At its core, a sieve test is the universally accepted method for determining the particle size distribution of a granular material. By passing a sample through a series of screens with specific mesh sizes, you can accurately separate and quantify the range of particle sizes present. This process provides a critical "fingerprint" of a material's physical makeup.
The true importance of sieve testing isn't just measuring particles; it's about controlling outcomes. Knowing the particle size distribution allows you to ensure product quality, predict performance, and guarantee compliance with industry standards.

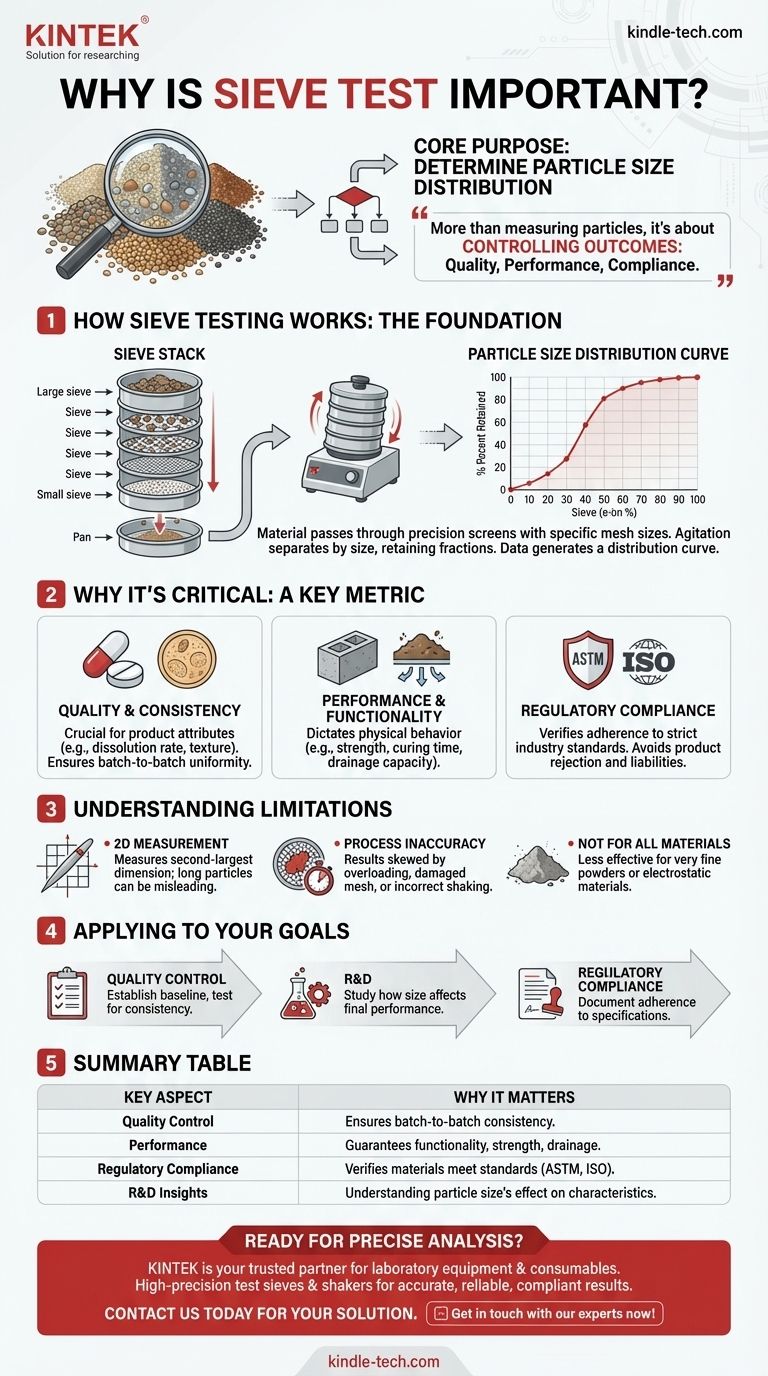
The Foundation: How Sieve Testing Works
Sieve analysis, or a gradation test, is a simple yet precise procedure for separating a material by its particle size. The a-mount of material retained on each sieve provides a clear picture of the sample's composition.
A Tool for Precise Separation
A test sieve is a high-precision instrument, typically a round metal frame holding a wire mesh screen with openings of a uniform and exact size. When a material is placed on the sieve, particles smaller than the openings pass through, while larger particles are retained.
Creating a Sieve Stack
For a full analysis, sieves are not used individually. Instead, they are stacked in descending order of opening size, with the largest openings at the top and the smallest at the bottom, followed by a solid pan.
This stack is placed in a mechanical sieve shaker, which agitates the entire column. The agitation causes the particles to bounce and reorient, allowing them to find their way through the appropriate mesh until they are retained on a sieve they cannot pass through.
The Result: A Particle Size Distribution Curve
After shaking, the material retained on each sieve is weighed. This data is used to generate a particle size distribution curve, a graph that visually represents the percentage of the material that falls into each size range. This curve is the fundamental output of a sieve test.
Why Particle Size Distribution is a Critical Metric
The "fingerprint" provided by a sieve test is essential because the size of a material's constituent particles directly dictates its physical behavior and properties.
Ensuring Product Quality and Consistency
For many products, particle size is a key quality attribute. In the pharmaceutical industry, the dissolution rate of a tablet is heavily influenced by the particle size of the active ingredient. In the food industry, the particle size of flour or sugar affects texture and "mouthfeel." Sieve testing is the primary method for ensuring this consistency from one batch to the next.
Guaranteeing Performance and Functionality
The function of many industrial and construction materials depends on a specific particle size distribution. The strength and curing time of concrete are affected by the gradation of the sand and aggregate. The drainage capacity of soil or backfill material is entirely dependent on its particle size composition.
Meeting Industry and Regulatory Standards
Many industries operate under strict standards (such as ASTM or ISO) that specify acceptable particle size ranges for a given material. Sieve testing is often the prescribed method for verifying and documenting compliance. Failing to meet these standards can result in rejected products, project failures, or legal liabilities.
Understanding the Limitations
While indispensable, sieve testing is not without its limitations. Understanding these is key to interpreting the results correctly.
It's a Two-Dimensional Measurement
A standard sieve measures a particle based on its ability to pass through a square opening. This means it effectively measures a particle's second-largest dimension. Long, needle-shaped particles may pass through a sieve that is much smaller than their total length, which can sometimes be misleading.
Potential for Process Inaccuracy
Results can be skewed if the procedure is not followed correctly. Overloading the sieves, using a damaged or clogged mesh, or applying incorrect shaking time and intensity can all lead to inaccurate data. Consistent methodology is paramount.
Not Ideal for All Materials
Sieve analysis is most effective for dry, free-flowing materials in the range of roughly 20 micrometers to several inches. It is less effective for very fine powders that may agglomerate or materials that hold a strong electrostatic charge. For these, other methods like laser diffraction may be more appropriate.
Applying Sieve Analysis to Your Goals
Use this guidance to determine how sieve testing applies to your specific objectives.
- If your primary focus is quality control: Use sieve testing to establish a baseline "fingerprint" for your material and test subsequent batches against it to ensure consistency.
- If your primary focus is research and development: Use sieve analysis to systematically study how variations in particle size affect your product's final performance and characteristics.
- If your primary focus is regulatory compliance: View sieve testing as the non-negotiable method for documenting that your materials meet the precise specifications required by industry or government standards.
Ultimately, sieve testing is a fundamental tool for transforming an abstract material property into actionable data.
Summary Table:
| Key Aspect | Why It Matters |
|---|---|
| Quality Control | Ensures batch-to-batch consistency for products like pharmaceuticals and food. |
| Performance | Guarantees functionality of materials like concrete and soil, affecting strength and drainage. |
| Regulatory Compliance | Verifies materials meet strict ASTM, ISO, and other industry standards. |
| R&D Insights | Provides data to understand how particle size affects final product characteristics. |
Ready to achieve precise particle analysis for your materials?
KINTEK is your trusted partner for all laboratory equipment and consumables. We specialize in providing high-precision test sieves and shakers to ensure your sieve testing delivers accurate, reliable, and compliant results—helping you guarantee product quality, optimize performance, and meet stringent industry standards.
Contact us today to discuss your specific application and find the perfect sieving solution for your lab.
Get in touch with our experts now!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Test Sieves and Vibratory Sieve Shaker Machine
- Three-dimensional electromagnetic sieving instrument
- Laboratory Vibratory Sieve Shaker Machine for Dry and Wet Three-Dimensional Sieving
- Laboratory Wet Three-Dimensional Vibratory Sieve Shaker Machine
- Laboratory Vibratory Sieve Shaker Machine Slap Vibrating Sieve
People Also Ask
- What is another example of sieving? From Kitchen Colanders to Industrial Screens
- What is the best material for a sieve? Match the Material to Your Application for Accurate Results
- What is sieve analysis of raw materials? Control Quality with Particle Size Data
- What is the use of sieve in laboratory? Measure Particle Size Distribution for Quality Control
- What are the two methods of sieve analysis? Choose the Right Method for Accurate Particle Sizing
- What are sieve analysis used for? A Guide to Particle Size Distribution Testing
- What is the process of sieve analysis? A Step-by-Step Guide to Particle Size Distribution
- How is a test sieve calibrated? Ensure Accurate Particle Size Analysis



















