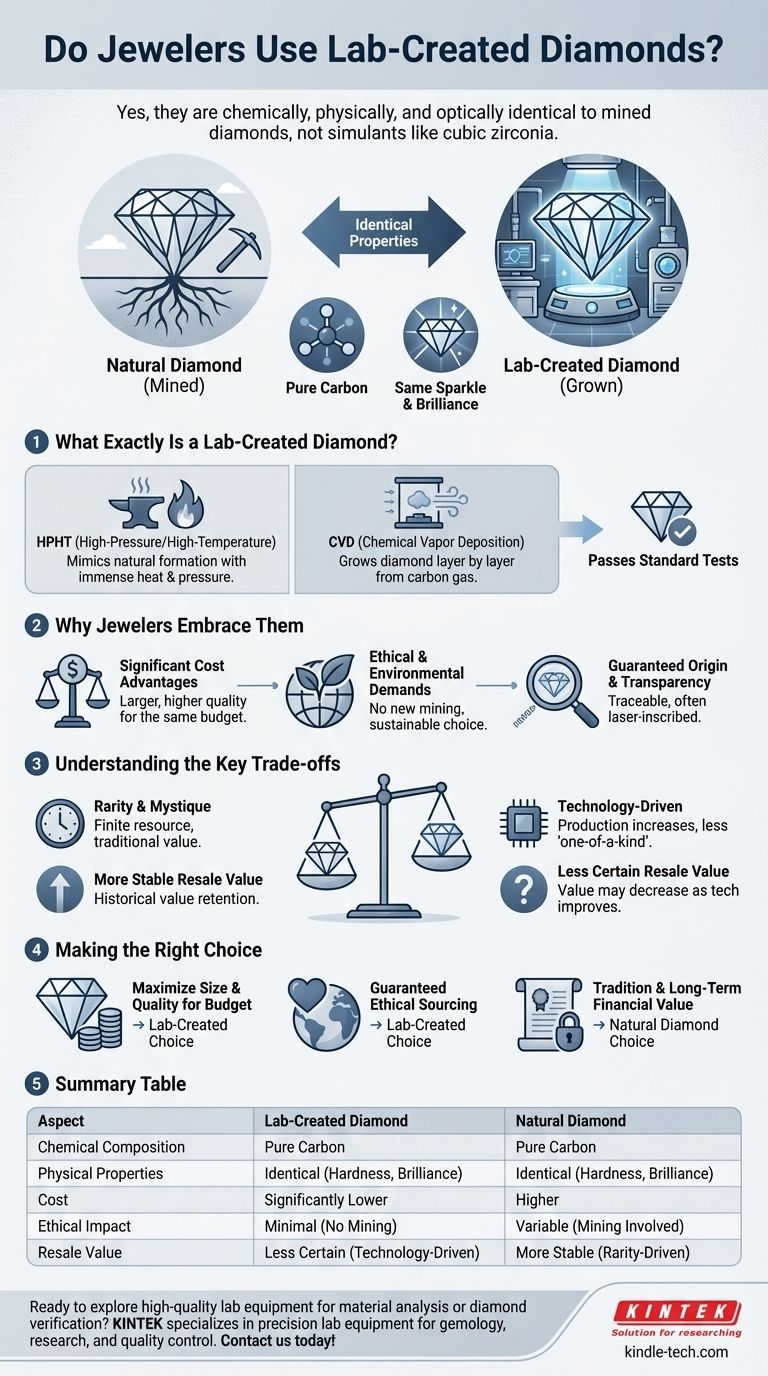
Yes, jewelers widely and increasingly use lab-created diamonds. They are not simulants like cubic zirconia; they are chemically, physically, and optically identical to mined diamonds. For this reason, they have become a mainstream and respected option offered by most jewelry retailers alongside their natural diamond collections.
The central decision is not between a "real" and "fake" diamond. It's a choice between two diamonds with different origins, each presenting a distinct set of trade-offs regarding cost, long-term value, and ethical considerations.

What Exactly Is a Lab-Created Diamond?
A lab-created diamond is a genuine diamond grown under controlled laboratory conditions. It possesses the same atomic structure and properties as a diamond that formed deep within the Earth.
Identical Chemical and Physical Properties
Lab diamonds are made of pure carbon, crystallized in an isometric cubic system. This means they exhibit the same signature sparkle, fire, and brilliance as their natural counterparts and are just as durable.
How They Pass Standard Diamond Tests
A lab diamond will pass any test designed to confirm a pure carbon diamond. Common diamond testers measure how efficiently heat and electricity move through the stone, and because lab diamonds are structurally identical to natural ones, they register positive results.
The Two Primary Creation Methods
Jewelers source diamonds created through two main processes. The High-Pressure/High-Temperature (HPHT) method mimics the natural formation process by subjecting pure carbon to immense heat and pressure.
The other method is Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD), where a diamond "seed" is placed in a chamber with carbon-rich gas. At high temperatures, the gas ionizes, allowing carbon particles to attach to the seed and crystallize, growing the diamond layer by layer.
Why Jewelers Embrace Lab-Created Diamonds
The jewelry industry has adopted lab-grown diamonds for several key reasons that directly benefit the consumer.
Significant Cost Advantages
For a comparable size and quality, lab-created diamonds cost significantly less than natural diamonds. This allows customers to purchase a larger or higher-quality stone for the same budget.
Meeting Ethical and Environmental Demands
Lab diamonds require no new mining, making them an appealing choice for consumers concerned about the environmental and ethical impact of traditional diamond extraction.
Guaranteed Origin and Transparency
Every lab diamond can be traced back to its origin. Reputable stones often have a microscopic laser inscription on their girdle that identifies them as lab-grown, ensuring full transparency for both the jeweler and the buyer.
Understanding the Key Trade-offs
While chemically identical, the different origins of lab-grown and natural diamonds create important distinctions you must consider.
The Perception of Rarity
Natural diamonds are seen as finite natural resources, and this rarity contributes to their mystique and value. Some buyers feel that a lab-grown diamond, being a product of technology, lacks the "one-of-a-kind" quality of a stone formed over billions of years.
Long-Term Resale Value
This is the most significant financial difference. While natural diamonds have a long history of holding and often increasing their value, the long-term value of lab-grown diamonds is less certain.
Lab diamonds hold their value far better than simulants, but as technology improves and production increases, their market price may decrease over time. Natural diamonds are generally considered a more stable store of value.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your decision should be based on which factors you prioritize most.
- If your primary focus is maximizing size and visual quality for your budget: A lab-created diamond is the unequivocal choice, offering more carat weight and clarity for your money.
- If your primary focus is on guaranteed ethical sourcing and environmental impact: A lab-created diamond provides a clear and transparent alternative to traditional mining.
- If your primary focus is on tradition and long-term financial value: A natural diamond remains the standard, with a historical track record of retaining its value.
Ultimately, understanding these distinctions empowers you to choose the diamond that aligns perfectly with your budget, your values, and your personal story.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Lab-Created Diamond | Natural Diamond |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Composition | Pure Carbon | Pure Carbon |
| Physical Properties | Identical (Hardness, Brilliance) | Identical (Hardness, Brilliance) |
| Cost | Significantly Lower | Higher |
| Ethical/Environmental Impact | Minimal (No Mining) | Variable (Mining Involved) |
| Resale Value | Less Certain (Technology-Driven) | More Stable (Rarity-Driven) |
Ready to explore high-quality lab equipment for material analysis or diamond verification? KINTEK specializes in precision lab equipment and consumables, serving laboratories that require reliable tools for gemology, research, and quality control. Whether you're testing diamond properties or advancing your research, our solutions ensure accuracy and efficiency. Contact us today to learn how KINTEK can support your laboratory's needs with trusted, performance-driven equipment!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- CVD Diamond Domes for Industrial and Scientific Applications
- Metallographic Specimen Mounting Machine for Laboratory Materials and Analysis
- Small Lab Rubber Calendering Machine
- Precision Machined Zirconia Ceramic Ball for Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics
- Custom PTFE Teflon Parts Manufacturer for Culture Dish and Evaporation Dish
People Also Ask
- What are the common sources of contamination during CVD diamond growth? Improve Purity and Quality Control
- How is something diamond coated? A Guide to CVD Growth vs. Plating Methods
- What is the newly discovered mechanism for diamond formation during CVD? Explore the Graphite-to-Diamond Transition
- How much does CVD diamond equipment cost? A Breakdown of Investment from Lab to Production
- What is the application of diamond coating? Solve Complex Wear, Heat, and Corrosion Problems









