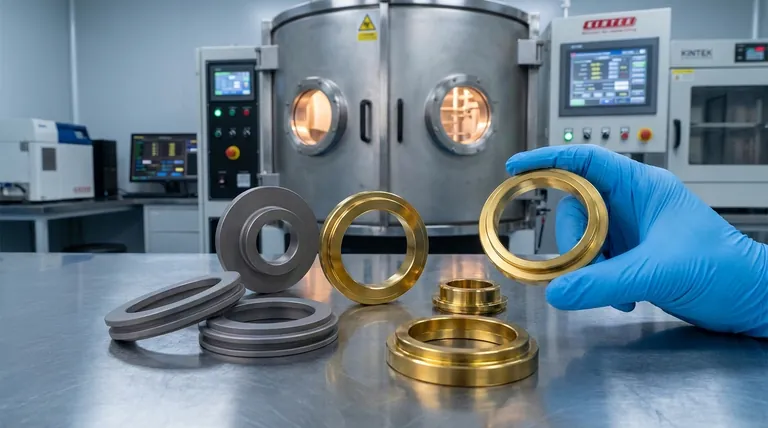
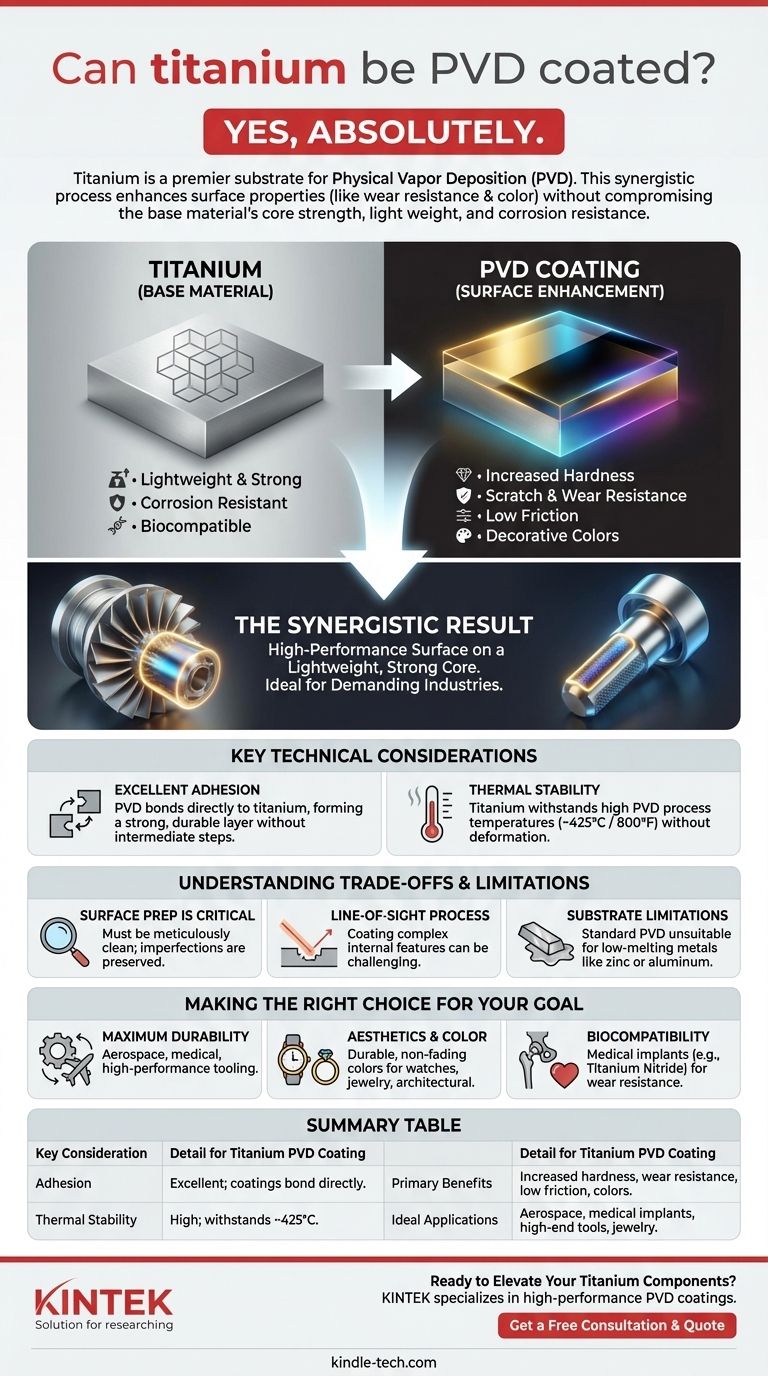
Yes, absolutely. Titanium is not only a material that can be PVD coated, it is one of the most common and ideal substrates for the process. Its inherent strength, light weight, and corrosion resistance make it a premier choice in demanding industries, and PVD coatings elevate these properties even further.
The core insight is that PVD coating isn't just possible on titanium; it's a synergistic combination. The process enhances titanium's surface properties (like wear resistance and color) without compromising the base material's exceptional strength-to-weight ratio and corrosion resistance.

Why PVD and Titanium Are an Ideal Match
Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD) is a surface modification process. It applies a very thin, extremely hard, and durable ceramic coating to a substrate in a vacuum environment. When that substrate is titanium, the benefits are compounded.
The Foundational Strength of Titanium
Titanium and its alloys are specified for their unique combination of properties. They are lightweight, exceptionally strong, and biocompatible, with a natural resistance to corrosion that few other metals can match.
What PVD Coating Adds
A PVD coating enhances the surface of the titanium. It can dramatically increase hardness, improve scratch and wear resistance, reduce the coefficient of friction, and provide a wide range of stable, decorative colors.
The Combined Benefits
The result of PVD on titanium is a product that retains its lightweight, strong core while gaining a high-performance surface. This is why the combination is so prevalent in industries where failure is not an option, such as aerospace components and medical implants.
Key Technical Considerations
The compatibility between PVD and titanium is rooted in the material's ability to withstand the process requirements and form a strong bond with the coating material.
Excellent Coating Adhesion
PVD coatings can be deposited directly onto titanium and its alloys. This creates a strong, durable bond without the need for multiple intermediate layers that might be required for less compatible materials.
Thermal Stability
The PVD process requires heating the substrate in a vacuum chamber, often to temperatures around 800°F (425°C). Titanium alloys handle this temperature with ease, ensuring the integrity and dimensions of the part are maintained throughout the coating cycle.
Understanding the Broader Context and Trade-offs
While titanium is an ideal candidate, the suitability of PVD depends on the specific substrate and the desired outcome. Understanding the limitations is key to making an informed decision.
Not All Substrates Are Equal
The PVD process is versatile and can be applied to many materials, including stainless steel, tool steels, and even some plastics and glass. However, the temperature requirement is a critical factor.
Standard PVD is generally not suitable for low-melting-point metals like zinc or aluminum, as the process heat could damage the part. Specialized low-temperature PVD processes exist but may involve different trade-offs.
Surface Preparation is Non-Negotiable
The final PVD finish is only as good as the surface underneath it. The titanium part must be meticulously cleaned and free of any oils, contaminants, or oxides to ensure proper coating adhesion. Any surface imperfection will be preserved, not hidden, by the thin PVD layer.
PVD is a Line-of-Sight Process
The coating material travels in a straight line from the source to the part. This means that coating complex internal channels or deeply recessed features can be challenging or impossible without specialized fixtures and part rotation.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting PVD on titanium should be a deliberate choice based on your project's specific requirements for performance, aesthetics, and cost.
- If your primary focus is maximum durability and performance: PVD on a titanium substrate is an industry-leading choice for critical aerospace, medical, and high-performance tooling applications.
- If your primary focus is aesthetics and custom color: PVD offers a vast palette of durable, non-fading colors for titanium products like watches, jewelry, and architectural components.
- If your primary focus is biocompatibility: Certain PVD coatings, such as Titanium Nitride (TiN), are biocompatible and commonly used to coat titanium medical implants to improve wear resistance.
Ultimately, combining PVD with a titanium substrate allows you to elevate an already exceptional material, creating a final product with an uncompromising surface and core.
Summary Table:
| Key Consideration | Detail for Titanium PVD Coating |
|---|---|
| Adhesion | Excellent; coatings bond directly without intermediate layers. |
| Thermal Stability | High; withstands process temperatures (~425°C / 800°F) with ease. |
| Primary Benefits | Increased hardness, wear resistance, low friction, and decorative colors. |
| Ideal Applications | Aerospace components, medical implants, high-end tools, and jewelry. |
Ready to Elevate Your Titanium Components?
At KINTEK, we specialize in applying high-performance PVD coatings to titanium substrates for the medical, aerospace, and manufacturing industries. Our advanced coating services enhance the inherent strength and corrosion resistance of your titanium parts, providing superior surface hardness, wear resistance, and custom aesthetics.
Contact us today to discuss how our PVD coating solutions can bring unmatched durability and performance to your laboratory equipment and critical components.
Get a Free Consultation & Quote
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom CVD Diamond Coating for Lab Applications
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition RF PECVD
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine for Lamination and Heating
- Split Chamber CVD Tube Furnace with Vacuum Station Chemical Vapor Deposition System Equipment Machine
- 1400℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace with Nitrogen and Inert Atmosphere
People Also Ask
- What are the three types of coating? A Guide to Architectural, Industrial, and Special Purpose
- What is CVD diamond coating? Grow a Super-Hard, High-Performance Diamond Layer
- How are tools coated with diamond? Achieve Superior Hardness and Low Friction for Your Tools
- What is diamond coating film? A Thin Layer of Diamond for Extreme Performance
- What is the process of CVD diamond coating? Grow a Superior, Chemically-Bonded Diamond Layer



















