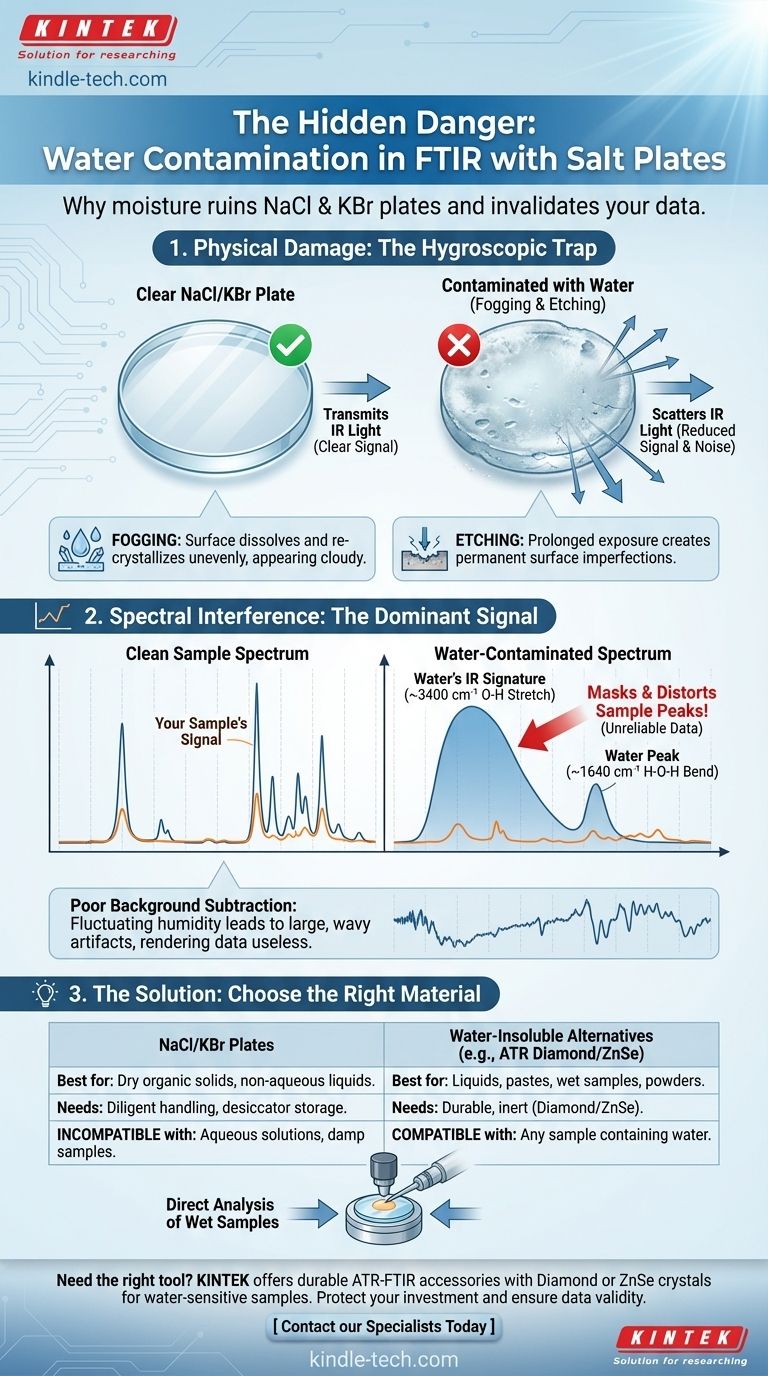
In short, you must avoid water contamination because the sodium chloride (NaCl) and potassium bromide (KBr) plates commonly used in FTIR are highly soluble in water. Any contact with moisture, even humidity from the air, will damage the plates by fogging or dissolving them, while water’s own strong infrared signal will overwhelm your sample's spectrum, rendering your data unreliable.
This isn't just a matter of minor inconvenience; it's a fundamental issue of both equipment integrity and data validity. Water contamination simultaneously destroys your expensive optical components and invalidates your scientific measurement.
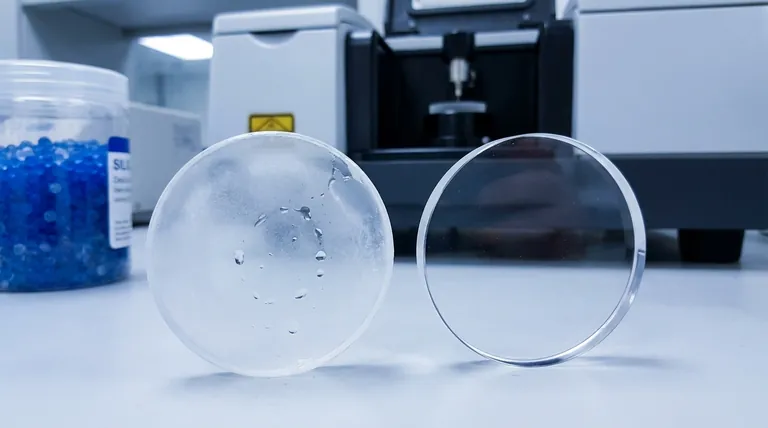

The Physical Impact of Water on Salt Plates
The core problem begins with the material properties of NaCl and KBr. They are alkali-halide salts, chosen for their transparency to mid-infrared radiation, but this comes with a significant drawback.
Hygroscopic Nature and Solubility
Hygroscopic materials actively absorb moisture from the atmosphere. NaCl and KBr are prime examples.
Just as table salt clumps on a humid day, these plates will draw water vapor from the air onto their surface. If they come into contact with liquid water, they will begin to dissolve immediately.
Fogging and Etching
The first sign of moisture damage is "fogging." The once-clear, polished surface of the plate will appear cloudy or milky.
This occurs as the very top layer of the salt plate dissolves and re-crystallizes unevenly. More significant water exposure will lead to etching or pitting, creating visible imperfections on the surface that cannot be easily polished away.
The Consequence: Compromised Transmission
A foggy or etched plate is no longer transparent to the IR beam. The surface imperfections scatter the infrared light instead of allowing it to pass through cleanly.
This scattering dramatically reduces the amount of energy (throughput) reaching the detector, leading to a poor signal-to-noise ratio and a low-quality, noisy spectrum.
The Spectral Interference of Water
Beyond the physical damage, water introduces a severe data contamination problem because it is a very strong infrared absorber.
Water's Strong Infrared Signature
Water (H₂O) has two major absorption regions that dominate an IR spectrum:
- A very broad and strong O-H stretching band around 3400 cm⁻¹.
- An H-O-H bending band of medium intensity around 1640 cm⁻¹.
These peaks are so intense that even trace amounts of water can produce significant signals.
Obscuring the Sample Signal
If your sample of interest has key functional groups in these regions (like alcohols or amines with O-H or N-H stretches), the massive water peak will completely mask or distort them.
This makes it impossible to accurately identify or quantify the components of your sample, defeating the purpose of the measurement.
The Problem with Background Subtraction
While FTIR software uses a background scan to subtract signals from the atmosphere (like CO₂ and water vapor), this process is often imperfect for water.
Levels of water vapor can fluctuate between the time you run the background and the time you run the sample. This leads to poor subtraction, resulting in large, derivative-shaped "wavy" artifacts in your final spectrum that are a classic sign of water contamination.
Understanding the Trade-offs: When to Avoid Salt Plates
The choice of NaCl or KBr is a deliberate trade-off: they offer excellent transparency and are inexpensive, but demand a perfectly dry environment.
The Limitation with Aqueous Samples
It must be stated plainly: NaCl and KBr plates are fundamentally incompatible with aqueous solutions or samples that contain significant amounts of water. Attempting to use them will destroy the plates and yield useless data.
Alternative Window Materials
When you must analyze a sample containing water, you have to switch to a water-insoluble material. Common alternatives include:
- Zinc Selenide (ZnSe): A very common water-insoluble material, but it is brittle and can be damaged by strong acids or bases.
- Attenuated Total Reflectance (ATR): An ATR-FTIR accessory is often the best solution. It uses a robust internal reflection crystal (like Diamond or ZnSe) that you press the sample against. The crystal is durable and inert, making it ideal for liquids, pastes, and wet samples.
How to Apply This to Your Project
Your choice of window material and handling procedure is dictated entirely by the nature of your sample.
- If your primary focus is dry organic solids or non-aqueous liquids: NaCl and KBr are cost-effective and excellent choices. Your priority must be diligent handling and storage in a desiccator.
- If your primary focus is analyzing powders that might be damp: You must thoroughly dry the sample before analysis or, if preparing a KBr pellet, do so quickly in a low-humidity environment.
- If your primary focus is any sample containing water: You must use water-insoluble optics. An ATR-FTIR with a Diamond or ZnSe crystal is the standard and most reliable method for this task.
Choosing the right experimental conditions is the first and most critical step toward acquiring meaningful spectroscopic data.
Summary Table:
| Consequence of Water Contamination | Impact on FTIR Measurement |
|---|---|
| Fogging/Etching of Plates | Scatters IR light, reduces signal-to-noise ratio |
| Strong Water IR Peaks (~3400 cm⁻¹, ~1640 cm⁻¹) | Masks sample signals, distorts spectrum |
| Poor Background Subtraction | Introduces wavy artifacts, invalidates data |
Need the right tool for your sample?
Water-sensitive samples require the right equipment for accurate results. KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables, including durable ATR-FTIR accessories with diamond or ZnSe crystals perfect for aqueous or wet samples. Our experts can help you select the ideal solution to protect your investment and ensure your data's validity.
Contact our specialists today to discuss your FTIR needs and find the perfect fit for your laboratory.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Optical Window Glass Substrate Wafer Barium Fluoride BaF2 Substrate Window
- Infrared Heating Quantitative Flat Plate Press Mold
- Metallographic Specimen Mounting Machine for Laboratory Materials and Analysis
- Three-dimensional electromagnetic sieving instrument
- Infrared High Resistance Single Crystal Silicon Lens
People Also Ask
- How do photoelectrode semiconductor properties improve P-MFC efficiency? Boost Wastewater Treatment with Photocatalysis
- How does potassium bromide affect humans? A Look at Its Risks and Obsolete Medical Use
- What are the factors that affect the filtration of the solution? Master the Key Variables for Optimal Performance
- What role does the dielectric window play in MW-SWP CVD equipment? Ensuring Stable Plasma Generation with Quartz
- What is the alternative to KBr in IR? Choosing the Right Sample Matrix for Accurate Spectroscopy



















