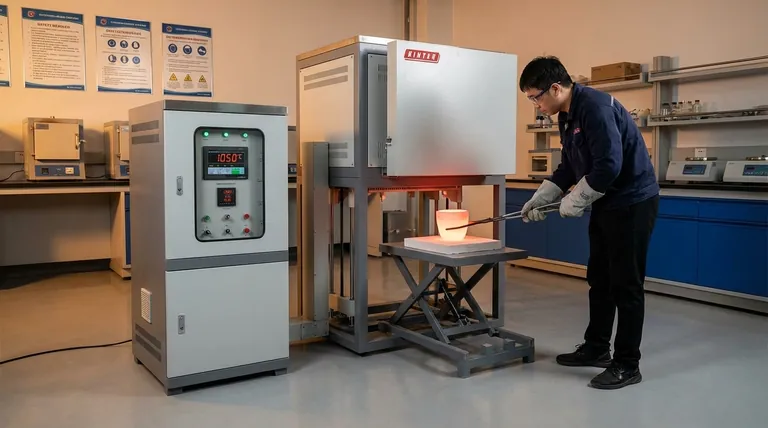
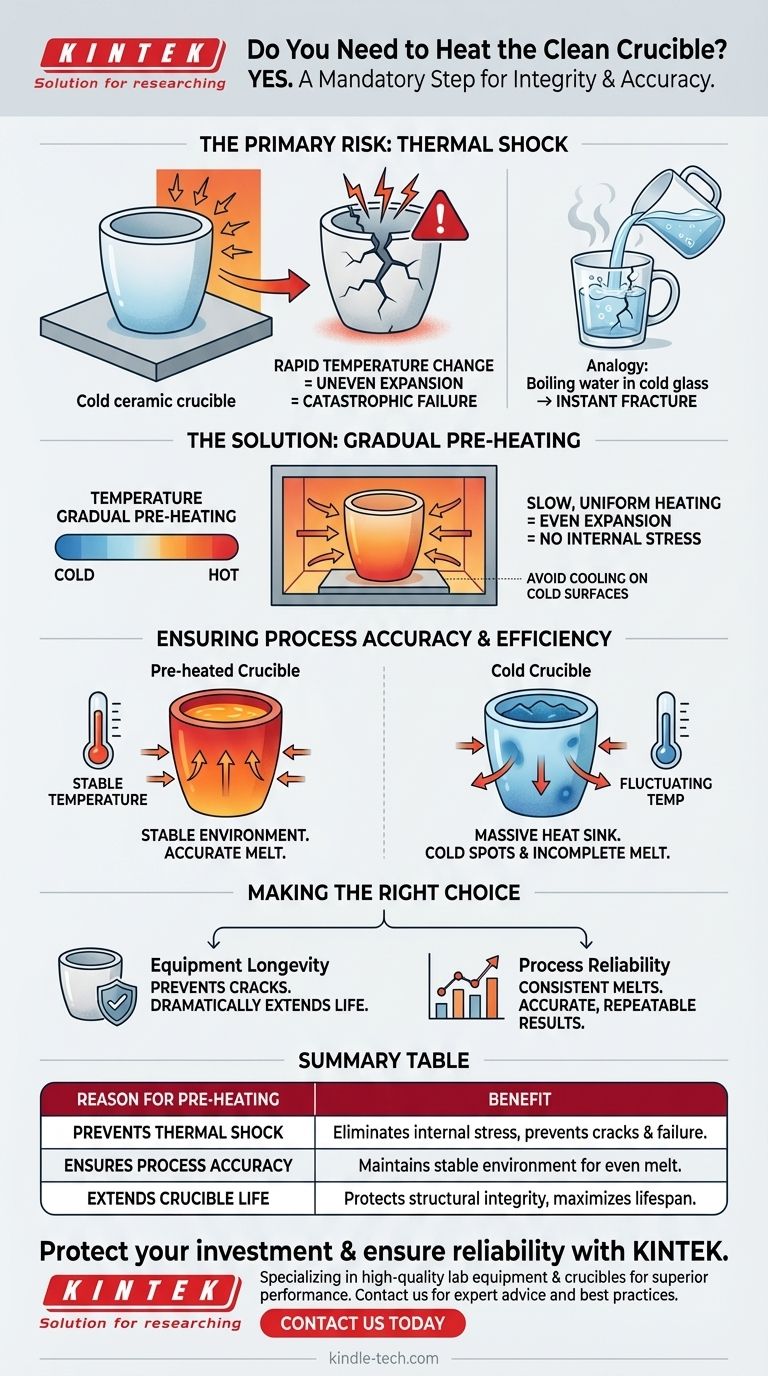
Yes, pre-heating a clean crucible before use is a critical and non-negotiable step. This procedure ensures the crucible reaches the necessary operating temperature before you introduce your material. Doing so is the primary method for preventing catastrophic failure from thermal shock and ensuring the accuracy of your high-temperature process.
The core principle is simple: gradual temperature changes protect your equipment and your results. Pre-heating a crucible prevents the extreme stress of rapid temperature change, which can crack the crucible and compromise the melting process.

The Primary Risk: Thermal Shock
Thermal shock is the single greatest threat to the structural integrity of a crucible. Understanding this phenomenon is key to proper handling.
What is Thermal Shock?
When a material is heated or cooled too quickly, different parts of it expand or contract at different rates. This uneven change creates immense internal stress that can easily exceed the material's strength, causing it to fracture.
Think of pouring boiling water into a cold, thick glass mug. The inside surface expands instantly while the outside remains cold, often causing the mug to crack. A crucible experiences this same stress, but at a far more extreme level.
How Pre-heating Prevents Catastrophic Failure
By slowly pre-heating the crucible, you allow the entire vessel to expand uniformly. This gradual process eliminates the internal stress that would be caused by dropping cold material into a hot furnace or introducing intense heat to a cold crucible.
This same principle applies in reverse. A heated crucible should never be placed on a cold surface, as the rapid cooling will cause it to contract unevenly and break.
Ensuring Process Accuracy and Efficiency
Beyond protecting the equipment, pre-heating is essential for maintaining the stability and reliability of your melting or heating process.
Maintaining a Stable Thermal Environment
When you add material to a properly pre-heated crucible, the system's temperature remains stable. The energy from the furnace goes directly into melting your material, not into slowly heating the crucible itself.
Achieving an Accurate and Complete Melt
Without pre-heating, the cold crucible acts as a massive heat sink. This can create cold spots, preventing your material from melting evenly or reaching the required temperature accurately, which compromises the quality of your results.
Making the Right Choice for Your Process
Adopting this practice is not about preference; it's about adhering to a fundamental principle of material science and process control.
- If your primary focus is equipment longevity: Pre-heating is the single most important step you can take to prevent cracks and dramatically extend the life of your crucibles.
- If your primary focus is process reliability: Pre-heating ensures your material melts consistently and completely, leading to accurate and repeatable results every time.
Ultimately, treating pre-heating as a mandatory step protects both your investment and the integrity of your work.
Summary Table:
| Reason for Pre-heating | Benefit |
|---|---|
| Prevents Thermal Shock | Eliminates internal stress from rapid temperature change, preventing cracks and catastrophic failure. |
| Ensures Process Accuracy | Maintains a stable thermal environment for an even, complete melt and reliable results. |
| Extends Crucible Life | Gradual heating protects the crucible's structural integrity, maximizing its lifespan. |
Protect your investment and ensure process reliability with the right crucible handling. KINTEK specializes in high-quality lab equipment and consumables, including crucibles designed for superior thermal performance. Our experts can help you select the right crucible for your application and provide best practices for its use. Contact us today to discuss your laboratory needs and enhance your high-temperature processes!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- 1800℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What is the power requirement for a muffle furnace? Ensure Safe and Efficient Operation
- What is the role of muffle furnace in fluid mechanics? A Key Tool for Material Preparation
- What is the working principle of a muffle furnace? Achieve Precise, Contamination-Free Heating
- What heat can a muffle furnace produce? Achieve Precise High Temperatures Up to 1800°C
- What is a muffle furnace used to estimate? A Key Tool for Precise Ash Determination



















