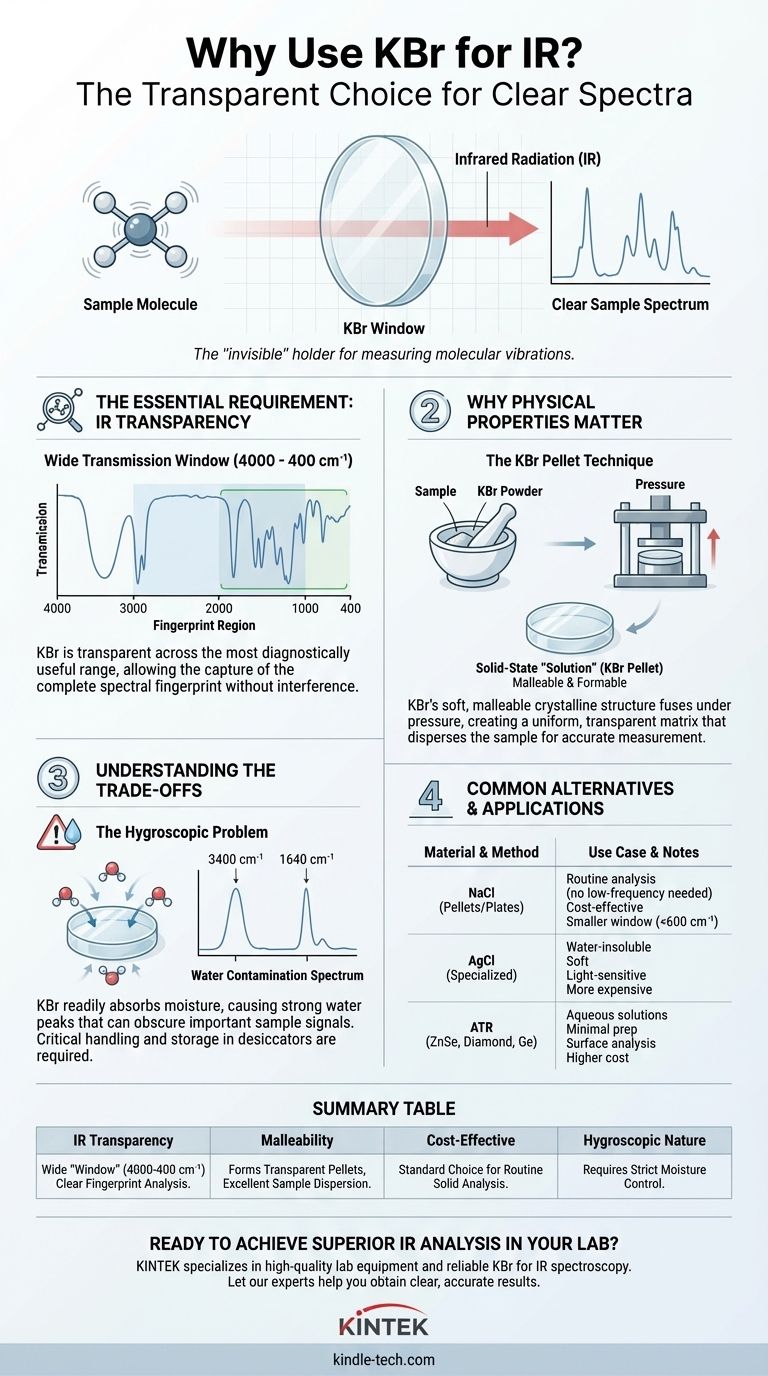
In short, Potassium Bromide (KBr) is used for IR spectroscopy because it is transparent to infrared radiation across the most diagnostically useful frequency range. This property ensures that the instrument measures the molecular vibrations of the sample itself, not the material used to hold or contain it.
The core principle is simple: to analyze a substance with light, the "window" you look through must be invisible. KBr acts as a perfectly clear window for infrared light, allowing the unique spectral fingerprint of your sample to be recorded without interference.

The Essential Requirement: Infrared Transparency
What "IR Transparent" Means
In spectroscopy, you are measuring how a sample absorbs, transmits, or reflects light at different energies. The resulting spectrum is a unique fingerprint of the sample's chemical bonds.
For this to work, the materials holding the sample—whether they are windows in a liquid cell or a matrix for a solid—must not absorb light in the same energy range.
KBr is an ionic salt. The vibration of the K-Br ionic bond occurs at a very low frequency (far-infrared), well below the standard mid-infrared region (4000 to 400 cm⁻¹) used for identifying most organic functional groups.
The KBr Transmission Window
Because its own absorption is out of the way, KBr is transparent from the near-UV all the way through the mid-IR range, down to about 400 cm⁻¹.
This wide, clear window is crucial. It covers the entire fingerprint region, where the complex vibrations that distinguish one molecule from another occur. Using KBr ensures you can capture the complete, unobstructed spectrum of your compound.
Why KBr's Physical Properties Matter
Beyond optical transparency, KBr's physical characteristics make it exceptionally well-suited for a common IR sampling technique: the KBr pellet.
Creating the Solid-State "Solution"
Many samples are solid powders, which are difficult to analyze directly with IR. The KBr pellet method overcomes this by effectively dissolving the solid sample in a solid, IR-transparent matrix.
A small amount of the sample is finely ground with pure, dry KBr powder. This mixture is then put into a die and compressed under immense pressure (several tons) to form a thin, transparent or translucent disc.
The Importance of Malleability
KBr is a relatively soft, plastic-like salt. Under pressure, its crystalline structure flows and fuses together to form a solid, glass-like disc without fracturing.
This process ensures the sample is dispersed evenly throughout the KBr matrix, minimizing light scattering and allowing the IR beam to pass through for an accurate measurement.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
While KBr is the workhorse of IR spectroscopy, it is not without its challenges. Its primary drawback is a significant one.
The Hygroscopic Problem
KBr is hygroscopic, meaning it readily absorbs moisture from the atmosphere. This is its single greatest weakness in a laboratory setting.
How Water Contamination Affects the Spectrum
Water (H₂O) has a very strong, broad absorption band in the IR spectrum, centered around 3400 cm⁻¹. It also has a bending vibration around 1640 cm⁻¹.
If your KBr has absorbed moisture, these water peaks will appear in your spectrum. They can easily overlap with or completely obscure important sample peaks, particularly the O-H and N-H stretching bands, leading to incorrect analysis.
Critical Handling and Storage
Because of its hygroscopic nature, KBr must be stored in a desiccator or dried in an oven before use. All grinding and pellet-pressing must be done as quickly as possible to minimize exposure to humid air.
Common Alternatives to KBr
While KBr is most common for pellets, other materials are used for different applications and techniques.
Sodium Chloride (NaCl)
Like KBr, NaCl is an inexpensive, IR-transparent salt. However, its transmission window is smaller, cutting off around 600 cm⁻¹. It is suitable for many analyses but cannot be used when the lower-frequency fingerprint region is critical.
Silver Chloride (AgCl)
AgCl is a softer material that is also not soluble in water, a major advantage over KBr. However, it is much more expensive, can be sensitive to light, and is generally used for specialized applications.
ZnSe, Diamond, and Germanium
These materials are not typically used for pellets. Instead, they are hard, durable, water-insoluble crystals used in a technique called Attenuated Total Reflectance (ATR). ATR is a modern alternative that places a liquid or solid sample in direct contact with the crystal, requiring minimal sample preparation.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
- If your primary focus is routine analysis of solid organic compounds: KBr pellets offer a cost-effective and reliable method for obtaining high-quality, full-range spectra, provided you manage moisture carefully.
- If your primary focus is analyzing aqueous solutions or avoiding sample prep: ATR-FTIR using a ZnSe or diamond crystal is the superior, though more expensive, choice.
- If your budget is tight and you don't need the full fingerprint region: NaCl plates or pellets can be a viable alternative to KBr for many standard analyses.
Ultimately, KBr's unique combination of a wide transparent window, ideal physical properties, and low cost makes it the default standard for solid-sample IR analysis.
Summary Table:
| Key Property | Why It Matters for IR Spectroscopy |
|---|---|
| IR Transparency (4000-400 cm⁻¹) | Provides a clear "window" to measure sample vibrations without interference. |
| Malleable Under Pressure | Allows formation of transparent pellets for solid sample analysis. |
| Cost-Effective | Makes it the standard choice for routine laboratory use. |
| Hygroscopic Nature | Requires careful handling and drying to avoid water peaks in the spectrum. |
Ready to achieve superior IR analysis in your lab?
KINTEK specializes in providing high-quality lab equipment and consumables, including reliable materials for IR spectroscopy like KBr. Whether you're preparing pellets for solid samples or need guidance on the best method for your analysis, our experts are here to help you obtain clear, accurate results.
Contact us today to discuss your laboratory needs and discover how KINTEK can support your research with the right tools and expertise!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Hydraulic Press Split Electric Lab Pellet Press
- Automatic Laboratory Hydraulic Pellet Press Machine for Lab Use
- Laboratory Manual Hydraulic Pellet Press for Lab Use
- Laboratory Hydraulic Pellet Press for XRF KBR FTIR Lab Applications
- kbr pellet press 2t
People Also Ask
- What is the pressed powder pellet method? A Guide to Accurate FTIR Sample Preparation
- What is the pellet technique in IR? Master Solid Sample Preparation for Clear Spectroscopy
- What is the use of KBr? Master Sample Prep for Accurate IR Spectroscopy
- How hot is a hydraulic press? Understanding the Critical Heat in Your Hydraulic System
- Are hydraulic presses powered by water? Discover the critical role of hydraulic oil.



















