Potassium Bromide (KBr) is the standard material for FTIR beamsplitters and sample holders primarily because it is transparent to infrared radiation across the wide mid-infrared range (4000 to 400 cm⁻¹). This critical property ensures that the KBr itself does not absorb the IR light, allowing the instrument to measure the absorption spectrum of the sample without interference from the supporting material.
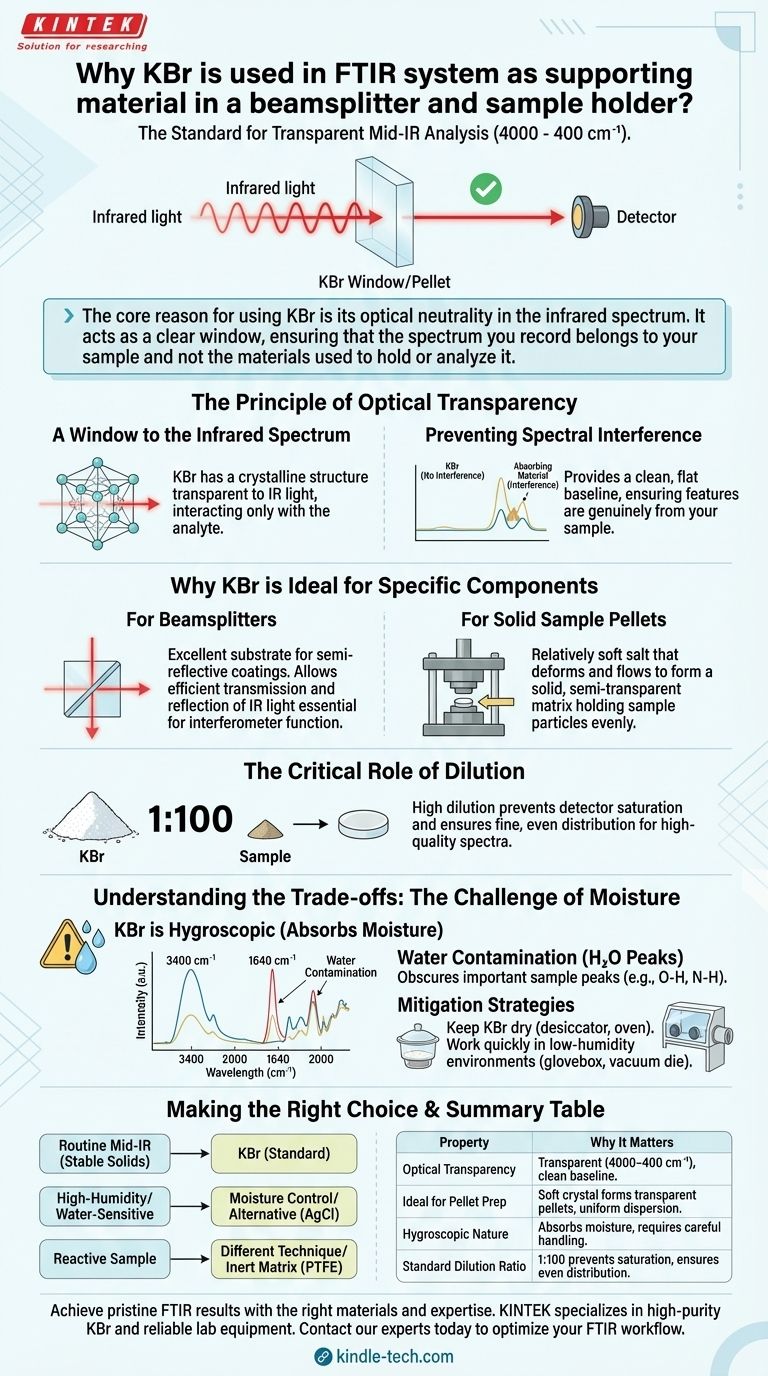
The core reason for using KBr is its optical neutrality in the infrared spectrum. It acts as a clear window, ensuring that the spectrum you record belongs to your sample and not the materials used to hold or analyze it.

The Principle of Optical Transparency
A Window to the Infrared Spectrum
The fundamental requirement for any material placed in the path of an FTIR spectrometer's beam is that it should not interfere with the measurement. KBr has a crystalline structure that does not absorb light in the most commonly analyzed region of the infrared spectrum.
This transparency allows the infrared light to pass through the KBr components—whether it's the beamsplitter substrate or the sample pellet—and interact solely with the analyte of interest.
Preventing Spectral Interference
If the supporting material absorbed infrared light, its own spectral peaks would appear in the final measurement. These interfering peaks could overlap with or obscure the peaks from the actual sample, making data interpretation difficult or impossible.
KBr's lack of absorption bands in this region provides a clean, flat baseline, ensuring the spectral features you see are genuinely from your sample.
Why KBr is Ideal for Specific Components
For Beamsplitters
A beamsplitter is a critical optical component that must divide the IR beam precisely. KBr serves as an excellent substrate material for the beamsplitter's semi-reflective coating.
Its wide transparency range and appropriate refractive index allow for the efficient transmission and reflection of infrared light, which is essential for the interferometer to function correctly.
For Solid Sample Pellets
KBr is a relatively soft, crystalline salt. When finely ground with a solid sample and subjected to high pressure (using a pellet press), it deforms and flows, forming a solid, semi-transparent disc or "pellet."
This process creates a solid matrix that holds the sample particles uniformly dispersed in the path of the IR beam. This is a simple and effective method for analyzing solid samples that are not soluble in IR-transparent solvents.
The Critical Role of Dilution
Typically, samples are mixed with KBr at a ratio of about 1:100 (sample to KBr). This high dilution is crucial for two reasons.
First, it prevents the sample's IR absorption from becoming too strong and saturating the detector. Second, it ensures the sample is distributed finely and evenly throughout the pellet, which minimizes light scattering and produces a higher quality spectrum.
Understanding the Trade-offs: The Challenge of Moisture
KBr is Hygroscopic
Despite its excellent optical properties, KBr has one significant drawback: it is hygroscopic. This means it readily absorbs moisture from the atmosphere.
This property is its primary limitation and requires careful handling procedures to ensure accurate measurements.
The Impact of Water Contamination
Water (H₂O) is a strong absorber of infrared radiation, displaying a very broad absorption band around 3400 cm⁻¹ and another sharp band near 1640 cm⁻¹.
If the KBr used for a pellet has absorbed moisture from the air, these large water peaks will appear in the spectrum. This can completely obscure important sample peaks in those regions, such as O-H and N-H stretching vibrations.
Mitigation Strategies
To achieve a clean spectrum, KBr must be kept scrupulously dry. It should be stored in a desiccator or dried in an oven before use.
When preparing pellets, especially in humid environments, work must be done quickly. For best results, grinding the sample and pressing the pellet should be performed in a low-humidity environment, such as inside a glovebox or by using a specialized vacuum die.
Making the Right Choice for Your Analysis
Understanding the properties of KBr allows you to use it effectively and troubleshoot potential issues.
- If your primary focus is routine mid-IR analysis of stable solid samples: KBr is the cost-effective industry standard, providing excellent results when handled correctly.
- If you are working in a high-humidity environment or analyzing water-sensitive samples: You must implement strict moisture control (like using a desiccator and glovebox) or consider alternative pellet materials like Silver Chloride (AgCl).
- If your sample is known to react with alkali halides: You must use a different analytical technique or an inert matrix like PTFE, being mindful of its own limited transparent regions.
Ultimately, mastering your materials is the first step toward achieving a clean, reliable, and accurate spectral analysis.
Summary Table:
| Property | Why It Matters for FTIR |
|---|---|
| Optical Transparency | Transparent across 4000-400 cm⁻¹, providing a clean baseline without spectral interference. |
| Ideal for Pellet Prep | Soft crystal forms transparent pellets when pressed, allowing uniform sample dispersion. |
| Hygroscopic Nature | Absorbs moisture, requiring careful handling (e.g., drying, glovebox use) to avoid water peaks in the spectrum. |
| Standard Dilution Ratio | Typical 1:100 sample-to-KBr ratio prevents detector saturation and ensures even particle distribution. |
Achieve pristine FTIR results with the right materials and expertise. KINTEK specializes in high-purity KBr and reliable lab equipment for accurate spectral analysis. Our team can help you select the perfect consumables and implement best practices to mitigate moisture issues. Contact our experts today to optimize your FTIR workflow and ensure the integrity of your data.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Disc Rotary Mixer for Efficient Sample Mixing and Homogenization
- High Temperature Constant Temperature Heating Circulator Water Bath Chiller Circulator for Reaction Bath
- 80L Chilling Circulator Cooling Water Circulator for Water Bath Cooling and Low Temperature Constant Temperature Reaction Bath
- Graphite Vacuum Continuous Graphitization Furnace
- 1200℃ Split Tube Furnace with Quartz Tube Laboratory Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is industrial application of bio-oil? A Guide to Renewable Heat, Power, and Chemicals
- How does a constant temperature reciprocating shaker influence adsorption kinetics? Optimize Your Pollutant Studies
- What are the disadvantages of hardening? The Critical Trade-offs of Increased Brittleness and Stress
- What role does a precision laboratory drying oven play in the synthesis of GO-PANI nanocomposites? Protect Material Integrity
- How long does vacuum casting take? A Detailed Breakdown of the 7-10 Day Timeline
- How does a controlled heating reaction system achieve morphology control for platinum nanoparticles?
- Why do we need magnetic field in magnetron sputtering? Boost Deposition Rates & Film Quality
- What is the thermal stability of graphene? A Guide to Temperature Limits and Material Selection



















