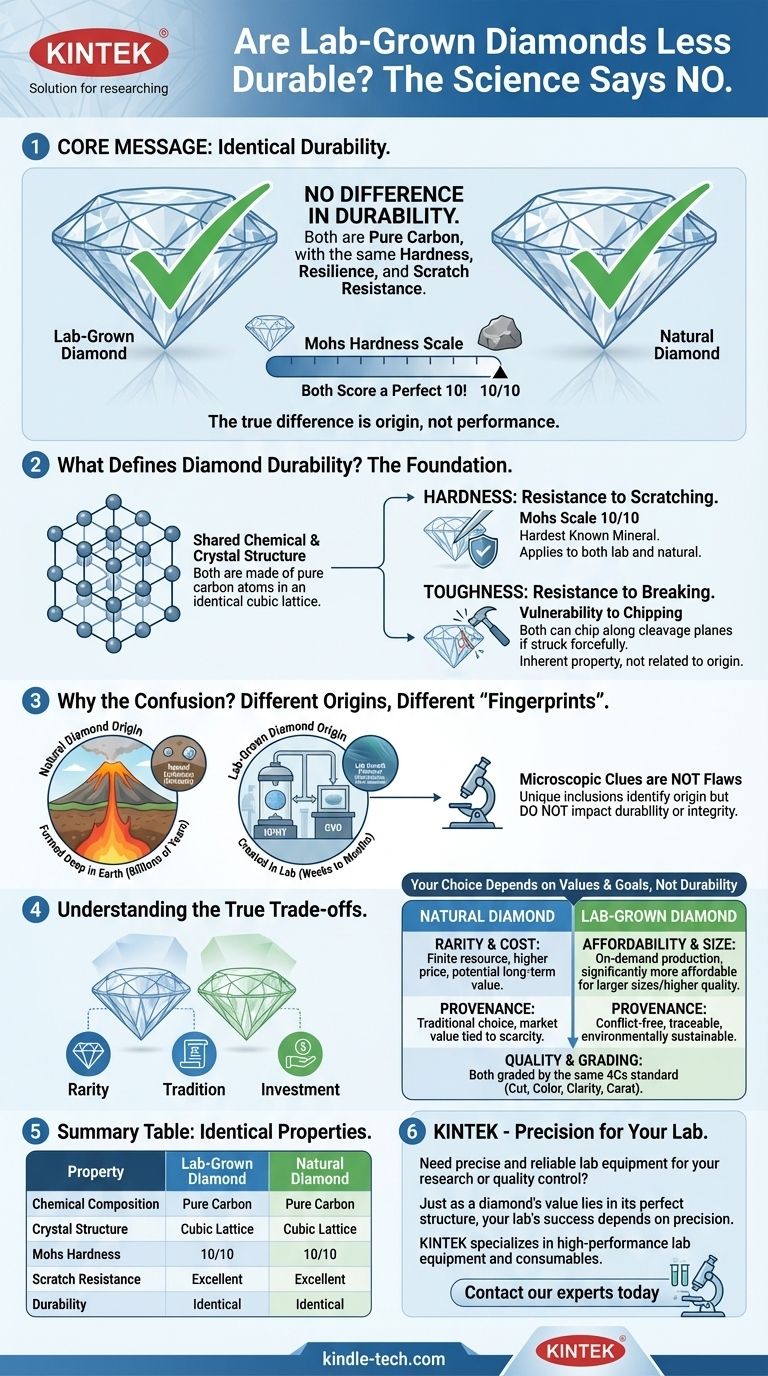
In terms of durability, no. A lab-grown diamond is not less durable than a natural diamond. Because they are physically and chemically identical, both have the same hardness, resilience, and resistance to scratching. They are both pure carbon crystallized in the same atomic structure, making them the hardest known mineral.
The question of durability between lab-grown and natural diamonds is based on a common misconception. Both types are chemically identical, score a perfect 10 on the Mohs hardness scale, and possess the same physical properties. The true differences are not in their performance or quality, but in their origin, rarity, and price.

What Defines Diamond Durability?
To understand why their durability is identical, we must first define what makes a diamond "durable." This is a function of its fundamental physical and chemical properties.
The Foundation: Chemical and Crystal Structure
A diamond's legendary hardness comes from its composition and structure. It is made of pure carbon atoms locked into a rigid, three-dimensional pattern known as a cubic crystal lattice.
This specific atomic arrangement is what makes a diamond a diamond. Both lab-grown and natural diamonds share this exact same carbon crystal structure, and therefore, the same physical properties.
Hardness: Resistance to Scratching
Durability is most often associated with hardness. On the Mohs scale of mineral hardness, which measures a material's resistance to being scratched, diamond is a 10 out of 10.
This rating applies to any stone that meets the chemical and structural definition of a diamond, regardless of whether it was formed in the earth or in a laboratory.
Toughness: Resistance to Breaking
While incredibly hard, any diamond—natural or lab-grown—can chip or fracture if struck with enough force at the right angle along its "cleavage planes." Hardness is not the same as invincibility.
This vulnerability has nothing to do with a diamond's origin. It is an inherent property of the crystal structure itself.
If They're Identical, Why the Confusion?
The confusion arises not from any physical difference, but from the methods used to distinguish them and the language used to describe them.
Different Origins, Different "Fingerprints"
Natural diamonds formed over billions of years under immense heat and pressure deep within the Earth. Lab-grown diamonds are created in a few months using processes like HPHT (High-Pressure, High-Temperature) or CVD (Chemical Vapor Deposition) that replicate these conditions.
These different growth environments leave behind microscopic clues. Natural diamonds may contain tiny mineral crystals that were trapped during formation. Lab diamonds might have trace metallic inclusions from the growth chamber.
Microscopic Clues Are Not Flaws
These unique inclusions and growth patterns are like "fingerprints" that allow a trained gemologist with specialized equipment to identify a diamond's origin.
They are not structural flaws and do not impact the diamond's durability, beauty, or physical integrity. They are simply indicators of a different journey.
Understanding the True Trade-offs
Choosing between a lab-grown and a natural diamond does not involve a trade-off in quality or durability. The real decision lies in other factors.
Quality and Grading: A Level Playing Field
Both lab-grown and natural diamonds are graded by gemological labs using the exact same standard: the 4Cs (Cut, Color, Clarity, and Carat weight). A VVS1 clarity, D color lab diamond is, by definition, just as clear and colorless as a VVS1, D color natural diamond.
The Real Difference: Rarity and Cost
The primary trade-off is economic. Natural diamonds are a finite resource mined from the earth, and their rarity drives a higher price. Lab-grown diamonds can be produced on demand, making them a significantly more affordable option. For the same budget, you can typically purchase a much larger or higher-quality lab-grown diamond.
The Other Difference: Provenance and Ethics
Your choice also reflects your values. Lab-grown diamonds offer a fully traceable, conflict-free, and more environmentally sustainable alternative to traditional mining. This has become a critical decision-making factor for many buyers.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your final decision should be guided by your personal priorities, not by any concern over durability.
- If your primary focus is getting the largest and highest-quality stone for your budget: A lab-grown diamond is the logical choice, as it offers identical visual performance and durability for a lower cost.
- If your primary focus is the tradition and potential long-term value retention of a rare gem: A natural diamond is the conventional choice, as its market value is tied to its natural scarcity.
- If your primary focus is a guaranteed conflict-free origin and environmental sustainability: A lab-grown diamond provides complete transparency and a significantly smaller ecological footprint.
Ultimately, the choice is not about sacrificing quality or durability, but about aligning your purchase with your personal values and financial goals.
Summary Table:
| Property | Lab-Grown Diamond | Natural Diamond |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Composition | Pure Carbon | Pure Carbon |
| Crystal Structure | Cubic Lattice | Cubic Lattice |
| Mohs Hardness | 10/10 | 10/10 |
| Scratch Resistance | Excellent | Excellent |
| Durability | Identical | Identical |
Need precise and reliable lab equipment for your research or quality control?
Just as a diamond's value lies in its perfect structure, your lab's success depends on the precision and reliability of its equipment. KINTEK specializes in high-performance lab equipment and consumables, ensuring your processes are as flawless and durable as the diamonds you study.
Contact our experts today to find the perfect solution for your laboratory's needs and achieve unparalleled accuracy in your work.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- CVD Diamond for Thermal Management Applications
- Customer Made Versatile CVD Tube Furnace Chemical Vapor Deposition Chamber System Equipment
- Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment System Chamber Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- Cylindrical Resonator MPCVD Machine System Reactor for Microwave Plasma Chemical Vapor Deposition and Lab Diamond Growth
- Split Chamber CVD Tube Furnace with Vacuum Station Chemical Vapor Deposition System Equipment Machine
People Also Ask
- What is the temperature of a plasma reactor? Harnessing Stellar Power on Earth
- What are the ethical benefits of lab-grown diamonds? A Conflict-Free, Sustainable Choice
- What are the advantages of microwave plasma? Faster, Purer Processing for Demanding Applications
- What is a diamond machine? Unlock the Power of Diamond Tooling for Your Toughest Materials
- What is the frequency of MPCVD? A Guide to Choosing 2.45 GHz vs. 915 MHz for Your Application
- What is CVD diamond technology? Grow High-Quality, Engineered Diamonds for Your Applications
- How plasma is used in diamond coating films? Unlock the Power of MPCVD for Superior Coatings
- What are the physical characteristics of synthetic diamonds? Identical to Natural Diamonds, Made in a Lab



















