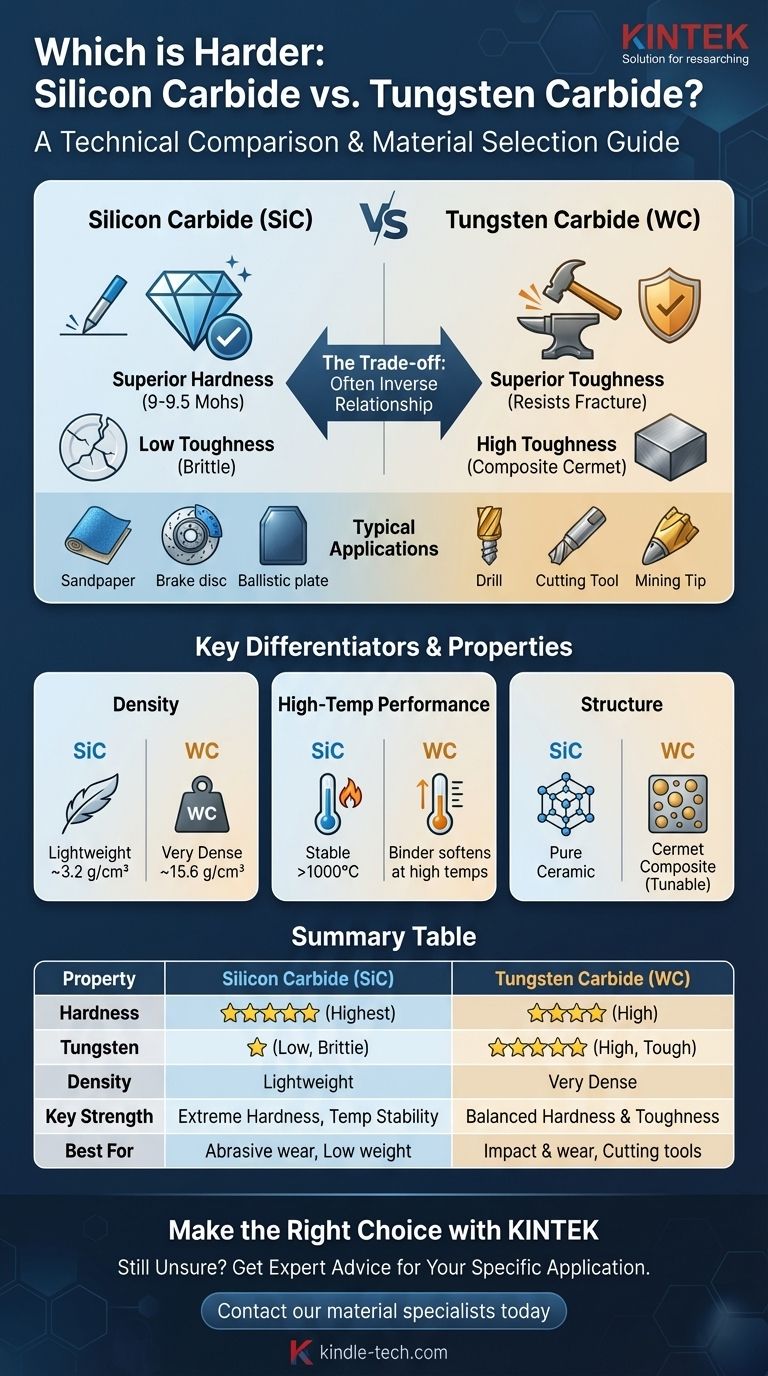
From a purely technical standpoint, silicon carbide (SiC) is harder than tungsten carbide (WC). On the Mohs scale of mineral hardness, silicon carbide scores around a 9 to 9.5, just under diamond at 10. Tungsten carbide is slightly softer, typically rating between 8.5 and 9. This difference is also clear on the Vickers hardness scale, where SiC consistently measures higher than WC.
While silicon carbide wins on pure hardness, this is only half the story. The most critical distinction is that tungsten carbide is significantly tougher. Your material choice will almost always depend on a trade-off between silicon carbide's superior hardness and tungsten carbide's superior resistance to fracture.

A Tale of Two Properties: Hardness vs. Toughness
Understanding the difference between hardness and toughness is the key to selecting the right material. They are not interchangeable terms and often have an inverse relationship.
Defining Hardness: Resistance to Scratching
Hardness is a material's ability to resist surface deformation, such as scratching, abrasion, or indentation. Materials with high hardness are excellent at cutting other materials and resisting abrasive wear.
Because it is one of the hardest materials known, silicon carbide excels in applications where pure abrasive wear resistance is the primary goal.
Defining Toughness: Resistance to Breaking
Toughness, or fracture toughness, is a material's ability to absorb energy and deform without fracturing. It measures resistance to chipping, cracking, and catastrophic failure under impact or load.
A material can be extremely hard but also very brittle, meaning it shatters easily. This is the case with most pure ceramics, including silicon carbide.
The Tungsten Carbide Advantage: A Composite Structure
Tungsten carbide is not a pure ceramic; it is a cermet, a composite of ceramic particles (tungsten carbide) held in a metallic binder matrix (usually cobalt).
This structure gives it a unique advantage. The hard WC particles provide wear resistance, while the ductile cobalt binder stops cracks from propagating, imparting a toughness that is impossible for pure silicon carbide to achieve.
Key Differentiators Beyond Hardness
The decision between SiC and WC rarely comes down to a single property. Several other factors are critical.
Density: A Question of Weight
Tungsten carbide is an extremely dense material, typically around 15.6 g/cm³. Silicon carbide is, by comparison, very lightweight at only 3.2 g/cm³.
This makes WC roughly three times heavier than steel and nearly five times heavier than SiC. For any application where weight is a concern, such as aerospace components or body armor, this difference is a deciding factor.
High-Temperature Performance
Silicon carbide generally exhibits superior strength, creep resistance, and oxidation resistance at very high temperatures (above 1000°C) compared to most grades of tungsten carbide.
The metallic binder in tungsten carbide can begin to soften at high temperatures, reducing its performance, whereas the strong covalent bonds in SiC maintain its integrity.
Typical Applications as a Guide
The common uses for each material perfectly illustrate their core strengths:
- Silicon Carbide: Used for sandpaper, grinding wheels, high-performance brake discs, and the ceramic plates in bulletproof vests. These applications leverage its extreme hardness and light weight.
- Tungsten Carbide: Used for cutting tools (drill bits, end mills), mining tips, and high-pressure industrial parts. These applications demand its unique combination of hardness and toughness to handle intense impact and wear.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing the wrong material based on a single metric like hardness is a common and costly mistake.
The Brittleness of Silicon Carbide
The primary trade-off for silicon carbide's extreme hardness is its brittleness. It is highly susceptible to fracture from sharp impacts or shock loading. If your application involves vibration, chatter, or sudden forces, SiC is often a fragile and unsuitable choice.
The Binder's Role in Tungsten Carbide
The properties of tungsten carbide are tunable based on its cobalt binder content. More binder (e.g., 15%) results in a tougher but softer material. Less binder (e.g., 6%) creates a harder material that is more brittle. This allows engineers to fine-tune a grade for a specific task.
Cost and Manufacturing Complexity
Both materials are significantly more expensive than traditional steels and require specialized manufacturing processes like sintering. The final cost is highly dependent on the part's geometry, purity, and the specific grade required for the application.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
To select the correct material, you must clearly define your primary operational challenge.
- If your primary focus is maximum scratch and wear resistance without significant impact: Silicon carbide is the superior choice for its unmatched hardness.
- If your primary focus is a balance of high wear resistance and the ability to withstand impact or shock: Tungsten carbide is the correct material due to its composite toughness.
- If your primary focus is minimizing weight while maintaining high hardness: Silicon carbide offers an exceptional hardness-to-weight ratio.
- If your primary focus is performance in extreme-temperature, oxidizing environments: Silicon carbide often provides better stability and resistance.
Ultimately, selecting the right material requires moving beyond the simple question of hardness to a deeper understanding of toughness and the specific demands of your task.
Summary Table:
| Property | Silicon Carbide (SiC) | Tungsten Carbide (WC) |
|---|---|---|
| Mohs Hardness | 9 - 9.5 | 8.5 - 9 |
| Toughness | Low (Brittle) | High (Tough) |
| Density | ~3.2 g/cm³ (Lightweight) | ~15.6 g/cm³ (Very Dense) |
| Key Strength | Superior Hardness, High-Temp Stability | Excellent Hardness-Toughness Balance |
| Typical Uses | Abrasives, Grinding, High-Temp Components | Cutting Tools, Mining Tips, Wear Parts |
Still Unsure Which Material is Right for Your Project?
Choosing between silicon carbide and tungsten carbide is a critical decision that impacts performance, durability, and cost. KINTEK, your trusted partner for laboratory equipment and consumables, can help you navigate this complex material selection.
We provide expert guidance and high-quality materials tailored to your specific application needs, whether you require extreme hardness, superior toughness, or a precise balance of both.
Contact our material specialists today for a personalized consultation. Let us help you select the ideal material to ensure your project's success.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Silicon Carbide (SIC) Ceramic Plate for Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics
- Silicon Carbide (SIC) Ceramic Sheet Wear-Resistant Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics
- Silicon Carbide SiC Thermal Heating Elements for Electric Furnace
- Zirconia Ceramic Gasket Insulating Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics
- Precision Machined Silicon Nitride (SiN) Ceramic Sheet for Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics
People Also Ask
- Is silicon carbide better than ceramic? Discover the Superior Technical Ceramic for Your Application
- What is refractory ceramic? The Engineered Barrier for Extreme Heat and Harsh Environments
- What are the different types of hot plates? Find the Perfect Match for Your Lab's Heating Needs
- What is the function of alumina setter plates for LATP? Protect Material Purity & Prevent Adhesion
- Why is it necessary to use high-temperature and corrosion-resistant ceramics for H2SO4 decomposers in the IS process?



















