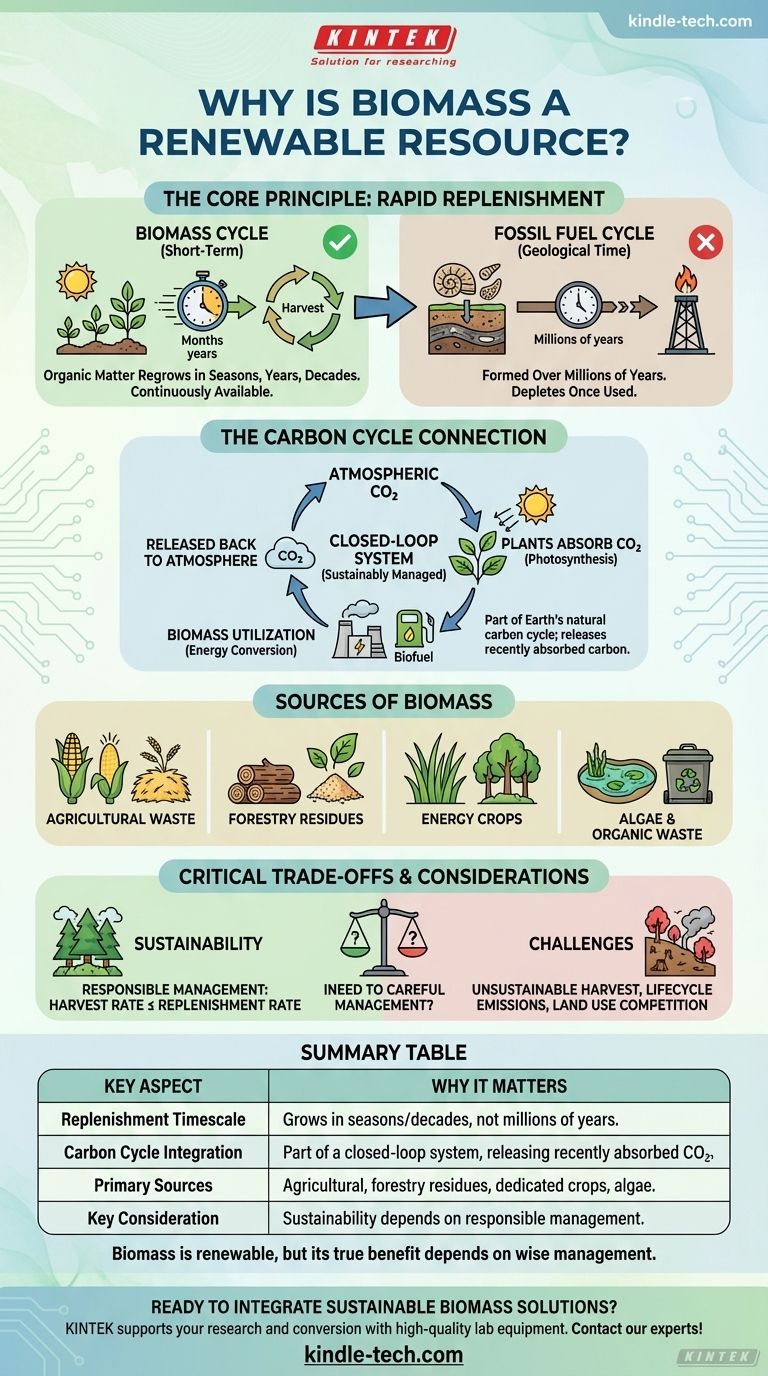
Biomass is considered a renewable resource because it originates from organic matter, such as plants and wood, which can be regrown or replenished within a human lifespan. This rapid replenishment cycle stands in stark contrast to fossil fuels, which are formed over millions of years and are therefore finite. By utilizing sources like agricultural waste, dedicated energy crops, and algae, we can create a continuous energy supply that is not depleted over time.
At its core, biomass is renewable because it is part of the Earth's natural and relatively fast carbon cycle. Plants capture solar energy and atmospheric carbon to grow, and that stored energy can then be harnessed, all within a timeframe that allows for its resources to be sustainably managed and replenished.

The Core Principle of Renewability
The distinction between renewable and non-renewable energy comes down to a single factor: the timescale of replenishment. Biomass operates on a biological timescale, not a geological one.
A Matter of Timescale
Fossil fuels like coal, oil, and natural gas are the remnants of organic matter from millions of years ago. Once we extract and burn them, they are gone for good on any human-relevant timescale.
Biomass, however, comes from plants that can be harvested and regrown in seasons, years, or decades. This makes it a resource we can manage and renew continuously.
The Carbon Cycle Connection
Biomass energy is fundamentally linked to the current carbon cycle. As plants grow, they absorb carbon dioxide (CO2) from the atmosphere through photosynthesis.
When this biomass is used for energy, it releases that same CO2 back into the atmosphere. In a sustainably managed system, this creates a closed loop, unlike burning fossil fuels, which releases ancient carbon that has been locked away for millennia.
Where Does Biomass Come From?
Biomass is not a single entity but a category of organic materials that can be converted into energy. The variety of sources is key to its flexibility as a resource.
Agricultural and Forestry Sources
The most common sources of biomass include waste products from farming and forestry. This includes wood, leftover sawdust from mills, and agricultural residues like corn stalks or rice husks that would otherwise be discarded.
Dedicated Energy Crops
Some land is used specifically to grow "energy crops." These are fast-growing plants, such as switchgrass or poplar trees, cultivated solely for their potential as a biomass fuel source.
Algae and Organic Wastes
Emerging sources like algae are also highly promising. Algae can be grown quickly in various water environments and have a high energy content. Other organic wastes, like municipal solid waste and animal manure, can also be converted into energy.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While biomass is renewable, its use is not without important considerations. Understanding its limitations is critical for its responsible application.
Sustainability vs. Renewability
A resource can be renewable but harvested unsustainably. If forests are clear-cut for wood pellets faster than they can regrow, the practice is not sustainable, even though trees are a renewable resource.
True sustainability requires careful management practices that ensure the rate of harvest does not exceed the rate of replenishment.
The Question of "Carbon Neutrality"
The idea that biomass is "carbon neutral" is an oversimplification. Energy is required to harvest, process, and transport the biomass, and this energy often comes from fossil fuels.
These "lifecycle" emissions must be accounted for to get a true picture of the overall carbon impact. The net benefit depends heavily on the source of the biomass and the efficiency of the conversion process.
Land and Resource Use
Growing dedicated energy crops can create competition for land that might otherwise be used to grow food. This can impact food prices and availability. Furthermore, like any form of agriculture, growing biomass requires significant water resources.
The Role of Biomass in a Sustainable Future
Harnessing biomass effectively means choosing the right source to achieve a specific sustainability goal. Its value lies in its versatility as part of a broader energy strategy.
- If your primary focus is waste reduction: Utilizing agricultural, forestry, or municipal waste for energy is a highly effective way to create value from materials that would otherwise be discarded.
- If your primary focus is large-scale energy production: Sustainably managed forests and dedicated energy crops are essential, but require careful planning to avoid negative impacts on land use and biodiversity.
- If your primary focus is reducing fossil fuel dependence: All forms of sustainably sourced biomass provide a direct, renewable alternative for generating heat, electricity, and biofuels.
Ultimately, biomass is a renewable resource because we can always grow more, but its true benefit to our energy future depends entirely on how wisely we manage it.
Summary Table:
| Key Aspect | Why It Matters |
|---|---|
| Replenishment Timescale | Grows in seasons/decades, not millions of years like fossil fuels. |
| Carbon Cycle Integration | Part of a closed-loop system, releasing recently absorbed CO₂. |
| Primary Sources | Agricultural waste, forestry residues, dedicated energy crops, and algae. |
| Key Consideration | Sustainability depends on responsible harvesting and management practices. |
Ready to integrate sustainable biomass solutions into your operations? KINTEK specializes in providing high-quality lab equipment and consumables essential for biomass research, analysis, and conversion processes. Whether you're developing new biofuels, analyzing feedstock, or optimizing conversion efficiency, our products support the precise, reliable data you need to advance sustainable energy. Contact our experts today to find the right tools for your biomass and renewable energy projects!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace Biomass Pyrolysis Plant
- Electric Rotary Kiln Continuous Working Small Rotary Furnace Heating Pyrolysis Plant
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace for Activated Carbon Regeneration
- Carbon Graphite Plate Manufactured by Isostatic Pressing Method
- Electric Rotary Kiln Pyrolysis Furnace Plant Machine Calciner Small Rotary Kiln Rotating Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the conditions for biomass pyrolysis? Optimize Temperature, Heating Rate & Time
- What are the products of pyrolysis of biomass? Unlock Bio-Char, Bio-Oil, and Syngas
- What is the process of biomass fast pyrolysis? Turn Biomass into Bio-Oil in Seconds
- What are the advantages of pyrolysis technology? Turn Waste into Profit and Reduce Emissions
- Is pyrolysis viable? A Guide to Economic, Technological, and Environmental Success




