In simple terms, an ultra-low temperature (ULT) freezer is a specialized piece of laboratory equipment designed to maintain extremely cold temperatures, typically between -45°C and -86°C. Unlike a standard freezer, its primary function is to preserve the long-term integrity and viability of highly sensitive biological samples, such as cells, enzymes, vaccines, and research tissues, by effectively halting biological activity.
A ULT freezer is more than just a cold box; it is a precision instrument engineered for stability. Its core purpose is not merely storage, but the active protection of irreplaceable biological assets against degradation over time.
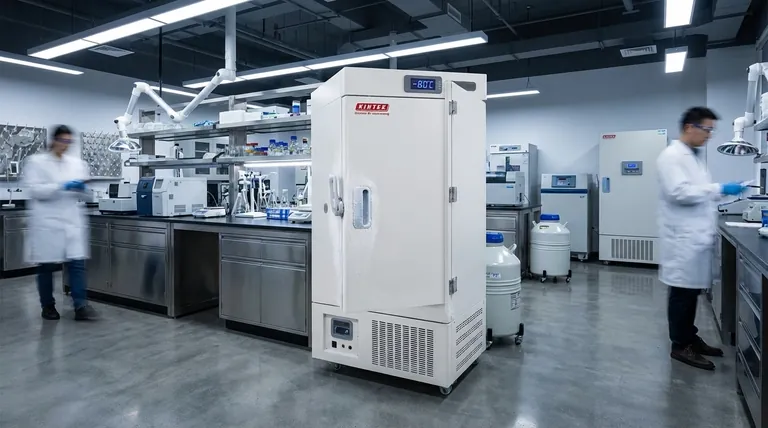

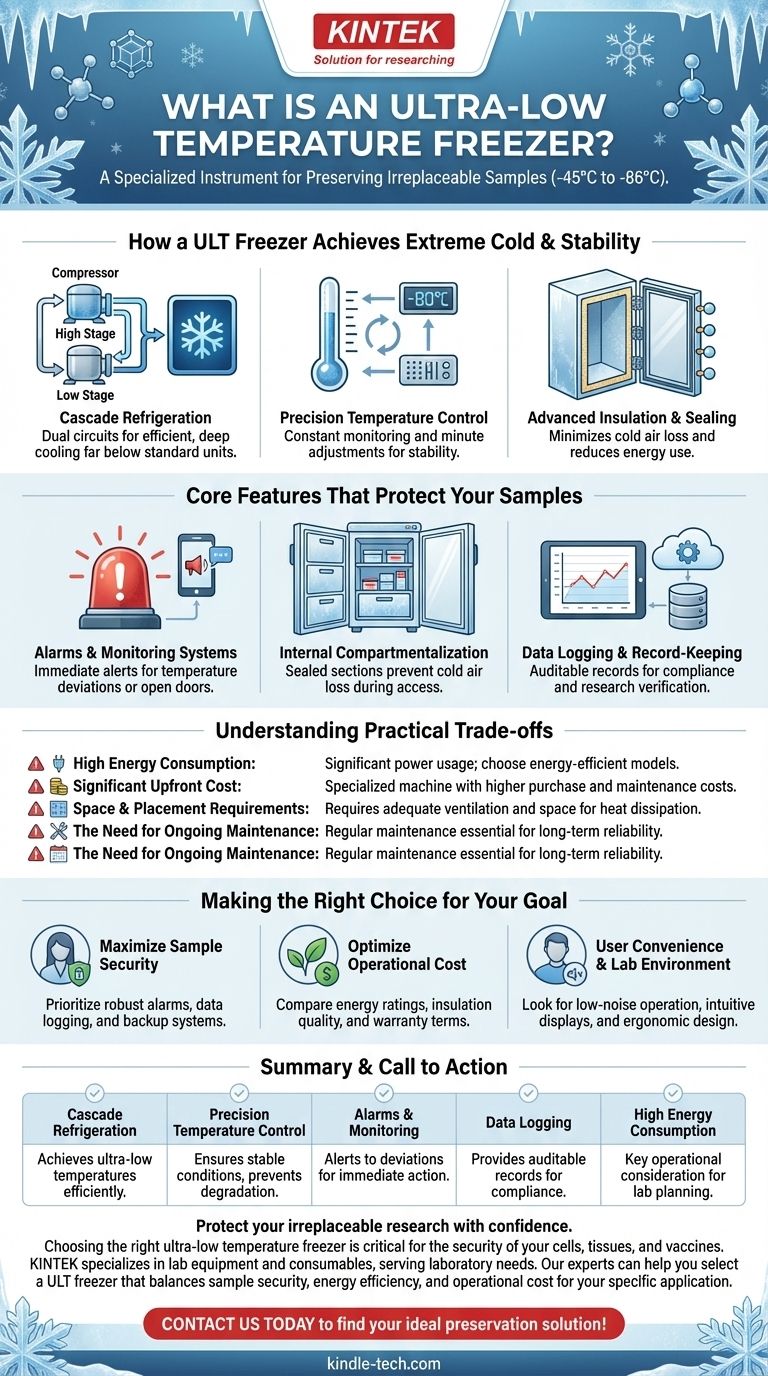
How a ULT Freezer Achieves Extreme Cold and Stability
A ULT freezer's performance relies on a combination of powerful refrigeration technology and sophisticated control systems. Understanding these components is key to appreciating their role in a laboratory.
The Specialized Refrigeration Cycle
Standard freezers use a single compressor. A ULT freezer, however, often uses a cascade refrigeration system with two separate circuits to reach and maintain such extreme temperatures efficiently.
This multi-stage process is what allows the unit to achieve temperatures far below the capability of household or standard commercial freezers.
Precision Temperature Control
The system uses highly sensitive sensors that constantly monitor the internal temperature. This data is fed into a control algorithm that makes continuous, minute adjustments to the refrigeration cycle.
This feedback loop ensures the temperature remains stable, preventing fluctuations that could damage sensitive samples.
Advanced Insulation and Sealing
To maintain efficiency and stability, ULT freezers feature thick, high-performance insulation. They also utilize multi-bulb gaskets around the doors to create multiple points of contact for an exceptionally tight seal.
This design minimizes cold air loss and reduces the freezer's energy consumption and workload.
Core Features That Protect Your Samples
The value of a ULT freezer is defined by its ability to safeguard its contents. Key features are designed specifically for security and reliability.
Alarms and Monitoring Systems
Virtually all ULT freezers include built-in alarms that trigger if the internal temperature deviates from the set point. These systems are the first line of defense, alerting staff to potential equipment failure or an open door before sample integrity is compromised.
Internal Compartmentalization
Most units feature a series of inner doors or drawers. When you open the main door to access one section, the other compartments remain sealed.
This drastically reduces the loss of cold air and minimizes temperature fluctuations for samples you are not accessing, protecting the entire inventory.
Data Logging and Record-Keeping
Many modern ULT freezers automatically log temperature data over time. This creates an auditable record that is crucial for regulatory compliance (e.g., in clinical trials) and for verifying that samples have been stored under proper conditions for research purposes.
Understanding the Practical Trade-offs
While essential, integrating a ULT freezer into a lab environment requires careful consideration of its operational demands and costs.
High Energy Consumption
Maintaining temperatures of -80°C is an energy-intensive process. ULT freezers are among the most power-hungry devices in a typical lab, contributing significantly to utility costs. Look for models with high energy efficiency ratings to mitigate this.
Significant Upfront and Lifetime Cost
These are highly specialized machines with a correspondingly high purchase price. The total cost of ownership also includes energy, potential backup systems (like CO2 or LN2), and essential preventative maintenance plans.
Space and Placement Requirements
ULT freezers generate a considerable amount of heat and require adequate ventilation to operate correctly. They cannot be placed in a tight, unventilated closet, which can impact lab layout and planning.
The Need for Ongoing Maintenance
Due to their complexity, ULT freezers require regular maintenance to ensure long-term reliability. A failure can be catastrophic, making a preventative maintenance plan and a good warranty essential investments.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting a ULT freezer means matching its features to the specific needs of your work and the value of the samples you are protecting.
- If your primary focus is maximizing sample security: Prioritize units with robust alarm systems, data logging capabilities, and options for CO2 or liquid nitrogen backup systems.
- If your primary focus is optimizing operational cost: Compare energy efficiency ratings, insulation quality, and the terms of available warranties and preventive maintenance plans.
- If your primary focus is user convenience and lab environment: Consider features like low-noise operation, an intuitive LED display with on-board diagnostics, and an ergonomic door handle.
Ultimately, the right ULT freezer is the one that provides the stability and security necessary to protect your most valuable work.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Purpose |
|---|---|
| Cascade Refrigeration | Achieves and maintains ultra-low temperatures efficiently. |
| Precision Temperature Control | Ensures stable conditions to prevent sample degradation. |
| Alarms & Monitoring | Alerts staff to temperature deviations for immediate action. |
| Data Logging | Provides auditable records for compliance and research integrity. |
| High Energy Consumption | Key operational consideration for lab planning and costs. |
Protect your irreplaceable research with confidence. Choosing the right ultra-low temperature freezer is critical for the security of your cells, tissues, and vaccines. KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables, serving laboratory needs. Our experts can help you select a ULT freezer that balances sample security, energy efficiency, and operational cost for your specific application. Contact us today to find your ideal preservation solution!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 708L Ultra Low Temperature Freezer High Performance Laboratory Freezer
- 158L Precision Vertical Ultra Low Freezer for Laboratory Applications
- 808L Precision Laboratory Vertical Ultra Low Temperature Freezer
- 208L Advanced Precision Laboratory Ultra Low Temperature Freezer for Cold Storage
- 608L Essential Laboratory Ultra Low Temperature Freezer For Critical Sample Preservation
People Also Ask
- What are ultra-low temperature freezers designed for? Preserving Your Most Valuable Biological Samples
- What temperature ranges are typically associated with ultra-low temperature freezers? Preserve Samples from -40°C to -86°C
- What are the key features to look for in an ultra-low temperature freezer for mRNA vaccine storage? Essential Features for Absolute Vaccine Integrity
- What is the purpose of ultra-low temperature (ULT) freezers? Preserve Critical Biological Samples
- Why are ULT freezers considered vital equipment in labs? Ensuring Uncompromised Sample Integrity for Critical Research



















