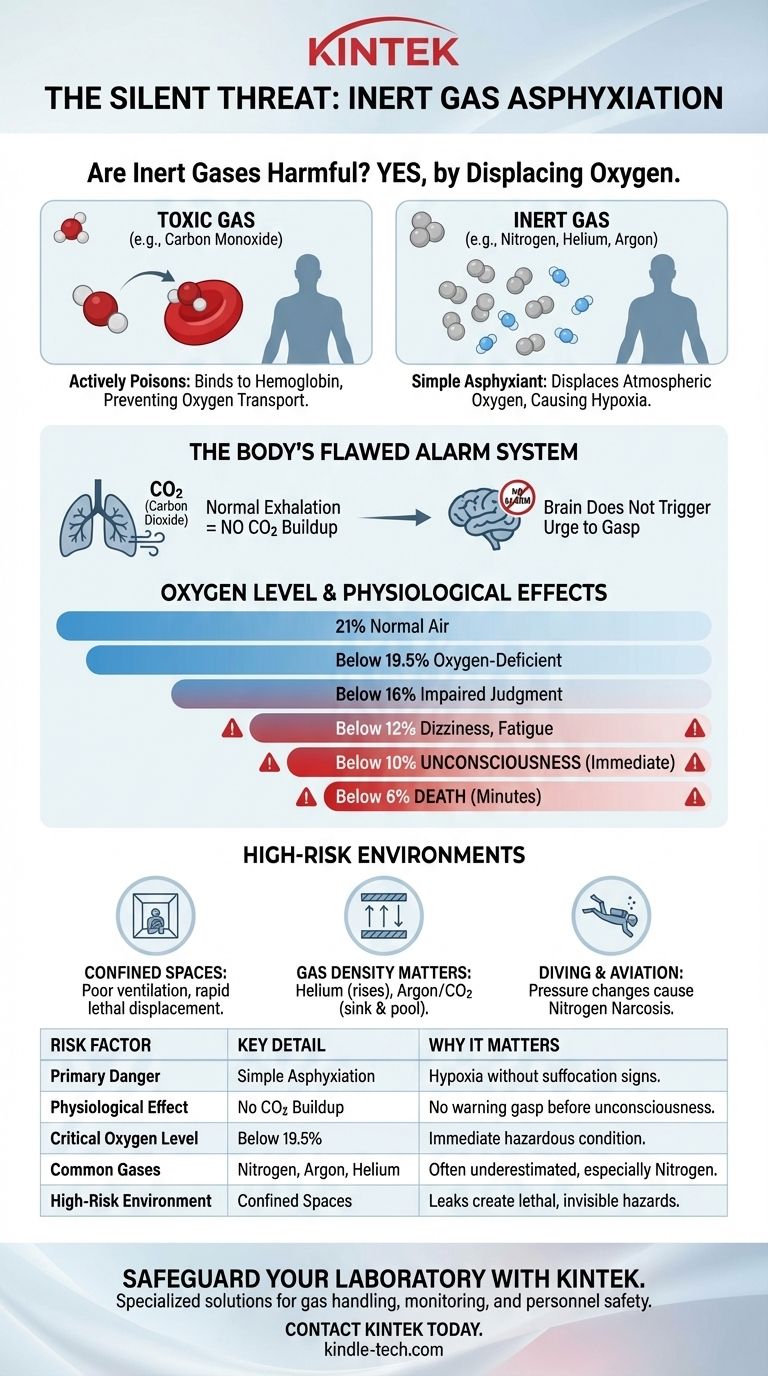
In short, yes, inert gases can be extremely harmful to humans, but not because they are toxic or poisonous. Their danger comes from their ability to displace the oxygen in the air we breathe. This process, known as simple asphyxiation, can lead to unconsciousness and death in minutes, often without any warning signs of suffocation.
The primary danger of an inert gas is not what it is, but what it displaces. These gases are hazardous because they dilute or replace the atmospheric oxygen our bodies require to function, a silent and rapid threat known as simple asphyxiation.

The Critical Distinction: Toxicity vs. Asphyxiation
To understand the risk, we must first distinguish between how a toxic gas and an inert gas cause harm. They are fundamentally different mechanisms.
What "Inert" Actually Means
The term inert refers to chemical non-reactivity. Gases like nitrogen, helium, and argon do not readily participate in chemical reactions within the body. They are not metabolized and do not interfere with cellular processes on a chemical level.
How a Toxic Gas Works
A toxic gas, like carbon monoxide, actively harms the body. Carbon monoxide binds to the hemoglobin in your red blood cells more strongly than oxygen does. This chemical interference actively prevents your blood from transporting oxygen, effectively poisoning you even when sufficient oxygen is in the air.
How a Simple Asphyxiant Works
A simple asphyxiant does not react with your body at all. Its danger lies entirely in its concentration. By occupying space in the air, it lowers the percentage of oxygen available with each breath. Once the oxygen concentration drops below approximately 19.5%, the environment is considered oxygen-deficient and dangerous.
The Silent Danger of Inert Gas Asphyxiation
The most deceptive aspect of inert gas asphyxiation is the lack of a physiological alarm. This is why it is a leading cause of workplace fatalities in certain industries.
The Body's Flawed Alarm System
Your body's primary urge to breathe is triggered by a buildup of carbon dioxide (CO2) in your bloodstream, not by a lack of oxygen.
When you are in an environment with a high concentration of an inert gas, you can still exhale CO2 normally. Because CO2 levels don't build up, you do not experience the typical, desperate feeling of suffocation or air hunger.
The Rapid Physiological Process
Without warning, a person breathing an oxygen-deficient atmosphere will experience the effects of hypoxia (oxygen starvation).
The process is swift:
- Below 16% Oxygen: Judgment and coordination become impaired.
- Below 12% Oxygen: Dizziness, headache, and rapid fatigue occur.
- Below 10% Oxygen: Unconsciousness is nearly immediate.
- Below 6% Oxygen: Death occurs in a matter of minutes.
Common Inert Gas Asphyxiants
While the noble gases (helium, neon, argon, krypton, xenon) are classic examples, the most common asphyxiant is nitrogen. Since nitrogen already makes up 78% of the air we breathe, its danger is often underestimated. Any of these gases can be lethal when they leak into an enclosed area.
Understanding the Contexts and Risks
The danger of an inert gas is almost entirely dependent on the environment.
Confined Spaces Are the Primary Hazard
The vast majority of inert gas incidents occur in confined or poorly ventilated spaces. A slow leak from a cylinder of nitrogen or argon in a small storage room can quickly displace enough oxygen to create a lethal, invisible, and odorless hazard.
Gas Density Changes the Risk Zone
The physical properties of the gas matter. Helium, being lighter than air, will rise and accumulate near the ceiling. Heavier-than-air gases like argon and carbon dioxide will sink and pool on the floor, creating a deadly hazard for anyone entering a pit or lower level. Nitrogen has a density similar to air and will mix more evenly.
Specialized Environments: Diving and Aviation
Under high pressure, such as in scuba diving, inert gases like nitrogen can have a narcotic effect, causing impairment known as nitrogen narcosis. In this context, the gas itself is having a direct physiological effect, moving beyond the definition of a simple asphyxiant.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your approach to safety depends entirely on your context.
- If your primary focus is industrial or laboratory safety: Always assume a confined space is hazardous. Use air monitoring equipment to test the oxygen level before entry and ensure continuous ventilation when working with or around inert gas systems.
- If your primary focus is education: Emphasize that the body's drive to breathe is a poor indicator of oxygen availability. The core lesson is that the absence of a warning sign (like the urge to gasp) does not mean the absence of danger.
- If your primary focus is diving or aviation: Recognize that pressure and altitude fundamentally change the rules. You must receive specialized training on the unique physiological effects of inert gases in these environments, such as narcosis.
Understanding that the danger lies in displacement, not toxicity, is the key to safely managing any environment containing inert gases.
Summary Table:
| Risk Factor | Key Detail | Why It Matters |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Danger | Simple Asphyxiation | Displaces oxygen, causing hypoxia without warning signs like suffocation. |
| Physiological Effect | No CO2 Buildup | Body's alarm system fails; no urge to gasp for air before unconsciousness. |
| Critical Oxygen Level | Below 19.5% | Environment becomes oxygen-deficient and immediately hazardous. |
| Common Hazardous Gases | Nitrogen, Argon, Helium | Often underestimated, especially nitrogen, which is abundant in air. |
| High-Risk Environment | Confined Spaces | Leaks in poorly ventilated areas can create lethal, invisible hazards rapidly. |
Safeguard Your Laboratory with KINTEK
Working with inert gases is essential in many lab processes, but managing the associated risks is critical for personnel safety. KINTEK specializes in providing reliable lab equipment and safety solutions tailored to your needs. From secure gas handling systems to environmental monitoring equipment, we help you create a safer workspace and prevent the silent threat of asphyxiation.
Let our experts help you enhance your lab's safety protocols. Contact KINTEK today to discuss your specific requirements and ensure your team is protected.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Desktop Fast High Pressure Laboratory Autoclave Sterilizer 16L 24L for Lab Use
- Lab Infrared Press Mold
- Lab Scale Rotary Single Punch Tablet Press Machine TDP Tablet Punching Machine
- High Temperature Constant Temperature Heating Circulator Water Bath Chiller Circulator for Reaction Bath
- Automatic Laboratory Hydraulic Press for XRF & KBR Pellet Press
People Also Ask
- Why is a 24-hour hydrothermal treatment in an autoclave necessary for BMO nanosheets? Unlock Superior Photocatalysis
- What is the purpose of treating polyester fabric in an autoclave? Ensure Reliable Results in Lab Experiments
- What role does an autoclave play in remediation experiments? Ensure Precision by Eliminating Biological Noise
- What role does a laboratory autoclave play in the separation of lignin? High-Purity Extraction for Biomass Research
- What is the primary difference between pharmaceutical and waste autoclaves? Purity vs. Sterility Explained



















