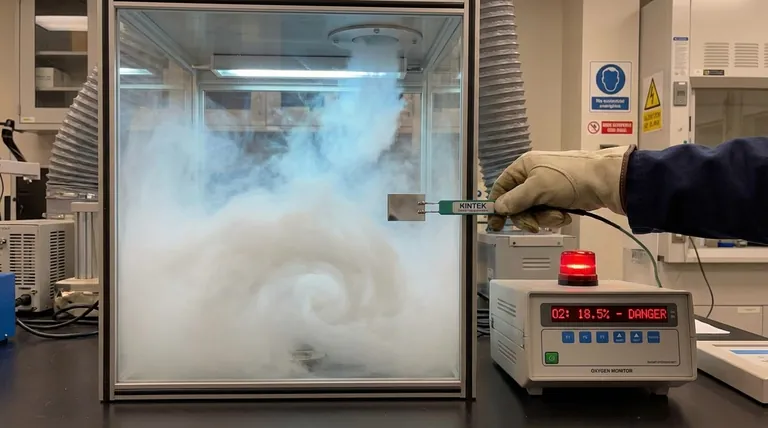
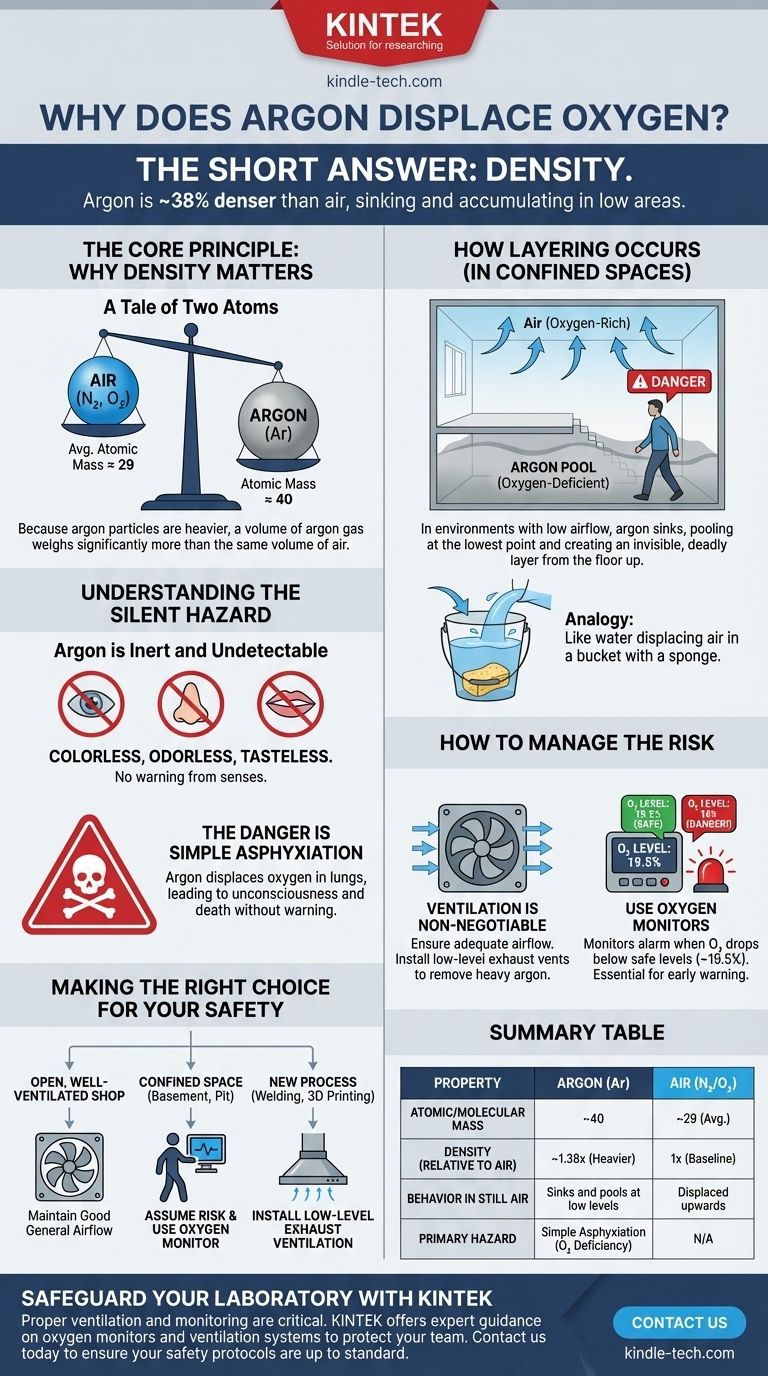
The short answer is density. Argon gas is approximately 38% denser than the air we breathe. Because it is heavier than air, it sinks and accumulates in low-lying areas, pushing the lighter, oxygen-rich air upwards and away.
The core issue isn't a chemical reaction, but a physical one. Argon's higher atomic mass makes it denser than air, causing it to settle and displace oxygen in enclosed spaces, creating a dangerous and invisible asphyxiation hazard.

The Core Principle: Why Density Matters
The behavior of gases in a shared space is primarily governed by their density. A denser gas will naturally sink below a less dense gas in a calm environment, much like oil floating on water, but with gases.
A Tale of Two Atoms
Air is primarily composed of nitrogen (N₂, atomic mass ≈ 28) and oxygen (O₂, atomic mass ≈ 32). An individual argon atom (Ar) has an atomic mass of approximately 40.
This difference in atomic mass is the source of the density difference. Because each particle of argon is heavier than the dominant particles in the air, a volume of argon gas weighs significantly more than the same volume of air.
How Layering Occurs
In an environment without significant airflow, such as a basement, a tank, or a poorly ventilated room, this density difference has a profound effect.
As argon is released, it doesn't mix evenly with the air right away. Instead, it flows downwards, pooling at the lowest point and creating a distinct, oxygen-deficient layer that grows from the floor upwards.
Understanding the Silent Hazard
The physical properties of argon are what make its ability to displace oxygen so dangerous. The risk is not that argon is toxic—it isn't—but that it quietly removes the oxygen necessary for life.
Argon is Inert and Undetectable
Argon is a noble gas, meaning it is chemically inert and does not react with other elements. Crucially, it is also colorless, odorless, and tasteless.
This means you cannot see, smell, or taste a dangerous concentration of argon. Human senses offer no warning that the "air" you are breathing is actually an oxygen-deficient atmosphere.
The Danger is Simple Asphyxiation
An asphyxiant is a substance that can cause unconsciousness or death by suffocation. Argon is a simple asphyxiant.
It doesn't harm you directly. It displaces the oxygen in your lungs. Breathing an atmosphere with too little oxygen leads to dizziness, confusion, unconsciousness, and ultimately, death, often within minutes and without any alarming symptoms like choking.
Behavior in a Confined Space
Imagine pouring water into a bucket that already has a sponge at the bottom. The water sinks, fills the bottom, and pushes the air out.
Argon behaves similarly in a room. It will "fill" a confined space from the bottom up, creating an invisible, deadly pool. Someone entering that space might take a few normal breaths before collapsing as they walk deeper into the oxygen-deficient zone.
How to Manage the Risk
Understanding that argon is a simple asphyxiant that displaces oxygen is the key to using it safely. The focus must always be on ensuring adequate breathable air is present.
Ventilation is Non-Negotiable
The single most important safety control is ventilation. Good air circulation, especially with exhaust vents placed at a low level, prevents argon from accumulating.
Mechanical ventilation (fans) is often required to ensure that any leaked or used argon is safely diluted and removed from the workspace.
The Role of Oxygen Monitors
Because you cannot detect argon with your senses, electronic oxygen monitors are a critical piece of safety equipment.
These devices sound an alarm when the oxygen level in the atmosphere drops below a safe threshold (typically 19.5%). They provide the only reliable warning of a dangerous argon accumulation.
Making the Right Choice for Your Safety
Your safety strategy depends entirely on recognizing the environment you are in and the risk that argon accumulation presents.
- If you are working in an open, well-ventilated shop: Your primary focus should be on maintaining good general airflow to prevent any localized pockets of argon from forming.
- If you are working in a basement, pit, or any confined space: You must assume that an oxygen-deficient atmosphere could exist and use an oxygen monitor before and during entry.
- If you are setting up a new process (e.g., welding, 3D printing): Your primary focus should be on engineering controls, installing low-level exhaust ventilation to safely remove the argon gas as it's used.
Ultimately, you must always treat argon with respect for its ability to silently and invisibly displace the very air you need to survive.
Summary Table:
| Property | Argon (Ar) | Air (Primary Components) |
|---|---|---|
| Atomic/Molecular Mass | ~40 | N₂: ~28, O₂: ~32 |
| Density (Relative to Air) | ~1.38x (Heavier) | 1x (Baseline) |
| Behavior in Still Air | Sinks and pools at low levels | Displaced upwards |
| Primary Hazard | Simple Asphyxiation (Oxygen Deficiency) | N/A |
Safeguard your laboratory from invisible gas hazards. Proper ventilation and monitoring are critical for safety. KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables, including safety solutions for gas handling. Our experts can help you select the right oxygen monitors and ventilation systems to protect your team. Contact us today to ensure your lab's safety protocols are up to standard.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Platinum Sheet Electrode for Laboratory and Industrial Applications
- High-Purity Titanium Foil and Sheet for Industrial Applications
- Isostatic Molding Pressing Molds for Lab
- Platinum Auxiliary Electrode for Laboratory Use
- Bomb Type Probe for Steelmaking Production Process
People Also Ask
- What is the expected lifespan of a platinum sheet electrode? Maximize Your Electrode's Service Life
- How should a platinum sheet electrode be pretreated before use? Ensure Accurate Electrochemical Measurements
- What are the key performance characteristics and applications of platinum sheets? Unmatched Reliability for Demanding Applications
- How should a platinum sheet electrode be operated during an experiment? Ensure Accurate and Reproducible Results
- What is the most critical guideline for immersing a platinum sheet electrode in an electrolyte? Ensure Accurate Electrochemical Measurements

















