In short, the most common techniques used for the deposition of metals are forms of Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD), such as thermal evaporation and sputtering. These processes involve vaporizing a solid metal source in a vacuum and allowing it to condense as a thin film onto a substrate.
The core principle behind metal deposition is moving metal from a source to a target surface on an atom-by-atom basis. Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD) is the definitive method for this, offering precise control over film thickness, purity, and adhesion in a high-vacuum environment.
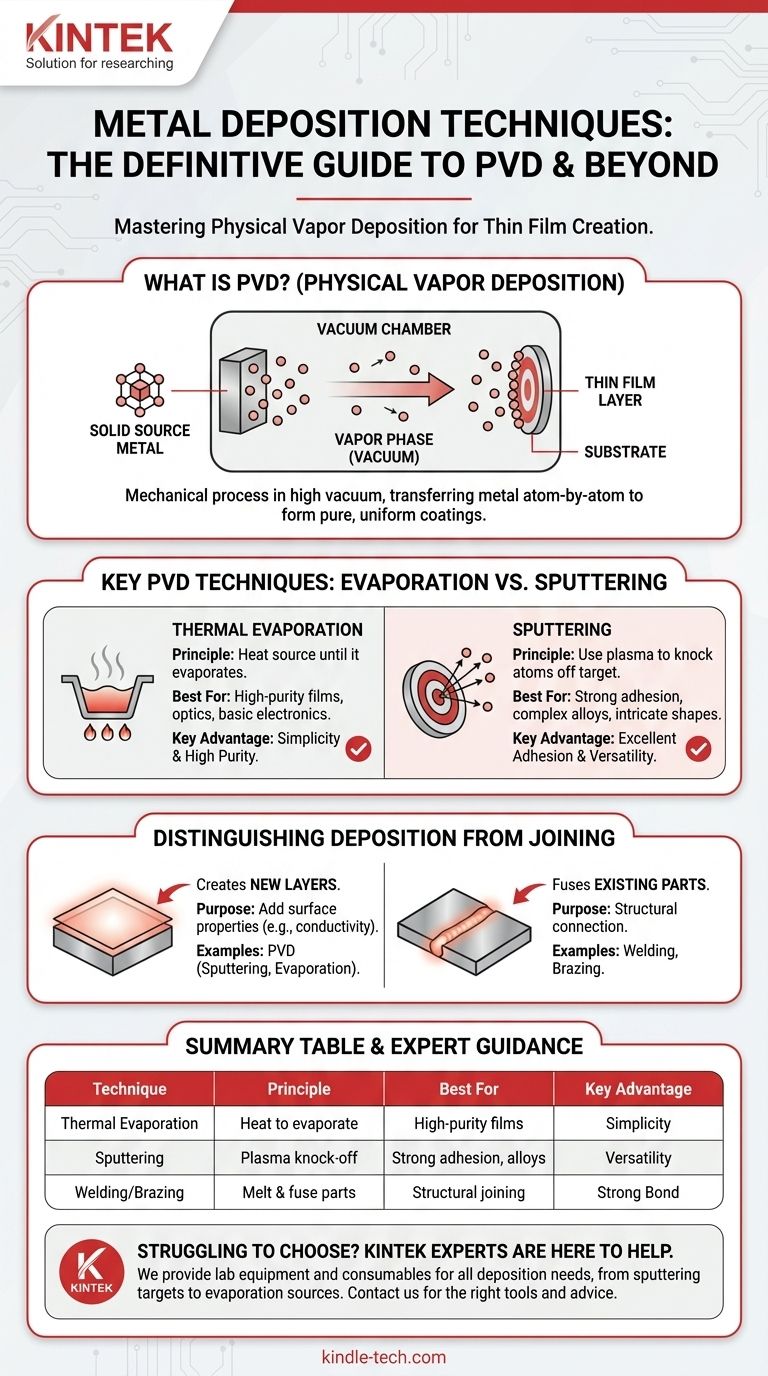
What is Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD)?
PVD is a category of vacuum deposition methods used to produce thin films and coatings. The process is fundamentally mechanical, not chemical.
A solid source material (the metal) is converted into a gaseous vapor phase. This vapor then travels through a vacuum chamber and condenses on the target object, known as the substrate, forming a thin, uniform metallic layer.
The entire process occurs in a high vacuum to prevent the metal vapor from reacting with or scattering off of air molecules, ensuring a pure and direct path to the substrate.
Key PVD Techniques for Metals
While there are many variations, two techniques form the foundation of metal PVD.
Thermal Evaporation
This is one of the most straightforward PVD methods. A solid piece of the source metal is heated in a high vacuum until it evaporates.
The metal vapor then expands throughout the chamber, coating everything in its line of sight, including the strategically placed substrate. This method is valued for its simplicity and ability to create very high-purity films.
Sputtering
Sputtering is a more energetic and versatile process. Instead of heat, it uses a high-energy plasma (typically an inert gas like Argon).
Positively charged ions from the plasma are accelerated into a negatively charged metal source, called the target. This collision is energetic enough to physically knock metal atoms off the target's surface. These "sputtered" atoms then travel and deposit onto the substrate.
Distinguishing Deposition from Joining
It is critical to distinguish between deposition, which creates a new layer, and joining, which fuses existing parts.
Deposition Creates Layers
PVD techniques like sputtering and evaporation are designed to create a thin film or coating on a surface. The goal is to add a new layer of material with specific properties (e.g., electrical conductivity, reflectivity, or corrosion resistance).
Joining Fuses Parts
Techniques like welding or brazing are used to join two separate components together. While they involve metal, their purpose is structural fusion, not the creation of a thin, uniform surface coating. They are fundamentally joining processes, not deposition processes.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing the right technique depends on the specific requirements of the final product.
Thermal Evaporation Challenges
While simple, evaporation offers less control over film adhesion and structure compared to sputtering. The low energy of the process means the atoms land gently, which may not be ideal for applications requiring maximum durability. It is also not suitable for materials with very high melting points or complex alloys.
Sputtering Considerations
Sputtering provides excellent film adhesion and density because the atoms arrive at the substrate with much higher energy. It is also ideal for depositing alloys, as the composition of the target is well-preserved in the final film. However, the equipment is more complex and expensive, and the process is typically slower than evaporation.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your application's specific needs will determine the best method.
- If your primary focus is high-purity, simple metal films for applications like optics or basic electronics: Thermal evaporation is often the most direct and cost-effective choice.
- If your primary focus is strong adhesion, complex alloys, or uniform coverage on intricate shapes: Sputtering provides superior control, density, and versatility for demanding applications.
- If your primary focus is structurally connecting two metal components: You should be investigating joining techniques like welding, which are entirely different from film deposition.
Ultimately, selecting the correct technique requires a clear understanding of whether you are creating a new surface or joining existing ones.
Summary Table:
| Technique | Principle | Best For | Key Advantage |
|---|---|---|---|
| Thermal Evaporation | Heating metal to evaporate in a vacuum | High-purity films, optics, basic electronics | Simplicity and high purity |
| Sputtering | Using plasma to knock atoms off a target | Strong adhesion, complex alloys, intricate shapes | Excellent film density and versatility |
| Welding/Brazing | Melting and fusing separate components | Structural joining of parts | Creates a strong mechanical bond |
Struggling to choose the right metal deposition technique for your project? The experts at KINTEK are here to help. We specialize in lab equipment and consumables for all your deposition needs, from sputtering targets to thermal evaporation sources. Our team can provide the right tools and expert advice to ensure your thin film coatings meet exact specifications for purity, adhesion, and performance. Contact KINTEL today to discuss your application and discover how our solutions can enhance your laboratory's capabilities.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Molybdenum Tungsten Tantalum Evaporation Boat for High Temperature Applications
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition RF PECVD
- Hemispherical Bottom Tungsten Molybdenum Evaporation Boat
- Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment System Chamber Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- Evaporation Boat for Organic Matter
People Also Ask
- What is the thermal evaporation technique? A Guide to Thin-Film Deposition for Your Lab
- What is vacuum thermal evaporation? A Guide to High-Purity Thin Film Deposition
- What are the drawbacks of thermal evaporation? Understanding the Limitations for High-Performance Applications
- What is the difference between sputtering and thermal evaporation? Choose the Right PVD Method for Your Thin Film
- What is the meaning of thermal evaporation? A Guide to Simple, Cost-Effective Thin Film Coating


















