In short, pyrolysis primarily removes carbon-based organic waste. This process is a form of thermal decomposition, meaning it uses high heat in the absence of oxygen to break down materials rather than burn them. Its main applications are for complex plastic streams and various forms of biomass that are otherwise difficult to dispose of or recycle.
The core principle to understand is that pyrolysis isn’t about disposal; it’s about chemical transformation. It targets materials rich in carbon—like plastics and plant matter—and converts them from a waste product into valuable outputs like synthetic fuels and chemicals.
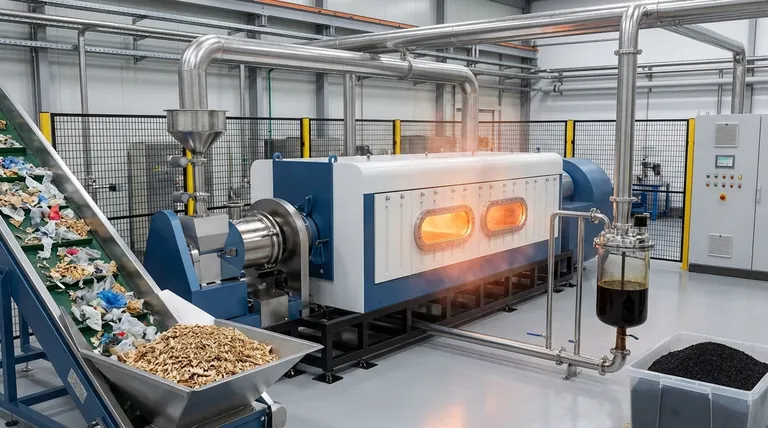

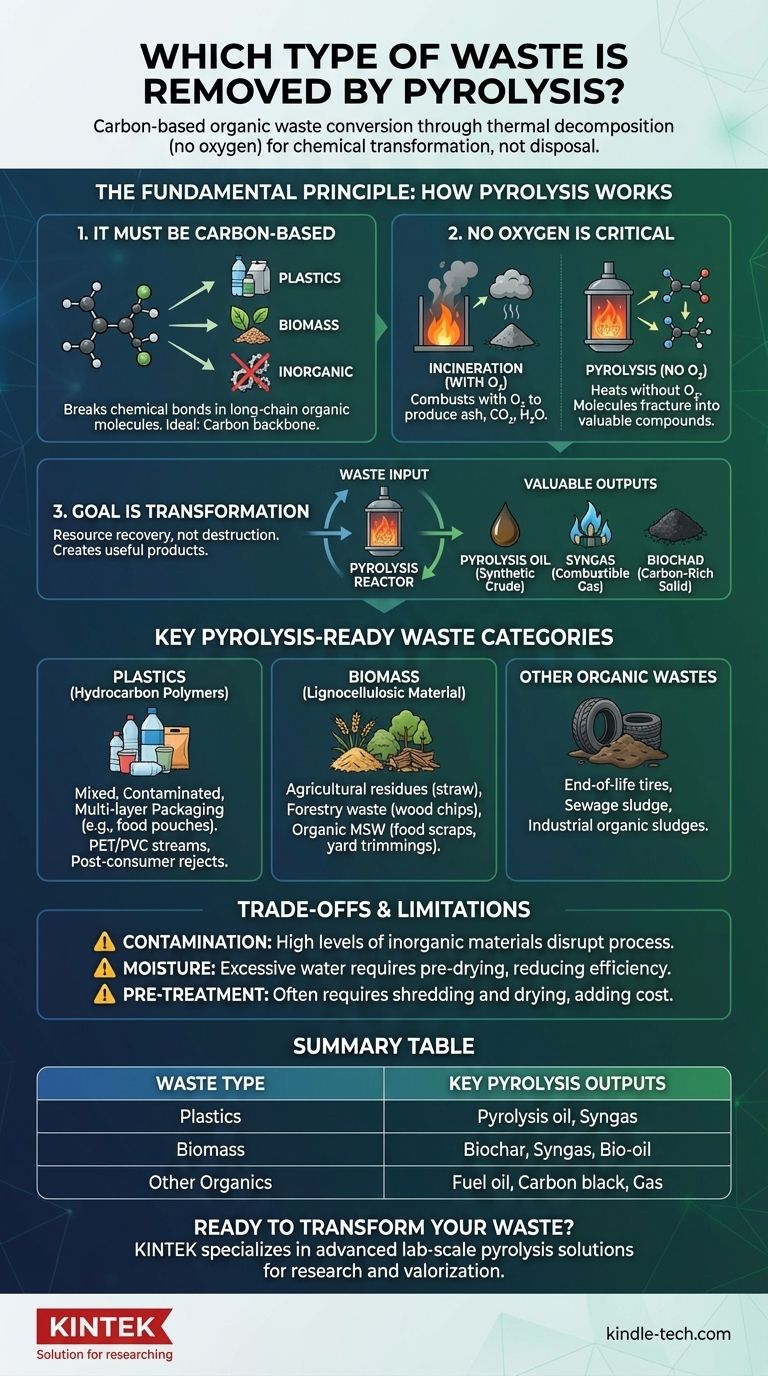
The Fundamental Principle: What Makes Waste Suitable for Pyrolysis?
To understand which wastes can be treated by pyrolysis, you must first understand how the process works. It is fundamentally different from incineration (burning).
It Must Be Carbon-Based
Pyrolysis works by breaking the chemical bonds within long-chain organic molecules. This means the ideal feedstock is any material built around a carbon backbone.
Inorganic materials like metals, glass, concrete, and rock cannot be broken down by this process and are therefore unsuitable.
The Absence of Oxygen is Critical
When you heat organic material with oxygen, it combusts, producing ash, carbon dioxide, and water. This is incineration.
Pyrolysis involves heating the material in a reactor with little to no oxygen. This prevents combustion and instead causes the molecules to fracture into smaller, valuable compounds.
The Goal is Transformation, Not Destruction
The output of pyrolysis is not ash but a collection of useful products. This makes it a technology for resource recovery, not just waste management.
The primary outputs are typically pyrolysis oil (a synthetic crude), syngas (a mixture of combustible gases), and biochar (a stable, carbon-rich solid).
Key Categories of Pyrolysis-Ready Waste
Because it targets organic materials, pyrolysis is highly versatile. It is particularly valuable for waste streams that challenge traditional recycling methods.
Plastics (Hydrocarbon Polymers)
Pyrolysis is exceptionally effective for plastics that are difficult to recycle mechanically.
This includes post-consumer plastics, rejects from recycling facilities, and complex multi-layer packaging (like food pouches) that combine different materials. It can even process mixed and contaminated plastics, such as PET/PVC streams.
Biomass (Lignocellulosic Material)
Any organic matter derived from plants or animals is a candidate for pyrolysis.
Common biomass feedstocks include agricultural residues (straw, corn stover), forestry waste (wood chips, sawdust), and the organic fraction of municipal solid waste (food scraps, yard trimmings).
Other Challenging Organic Wastes
The technology's application extends to other complex carbon-based waste streams that are often sent to landfills.
This includes materials like end-of-life tires, sewage sludge, and certain types of industrial organic sludges.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
While powerful, pyrolysis is not a universal solution for all waste. Understanding its limitations is critical for proper application.
The Problem of Contamination
While pyrolysis can handle some mixed materials, high levels of inorganic contaminants (like metal or glass) can disrupt the process and damage equipment.
Excessive moisture content in the feedstock also poses a challenge, as energy must be spent to evaporate the water before pyrolysis can begin, reducing the overall efficiency.
Pre-Treatment is Often Necessary
Most waste streams require some form of pre-treatment before entering a pyrolysis reactor.
This typically involves shredding to create a uniform particle size and drying to reduce moisture, which adds cost and complexity to the overall operation.
Economic and Energetic Viability
Pyrolysis is an energy-intensive process that requires significant heat. Its economic viability depends entirely on whether the market value of its outputs (oil, gas, char) exceeds the high operational costs.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The suitability of pyrolysis depends directly on the type of waste you need to manage and your desired outcome.
- If your primary focus is hard-to-recycle plastics: Pyrolysis is an excellent advanced recycling option for mixed, contaminated, or multi-layer plastic streams that would otherwise end up in a landfill.
- If your primary focus is agricultural or forestry waste: Biomass pyrolysis offers a clear path to convert low-value organic residues into biofuels and a valuable soil amendment (biochar).
- If your primary focus is general municipal solid waste (MSW): Pyrolysis should be applied after sorting, targeting the separated plastic and organic fractions rather than the entire raw waste stream.
Ultimately, pyrolysis serves as a powerful chemical recycling tool, best suited for transforming specific, high-carbon waste streams into new resources.
Summary Table:
| Waste Type | Examples | Key Pyrolysis Outputs |
|---|---|---|
| Plastics | Mixed plastics, multi-layer packaging | Pyrolysis oil, syngas |
| Biomass | Wood chips, agricultural residues, food waste | Biochar, syngas, bio-oil |
| Other Organics | Tires, sewage sludge | Fuel oil, carbon black, gas |
Ready to transform your carbon-based waste streams into valuable products?
KINTEK specializes in advanced pyrolysis solutions for laboratories and research facilities. Our equipment is designed to efficiently process challenging organic materials like plastics and biomass, helping you recover valuable resources and advance your sustainability goals.
Contact our experts today to discuss how our lab-scale pyrolysis systems can meet your specific research and waste valorization needs.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace Biomass Pyrolysis Plant
- Electric Rotary Kiln Continuous Working Small Rotary Furnace Heating Pyrolysis Plant
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Non Consumable Vacuum Arc Induction Melting Furnace
- Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment System Chamber Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
People Also Ask
- What are the products of pyrolysis of biomass? Unlock Bio-Char, Bio-Oil, and Syngas
- Is pyrolysis viable? A Guide to Economic, Technological, and Environmental Success
- What are the advantages of pyrolysis technology? Turn Waste into Profit and Reduce Emissions
- What are the different types of pyrolysis machines? Choose the Right System for Your Output
- What is a disadvantage of biomass energy? The Hidden Environmental and Economic Costs


















