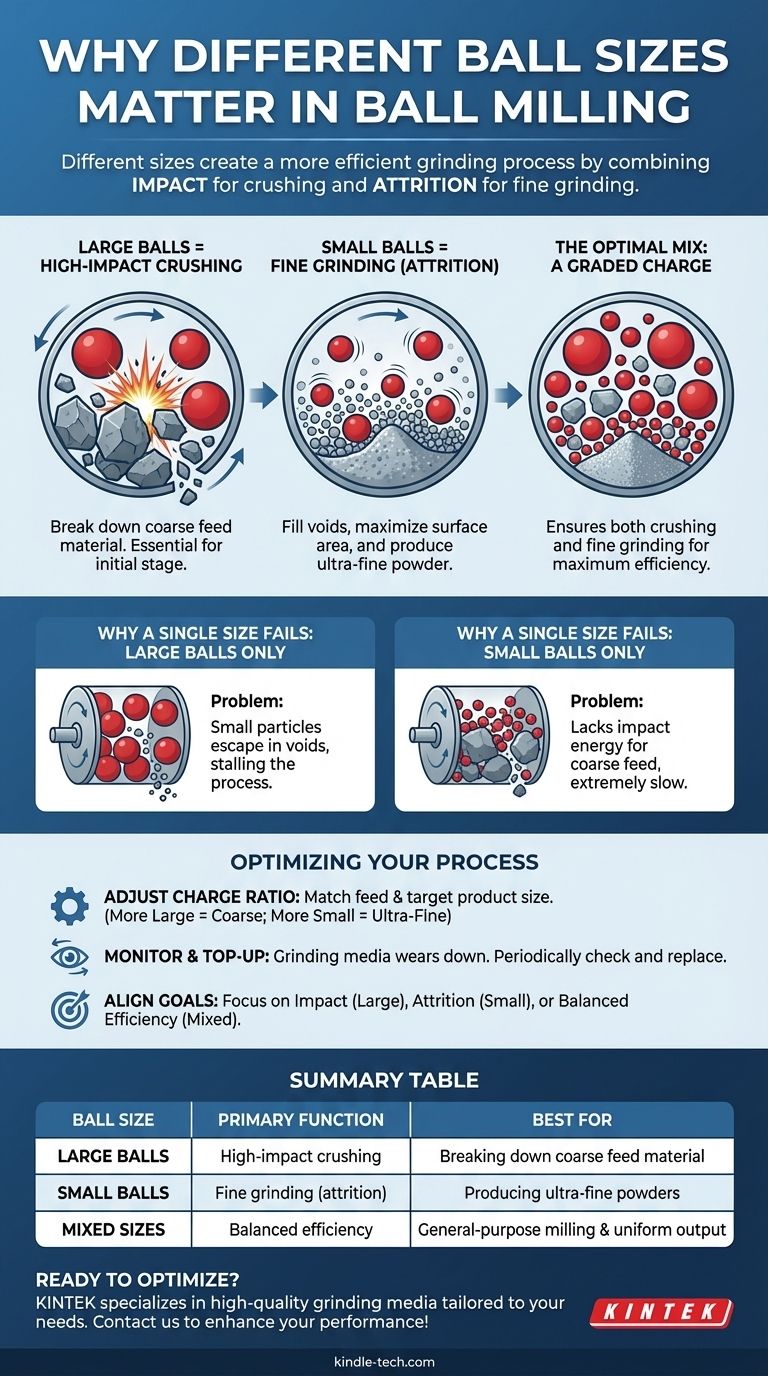
In short, different sizes of balls are used in a ball mill to create a more efficient grinding process. A mix of ball sizes ensures that both large chunks of material are broken down by high-impact collisions from large balls, while smaller particles are ground into a fine powder through the rubbing action of smaller balls.
The core principle is that a "graded charge" of various ball sizes optimizes the milling process. Large balls provide the raw crushing power for coarse material, while small balls provide the surface area and fill the gaps to effectively grind fine material, preventing wasted energy and time.

The Core Mechanics of Grinding
To understand why a mix of ball sizes is superior, you must first understand the two primary ways a ball mill reduces particle size: impact and attrition. The size of the grinding media directly influences which of these forces dominates.
Large Balls for High-Impact Crushing
Larger, heavier balls possess greater kinetic energy. As the mill tumbles, these balls are lifted higher and fall with more force, creating powerful impact events.
This high impact is essential for the initial stage of grinding, where you need to break down large, coarse pieces of the feed material. Without this force, the process would be incredibly slow.
Small Balls for Fine Grinding (Attrition)
Smaller balls, by contrast, have a much greater total surface area for a given weight. They fill the voids between the larger balls and the material being milled.
Their primary grinding action is attrition—a shearing and rubbing force that is highly effective at reducing already small particles into a very fine powder. They provide exponentially more contact points to ensure no particle escapes the grinding action.
The Critical Role of Void Spaces
Imagine filling a jar with only large marbles. You will notice significant empty spaces, or voids, between them. Small particles can easily fall into these voids, shielded from the crushing force of the large marbles.
By adding smaller balls (like sand in the jar analogy), you fill these voids. This dramatically increases the packing density and the number of ball-on-particle contact points, ensuring that particles of all sizes are continuously subjected to grinding forces.
Why a Single Ball Size Is Inefficient
Using a uniform ball size creates a system with inherent weaknesses, leading to longer milling times and a less uniform final product.
The "Large Balls Only" Problem
If you use only large balls, you get excellent initial size reduction. However, once the material breaks down into smaller particles, the large balls become inefficient.
The small particles get lost in the large voids between the balls, effectively hiding from the grinding action. This results in a process that stalls, unable to achieve a truly fine grind.
The "Small Balls Only" Problem
Conversely, if you only use small balls, you will lack the necessary impact energy to break down the coarse feed material.
The process would be extremely slow and energy-intensive, as the small media would chip away at the large particles with very little effect.
Understanding the Trade-offs
The ideal ratio of ball sizes is not universal. It is a calculated decision based on the specifics of your operation.
Optimizing the Ball Charge Ratio
The optimal mix depends heavily on your feed size and your target product size. A coarse feed material requires a higher proportion of large balls to handle the initial crushing. A requirement for an ultra-fine final product necessitates a greater proportion of small balls to maximize attrition.
Monitoring and Maintenance
Grinding media wears down over time. Smaller balls, due to their higher surface area-to-volume ratio, often wear down faster.
The ball charge must be periodically checked and "topped up" with new media to maintain the optimal size distribution and grinding efficiency.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the correct ball charge is about aligning the physics of grinding with your desired outcome.
- If your primary focus is breaking down coarse feed material: Prioritize a charge with a higher percentage of large-diameter balls for maximum impact force.
- If your primary focus is producing an ultra-fine powder: Use a graded charge with a significant proportion of smaller balls to maximize surface area contact and attrition grinding.
- If your primary focus is general-purpose, efficient milling: Employ a balanced, graded charge of multiple sizes to effectively handle particles from coarse to fine throughout the entire process.
Ultimately, mastering the blend of your grinding media gives you precise control over the efficiency and final output of your milling operation.
Summary Table:
| Ball Size | Primary Function | Best For |
|---|---|---|
| Large Balls | High-impact crushing | Breaking down coarse feed material |
| Small Balls | Fine grinding (attrition) | Producing ultra-fine powders |
| Mixed Sizes | Balanced efficiency | General-purpose milling & uniform output |
Ready to optimize your ball milling process? KINTEK specializes in high-quality lab equipment and consumables, including precision grinding media tailored to your specific needs. Whether you're processing coarse materials or aiming for an ultra-fine powder, our experts can help you select the ideal ball charge for maximum efficiency and control. Contact us today to enhance your laboratory's grinding performance!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- High Energy Planetary Ball Mill Machine for Laboratory Horizontal Tank Type
- Mini Planetary Ball Mill Machine for Laboratory Milling
- Liquid Nitrogen Cryogenic Grinder Mill Cryomill Airflow Ultrafine Pulverizer
- Small Injection Molding Machine for Lab Use
- Metallographic Specimen Mounting Machine for Laboratory Materials and Analysis
People Also Ask
- What role does a planetary ball mill play in SHS? Optimize Powder Activation for Superior Alloy Synthesis
- How does a planetary ball mill enhance the electrocatalytic activity of La0.6Sr0.4CoO3-δ? Boost Your Catalyst Performance
- What is the function of a high-energy planetary ball mill in zirconium-doped CaO synthesis? Optimize Material Stability
- What is the specific role of a high-energy planetary ball mill in the synthesis of Ag-doped sulfide solid-state electrolytes?
- Why is a high-energy planetary ball mill preferred over traditional casting for nanocrystalline HEAs?



















