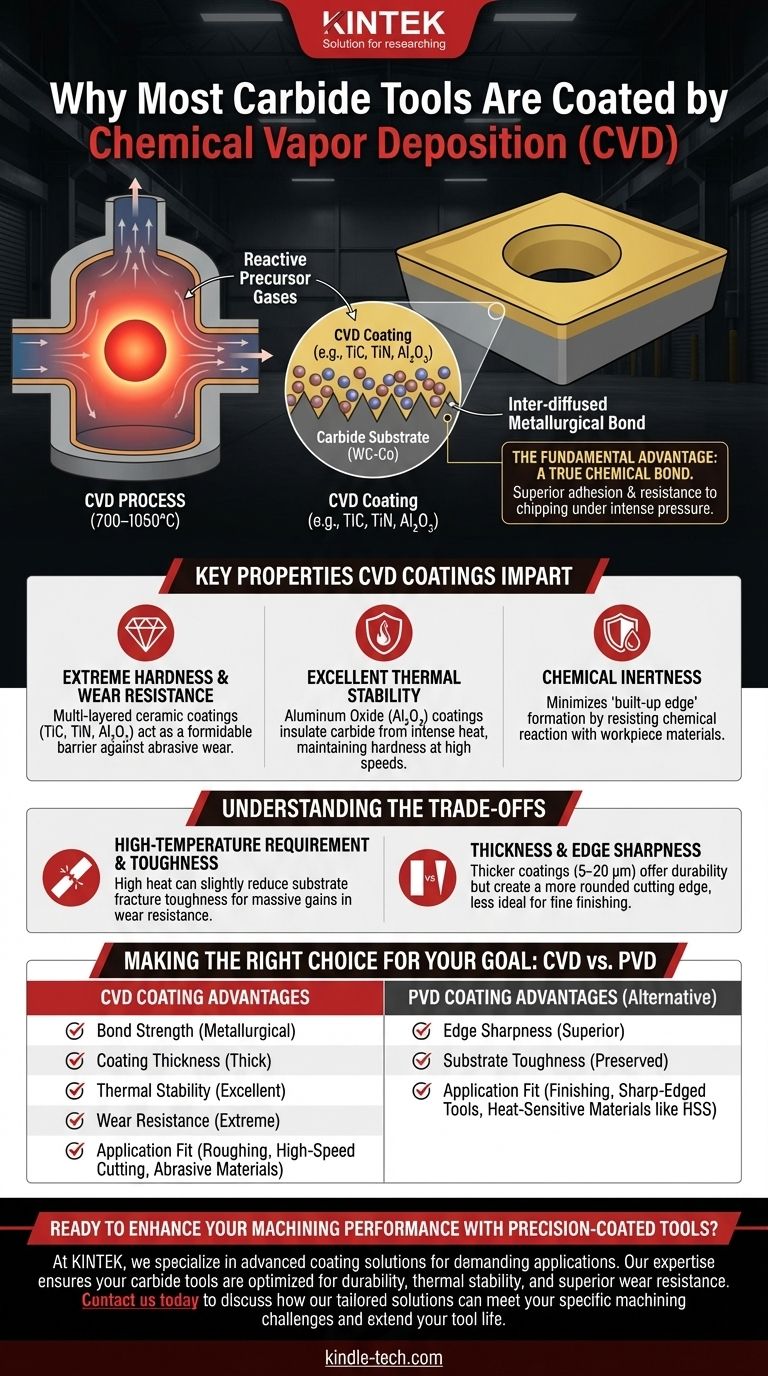
Carbide tools are coated using Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) primarily because the process creates exceptionally thick, durable, and strongly bonded layers that can withstand the extreme heat and abrasion of high-speed machining. At the high temperatures used in CVD, the coating materials don't just sit on the surface; they chemically react with the carbide substrate, forming an inter-diffused layer that results in superior adhesion and resistance to chipping or flaking under intense pressure.
The choice of CVD for carbide tools is not merely about applying a hard layer. It is a strategic decision to create a metallurgical bond between the tool and the coating, resulting in a composite material with unparalleled wear resistance and thermal stability for the most demanding cutting applications.
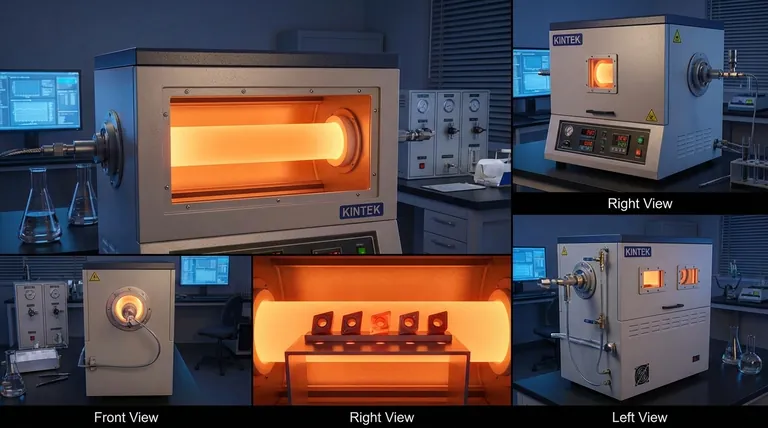

The Fundamental Advantage: A True Chemical Bond
The defining characteristic of the CVD process is its use of high temperatures (typically 700–1050°C) and reactive precursor gases. This environment is what sets it apart and makes it ideal for robust carbide tooling.
How CVD Creates a Superior Bond
In CVD, volatile chemical precursors are introduced into a reaction chamber where they decompose on the hot surface of the carbide tool.
This isn't a simple physical layering. The high heat initiates a chemical reaction, causing atoms from the coating material and the carbide substrate to inter-diffuse, creating a new, chemically bonded interface layer.
This process is fundamentally different from lower-temperature Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD), which is more akin to a mechanical or atomic bond.
The Impact of Strong Adhesion
This deep chemical bond provides incredible adhesion. Under the immense stress and vibration of cutting metal, a weakly bonded coating would quickly chip or peel away, rendering it useless.
The CVD bond ensures the coating remains intact, providing continuous protection to the carbide substrate throughout the tool's life.
Uniformity and Coverage
Because the coating is formed from a gas, CVD can deposit a highly uniform layer over complex tool geometries, like the intricate shapes of cutting inserts. This ensures consistent protection and wear characteristics across all cutting edges and faces of the tool.
Key Properties CVD Coatings Impart
The purpose of the coating is to enhance the performance of the underlying carbide. CVD excels at depositing materials that provide a synergistic combination of protective properties.
Extreme Hardness and Wear Resistance
CVD is used to apply very hard ceramic layers like Titanium Carbide (TiC), Titanium Nitride (TiN), and Aluminum Oxide (Al₂O₃).
These multi-layered coatings act as a formidable barrier against the abrasive wear that occurs when cutting through tough materials.
Excellent Thermal Stability
Machining generates intense, localized heat that can soften the carbide substrate and accelerate tool failure.
CVD coatings, particularly Aluminum Oxide, act as an excellent thermal barrier. They insulate the carbide from the heat of the cutting zone, allowing the tool to maintain its hardness and structural integrity at higher cutting speeds.
Chemical Inertness
At high temperatures, there is a tendency for the workpiece material to chemically react with or weld to the cutting tool, a phenomenon known as a "built-up edge."
The chemically inert nature of CVD ceramic coatings minimizes this reaction, ensuring a cleaner cut and extending the life of the tool.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, CVD is not the solution for every application. The high temperatures that give it its primary advantage also create its main limitations.
The High-Temperature Requirement
The intense heat of the CVD process can have a subtle but important effect on the carbide substrate itself. It can potentially reduce the substrate's fracture toughness, making it slightly more brittle.
This is a carefully managed trade-off, where a slight reduction in toughness is accepted to gain a massive increase in wear resistance and thermal stability.
Coating Thickness and Edge Sharpness
CVD coatings are typically thicker (5–20 µm) than PVD coatings. This thickness is excellent for durability and thermal protection in demanding roughing operations.
However, it also creates a more rounded cutting edge. For finishing operations that require a razor-sharp edge to achieve a fine surface finish, this rounded profile can be a disadvantage.
The Alternative: Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD)
PVD is a lower-temperature (200-500°C) "line-of-sight" process. It doesn't create the same deep chemical bond as CVD, but it preserves the substrate's toughness and can create thinner, sharper coatings. This makes PVD the preferred choice for tools where edge sharpness is the highest priority.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The decision between a CVD-coated or a PVD-coated tool depends entirely on the specific demands of the machining application.
- If your primary focus is high-speed cutting, heavy roughing, or machining abrasive materials: CVD is the superior choice due to its thick, thermally stable, and tenaciously bonded coatings.
- If your primary focus is finishing operations, milling with sharp-edged end mills, or cutting "gummy" materials: PVD coatings are often preferred for their sharper edge profile and the higher toughness they preserve in the substrate.
- If you are working with heat-sensitive tool materials like high-speed steel (HSS): PVD is the only viable choice, as the high heat of CVD would destroy the tool's heat treatment.
Ultimately, understanding the fundamental process behind the coating allows you to select a tool that is not just coated, but truly engineered for your specific machining challenge.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | CVD Coating Advantage |
|---|---|
| Bond Strength | Creates a metallurgical, chemical bond for superior adhesion |
| Coating Thickness | Thick layers (5–20 µm) for maximum durability and thermal protection |
| Thermal Stability | Excellent heat resistance, ideal for high-speed machining |
| Wear Resistance | Hard ceramic layers (TiC, TiN, Al₂O₃) provide extreme abrasion resistance |
| Application Fit | Best for roughing, high-speed cutting, and abrasive materials |
Ready to enhance your machining performance with precision-coated tools? At KINTEK, we specialize in high-performance lab equipment and consumables, including advanced coating solutions for demanding industrial applications. Our expertise ensures your carbide tools are optimized for durability, thermal stability, and superior wear resistance. Contact us today to discuss how our tailored solutions can meet your specific machining challenges and extend your tool life.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment System Chamber Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition RF PECVD
- Customer Made Versatile CVD Tube Furnace Chemical Vapor Deposition Chamber System Equipment
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine for Lamination and Heating
- 1200℃ Split Tube Furnace with Quartz Tube Laboratory Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the process of vacuum vapor deposition? Mastering CVD and PVD Thin-Film Coating
- What is PECVD in semiconductor? Enable Low-Temperature Thin Film Deposition for ICs
- What is the difference between PECVD and CVD? Unlock the Right Thin-Film Deposition Method
- What are the steps of the CVD process? A Guide to Precision Thin Film Deposition
- How does PECVD work? Enable Low-Temperature, High-Quality Thin Film Deposition



















