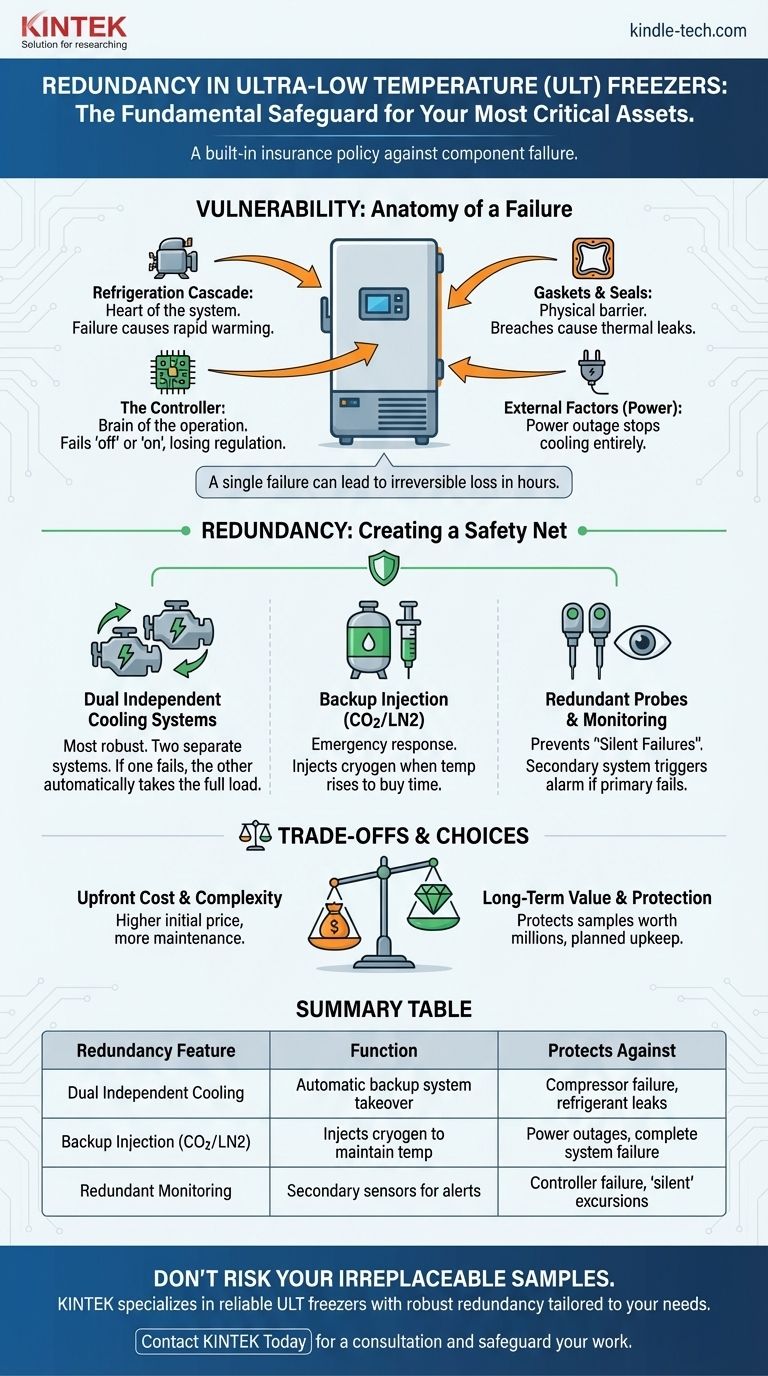
In ultra-low temperature (ULT) storage, redundancy is not a luxury; it is the fundamental safeguard for your most critical assets. It functions as a built-in insurance policy against the inevitable failure of mechanical or electronic components. By incorporating backup systems, redundancy ensures the internal temperature remains stable even if a primary part fails, preventing catastrophic temperature excursions that would destroy irreplaceable biological materials.
A single component failure in a standard ULT freezer can lead to irreversible sample loss in a matter of hours. Redundancy fundamentally changes this equation, creating a fail-safe system that automatically stabilizes the environment and alerts personnel, turning a potential catastrophe into a routine maintenance event.

The Anatomy of a Failure: Where ULT Systems Are Vulnerable
To appreciate redundancy, one must first understand that a ULT freezer is a complex machine with multiple single points of failure. The extreme -80°C environment places immense stress on its components.
The Refrigeration Cascade: The Heart of the System
Most ULT freezers use a cascade refrigeration system, with two independent cooling circuits working in tandem. The failure of one compressor or a leak in one refrigerant line will cause the entire system to fail, leading to a rapid rise in temperature.
The Controller: The Brain of the Operation
The electronic controller is responsible for monitoring temperature and activating the compressors. If this single electronic board fails, the freezer loses its ability to regulate itself. The system can fail "off," shutting down cooling, or fail "on," causing continuous running that can also lead to eventual component burnout.
Gaskets and Seals: The Physical Barrier
The integrity of door gaskets and vacuum insulation panels is critical. A small tear in a gasket or a breach in the insulation creates a thermal leak. This forces the compressors to run constantly, leading to premature wear and eventual failure.
External Factors: Power and Environment
The most common external point of failure is a power outage. Without electricity, the cooling system stops entirely. Furthermore, high ambient room temperatures force the freezer to work harder, increasing strain and the likelihood of a breakdown.
How Redundancy Creates a Safety Net
Redundancy introduces parallel systems that can take over or mitigate the impact when a primary component fails. This provides a crucial window of time to address the problem without losing samples.
Dual Independent Cooling Systems
This is the most robust form of redundancy. The freezer is equipped with two completely separate and independent refrigeration systems. Each system—compressor, condenser, and refrigerant loop—is capable of maintaining the target temperature on its own.
In normal operation, they may alternate to balance wear. If one system fails, the other automatically takes over the full cooling load, ensuring no change in chamber temperature. This transforms a system-down emergency into a non-critical maintenance alert.
Backup Injection Systems (CO2 or LN2)
These are emergency backup systems designed to respond to a catastrophic failure or power outage. When the internal temperature rises above a set threshold, the system injects a cryogen like liquid carbon dioxide (CO2) or liquid nitrogen (LN2) into the chamber.
This does not fix the freezer, but it temporarily holds the temperature down, "buying time" for hours or even days until the primary issue can be resolved or samples can be moved.
Redundant Probes and Monitoring
Some systems include secondary temperature probes and monitoring alarms. If the primary controller's probe fails, the secondary system can still provide accurate temperature data and trigger an external alarm, preventing a "silent failure" where the freezer warms up without anyone knowing.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Implementing redundancy involves balancing cost, complexity, and the value of what you are protecting.
Upfront Cost vs. Long-Term Value
Freezers with dual-cooling systems have a significantly higher upfront purchase price. However, this cost must be weighed against the financial and scientific value of the samples inside, which can often be worth millions of dollars and represent years of work.
Increased Complexity
A redundant system has more components, which can mean a more complex maintenance schedule. However, this is planned, preventative maintenance, which is far preferable to emergency repairs and sample relocation efforts.
Backup Systems Require Their Own Upkeep
CO2 and LN2 backup systems are only effective if their supply tanks are full and the injection system is periodically tested. Neglecting the backup system renders it useless in an emergency.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your choice of redundancy should directly reflect the value and irreplaceability of your samples.
- If your primary focus is protecting irreplaceable assets (e.g., clinical trial samples, cell banks, long-term epidemiological collections): A freezer with dual independent refrigeration systems is the only acceptable standard.
- If your primary focus is protecting valuable but replaceable materials: A high-performance single-compressor freezer paired with a CO2/LN2 backup system and a robust external alarm offers a strong, cost-effective layer of security.
- If your primary focus is mitigating power grid instability: A CO2/LN2 backup system is essential, as it is specifically designed to protect against power outages regardless of the freezer's mechanical health.
Ultimately, investing in the right redundancy strategy is an investment in the continuity and integrity of your work.
Summary Table:
| Redundancy Feature | Function | Protects Against |
|---|---|---|
| Dual Independent Cooling Systems | Two separate refrigeration systems; one takes over if the other fails. | Compressor failure, refrigerant leaks. |
| Backup Injection (CO2/LN2) | Injects cryogen to maintain temperature during a failure or power loss. | Power outages, complete system failure. |
| Redundant Probes & Monitoring | Secondary sensors provide accurate data if the primary controller fails. | Controller failure, 'silent' temperature excursions. |
Don't risk your irreplaceable biological samples. KINTEK specializes in reliable lab equipment and consumables, including ultra-low temperature freezers with robust redundancy features tailored to your laboratory's needs. Our experts can help you select the right system to safeguard your valuable work. Contact us today for a consultation and ensure your samples are protected against the unexpected.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 808L Precision Laboratory Vertical Ultra Low Temperature Freezer
- 938L Vertical Ultra Low Temperature Freezer for Advanced Laboratory Storage
- 158L Precision Vertical Ultra Low Freezer for Laboratory Applications
- 58L Precision Laboratory Ultra Low Temperature Upright Freezer for Critical Sample Storage
- 508L Advanced Vertical Ultra Low Temperature Freezer for Critical Laboratory Storage
People Also Ask
- What temperature ranges are typically associated with ultra-low temperature freezers? Preserve Samples from -40°C to -86°C
- How does fast temperature recovery benefit ultra-low freezers? Protect Sample Integrity and Lab Efficiency
- What factors should be considered when selecting an ultra-low temperature freezer? Ensure Sample Integrity and Long-Term Value
- What are the key features to look for in an ultra-low temperature freezer for mRNA vaccine storage? Essential Features for Absolute Vaccine Integrity
- What are ultra-low temperature freezers designed for? Preserving Your Most Valuable Biological Samples



















