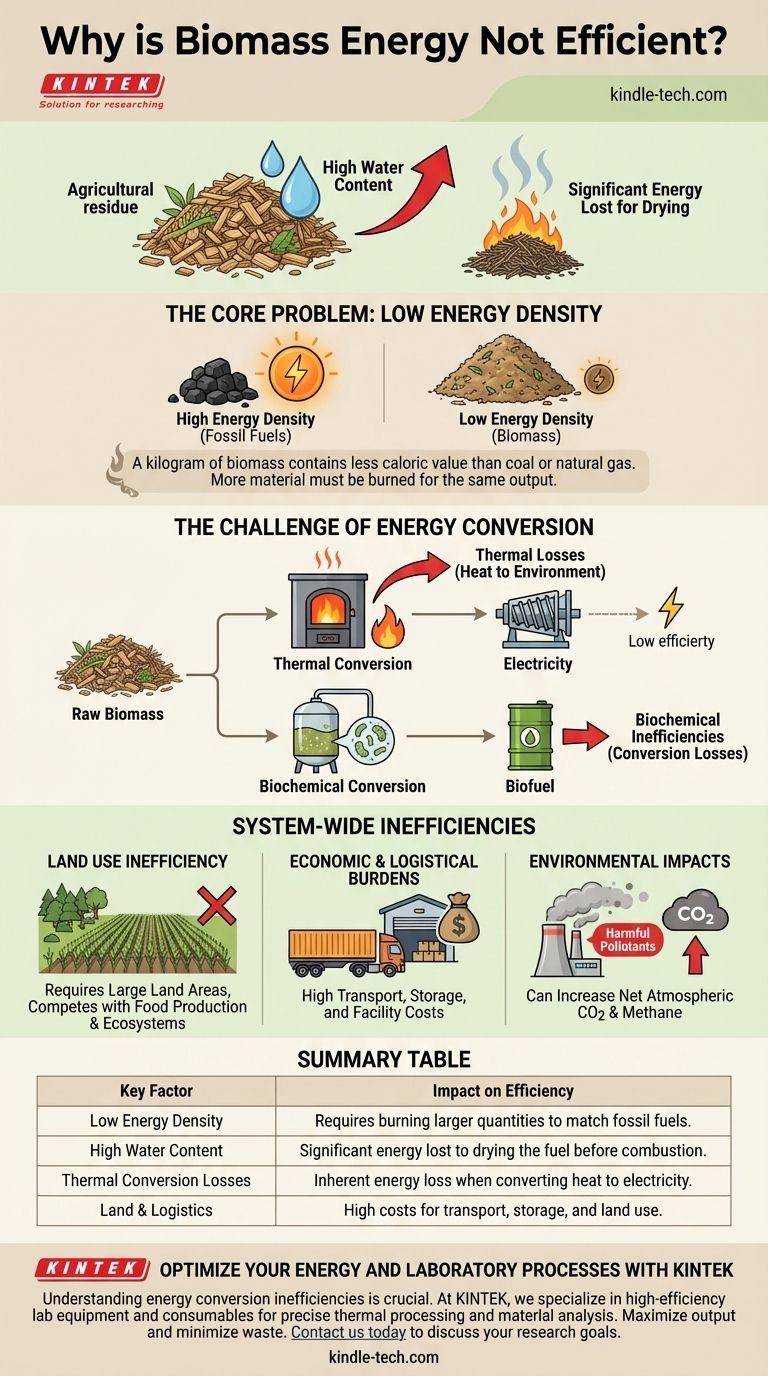
To be direct, biomass energy is considered inefficient primarily due to its low energy density and the significant energy losses that occur during its conversion into usable forms like electricity. The high water content in raw biomass means a large portion of its own energy must be spent simply to dry the material before any net energy can be harvested.
The core issue with biomass is not just about the final energy output. Its inefficiency is a systemic problem, stemming from the large amounts of land, labor, and energy required to grow, harvest, transport, and convert a low-potency fuel source, which diminishes its overall viability compared to more concentrated energy forms.

The Core Problem: Low Energy Density
Energy density is the amount of energy stored in a given volume or mass of a substance. Biomass, when compared to fossil fuels, is fundamentally handicapped in this area.
The High Water Content Dilemma
Raw biomass, such as freshly cut wood or agricultural residue, can contain up to 50% water. During the combustion process, a significant amount of energy is consumed just to boil this water into steam before the organic material itself can burn to produce useful heat.
This initial energy expenditure is a direct and unavoidable loss, immediately reducing the net energy gain from the fuel.
Inherent Material Composition
Unlike fossil fuels, which are the result of millions of years of geological compression, biomass is less energy-packed. A kilogram of wood simply does not contain the same caloric value as a kilogram of coal or natural gas.
This means you must burn a much larger quantity of biomass to produce the same amount of heat, which introduces logistical and operational inefficiencies.
The Challenge of Energy Conversion
Getting energy from raw biomass into the power grid or a vehicle's fuel tank is a multi-step process, and energy is lost at every stage.
Thermal Conversion Losses
The most common method for electricity generation is burning biomass to heat water, creating steam that turns a turbine. This thermal process is subject to the same laws of thermodynamics as a coal or gas plant.
A substantial portion of the heat energy is inevitably lost to the environment rather than being converted into electrical energy, and these losses are amplified when you start with a lower-potency fuel.
Biochemical Conversion Inefficiencies
Creating liquid biofuels like ethanol from crops involves fermentation or other chemical processes. These conversions are not perfectly efficient.
The microorganisms or chemical reactions used to break down the biomass consume energy themselves, and not all of the plant matter can be successfully converted into the final fuel product.
Understanding the Trade-offs: System-Wide Inefficiencies
The inefficiency of biomass extends beyond the power plant, impacting land use, economics, and the environment in ways that more energy-dense sources do not.
Land Use Inefficiency
Because biomass has low energy density, generating power on a large scale requires vast areas of land dedicated to growing energy crops.
This creates a direct conflict with land needed for food production and natural ecosystems. It can also lead to deforestation and land degradation if not managed with extreme care.
Economic and Logistical Burdens
The sheer bulk of biomass makes it expensive to transport and store. A facility requires a constant, large-volume supply chain to operate.
These high logistical costs, combined with the expensive maintenance of processing facilities, often make biomass less economically competitive than other energy sources.
The "Clean Energy" Misconception
While biomass can be carbon-neutral in theory if new plants absorb the carbon emitted, this is not the full story. The combustion of biomass releases harmful air pollutants, including particulates and carbon monoxide, which can cause significant health issues.
Furthermore, if biomass sources are not managed sustainably, the process contributes to a net increase in atmospheric CO2 and the release of methane, a potent greenhouse gas.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Evaluating biomass requires looking past a simple "good" or "bad" label and assessing its role based on the specific objective.
- If your primary focus is waste reduction: Biomass is an excellent solution for converting agricultural, forestry, or municipal waste into energy, turning a disposal liability into a valuable asset.
- If your primary focus is large-scale grid power: Biomass is generally less efficient and more resource-intensive than solar, wind, or nuclear for providing reliable, utility-scale electricity.
- If your primary focus is local energy independence: Using locally sourced biomass can provide reliable power and heat in rural areas that have abundant organic material but limited access to a central energy grid.
Ultimately, understanding the inherent inefficiencies of biomass is key to deploying it strategically where its unique benefits truly outweigh its significant limitations.
Summary Table:
| Key Factor | Impact on Efficiency |
|---|---|
| Low Energy Density | Requires burning larger quantities to match fossil fuels. |
| High Water Content | Significant energy lost to drying the fuel before combustion. |
| Thermal Conversion Losses | Inherent energy loss when converting heat to electricity. |
| Land & Logistics | High costs for transport, storage, and land use. |
Optimize Your Energy and Laboratory Processes with KINTEK
Understanding energy conversion inefficiencies is crucial, whether you're working with biomass or optimizing laboratory processes. At KINTEK, we specialize in providing high-efficiency lab equipment and consumables that help you maximize output and minimize waste.
Our range of products supports precise thermal processing and material analysis, enabling you to conduct research and development more effectively. If you're working on improving energy systems or any laboratory-based project, our expertise can help you achieve more reliable and efficient results.
Contact us today to discuss how KINTEK's solutions can enhance your laboratory's performance and support your specific research goals.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace Biomass Pyrolysis Plant
- Electric Rotary Kiln Continuous Working Small Rotary Furnace Heating Pyrolysis Plant
- Graphite Vacuum Furnace High Thermal Conductivity Film Graphitization Furnace
- Laboratory Test Sieves and Vibratory Sieve Shaker Machine
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace for Activated Carbon Regeneration
People Also Ask
- What are the advantages of pyrolysis technology? Turn Waste into Profit and Reduce Emissions
- What is the process of biomass fast pyrolysis? Turn Biomass into Bio-Oil in Seconds
- What are the reactions involved in pyrolysis of biomass? Unlock the Chemistry for Tailored Bio-Products
- What are the conditions for biomass pyrolysis? Optimize Temperature, Heating Rate & Time
- What is a disadvantage of biomass energy? The Hidden Environmental and Economic Costs




