Tungsten's exceptional heat resistance is a direct result of the powerful metallic bonds that hold its atoms together in a highly stable crystal structure. This atomic configuration requires an immense amount of thermal energy to disrupt, giving tungsten the highest melting point of any pure metal at 3,422 °C (6,192 °F). Its heavy atoms and dense packing further contribute to this stability.
A metal's resistance to heat is fundamentally determined by the strength of its inter-atomic bonds. Tungsten excels because its atomic structure, with a high number of bonding electrons and a dense crystal lattice, creates incredibly strong bonds that demand enormous energy to break apart.
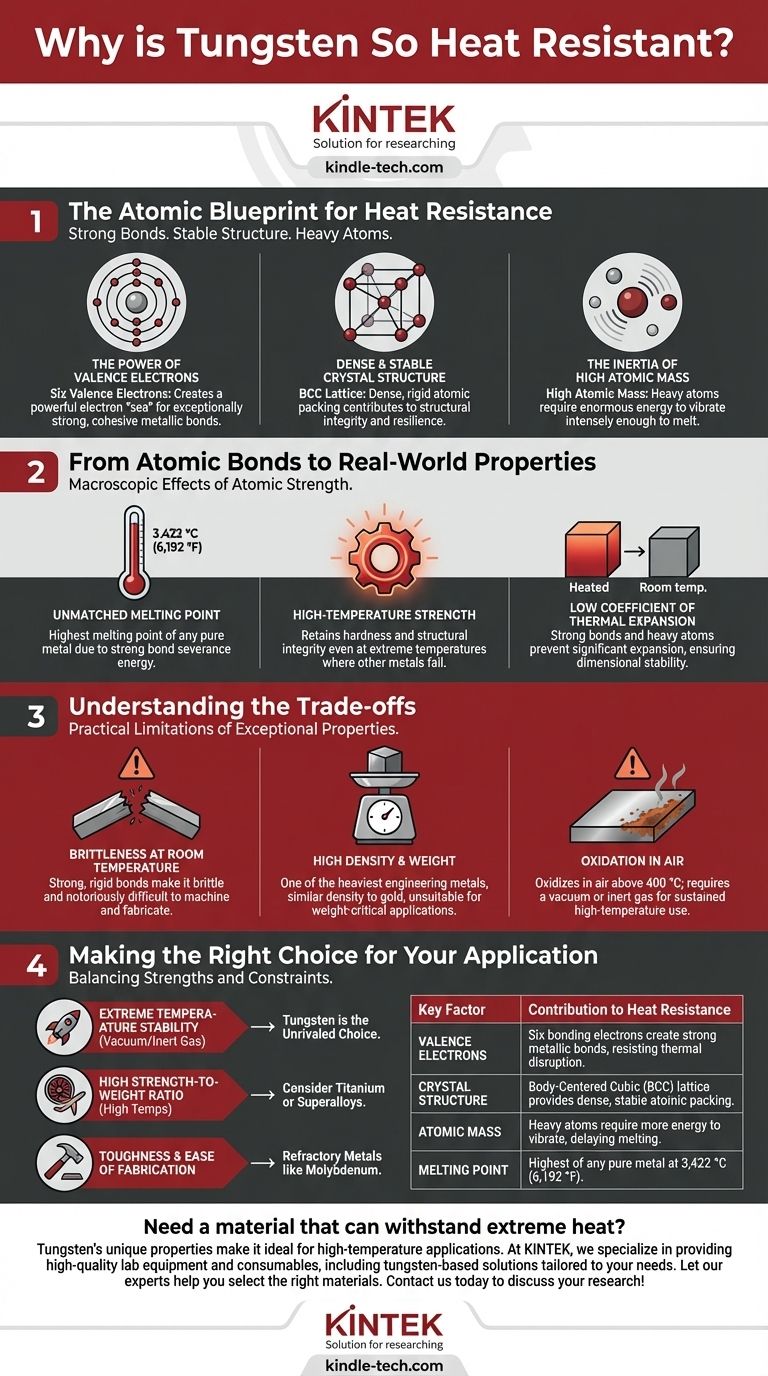
The Atomic Blueprint for Heat Resistance
To understand tungsten's properties, we must look at its atomic-level design. Its unique combination of electrons, crystal structure, and atomic mass creates a fortress against thermal energy.
The Power of Valence Electrons
Tungsten is a transition metal with six valence electrons, the outermost electrons that participate in chemical bonding.
In a metallic bond, these valence electrons are delocalized, forming a shared "sea" of electrons that acts as a powerful glue holding the positively charged atomic nuclei together.
With six bonding electrons per atom, tungsten creates significantly more of this "glue" than metals like aluminum (three valence electrons) or sodium (one). This results in exceptionally strong, cohesive bonds.
A Dense and Stable Crystal Structure
Tungsten atoms arrange themselves in a Body-Centered Cubic (BCC) lattice. This structure consists of an atom at each corner of a cube and one atom in the very center.
The BCC arrangement is a dense and highly stable way to pack atoms. This tight packing, combined with the powerful metallic bonds, creates a rigid and resilient atomic lattice.
The Inertia of High Atomic Mass
Tungsten is a very heavy element, with a high atomic mass. When thermal energy is applied to a material, its atoms begin to vibrate.
Heavier atoms have more inertia and vibrate more slowly than lighter atoms for a given amount of energy. It simply takes more energy to get heavy tungsten atoms vibrating intensely enough to break free from their lattice positions and melt.
From Atomic Bonds to Real-World Properties
These atomic characteristics directly translate into the macroscopic properties that make tungsten a premier high-temperature material.
Unmatched Melting Point
Melting is the process of giving atoms enough energy to break their bonds and move freely as a liquid. Because tungsten's metallic bonds are so strong, an extraordinary amount of energy is required to sever them, resulting in the highest melting point of any metal.
High-Temperature Strength
The same bonds that resist melting also resist deformation. Even at temperatures where other metals would soften and fail, tungsten's rigid atomic lattice allows it to retain its hardness and structural integrity.
Low Coefficient of Thermal Expansion
The strong bonds and heavy atoms hold the structure in a tight, rigid configuration. When heated, the atoms vibrate but are held so firmly in place that the overall material does not expand significantly. This dimensional stability is critical for precision components in high-heat environments.
Understanding the Trade-offs
No material is perfect. The very properties that make tungsten excel in heat resistance also create practical limitations.
Brittleness at Room Temperature
The extremely strong and rigid atomic bonds that provide high-temperature strength also make pure tungsten brittle at room temperature. The lattice resists bending, so under stress, it is more likely to fracture than deform plastically. This makes it notoriously difficult to machine and fabricate.
High Density and Weight
The combination of heavy atoms and a dense BCC structure makes tungsten one of the heaviest engineering metals, with a density similar to that of gold. This extreme weight makes it unsuitable for applications where weight is a primary concern, such as in most aerospace structural components.
Oxidation in Air
While its melting point is incredibly high, tungsten will begin to oxidize (react with oxygen) in air at temperatures above 400 °C. For sustained high-temperature use, it must be protected by a vacuum or an inert gas atmosphere, such as in an incandescent light bulb or a TIG welding torch.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Choosing a material requires balancing its exceptional strengths against its inherent limitations. Your end goal will determine if tungsten is the right fit.
- If your primary focus is extreme temperature stability in a vacuum or inert gas: Tungsten is the unrivaled choice for applications like vacuum furnace elements, rocket nozzles, or incandescent filaments.
- If your primary focus is high strength-to-weight ratio at high temperatures: You should consider materials like titanium alloys or nickel-based superalloys, which offer better performance where weight is a critical penalty.
- If your primary focus is toughness and ease of fabrication: You would be better served by refractory metals like molybdenum or niobium, which offer a compromise between heat resistance and improved ductility.
By understanding the atomic origins of tungsten's properties, you can effectively leverage its incredible heat resistance while respecting its practical constraints.
Summary Table:
| Key Factor | Contribution to Heat Resistance |
|---|---|
| Valence Electrons | Six bonding electrons create strong metallic bonds, resisting thermal disruption. |
| Crystal Structure | Body-Centered Cubic (BCC) lattice provides dense, stable atomic packing. |
| Atomic Mass | Heavy atoms require more energy to vibrate, delaying melting. |
| Melting Point | Highest of any pure metal at 3,422 °C (6,192 °F). |
Need a material that can withstand extreme heat? Tungsten's unique properties make it ideal for high-temperature applications like furnace components, rocket nozzles, and welding electrodes. At KINTEK, we specialize in providing high-quality lab equipment and consumables, including tungsten-based solutions tailored to your laboratory's specific needs. Let our experts help you select the right materials for your high-temperature challenges. Contact us today to discuss how we can support your research and industrial processes!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- High Purity Gold Platinum Copper Iron Metal Sheets
- High Temperature Wear-Resistant Alumina Al2O3 Plate for Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics
- Manual High Temperature Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Heated Plates for Lab
- Zirconia Ceramic Gasket Insulating Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics
- Custom PTFE Teflon Parts Manufacturer for PTFE Mesh F4 Sieve
People Also Ask
- What temperature can graphite handle? Unlocking its extreme heat resistance in inert environments
- What is the difference between induction and resistance heating? A Guide to Choosing the Right Heat Source
- What is graphite heating? A Guide to Durable, High-Temp Industrial Furnace Solutions
- How does an electric oven heating element work? The Science of Resistive Heating Explained
- Is graphite good heating element? Discover Its Superior Performance in High-Temperature Vacuum Furnaces
- What role do ceramic heaters play in silver nanoparticle preparation? Achieve Precision and Stability in Synthesis
- How do integrated Pt100 temperature sensors assist in the study of dissolution kinetics of materials in liquid tin?
- Why must YAG:Ce powder from aerosol pyrolysis undergo thermal annealing? Unlock Peak Phosphor Performance



















