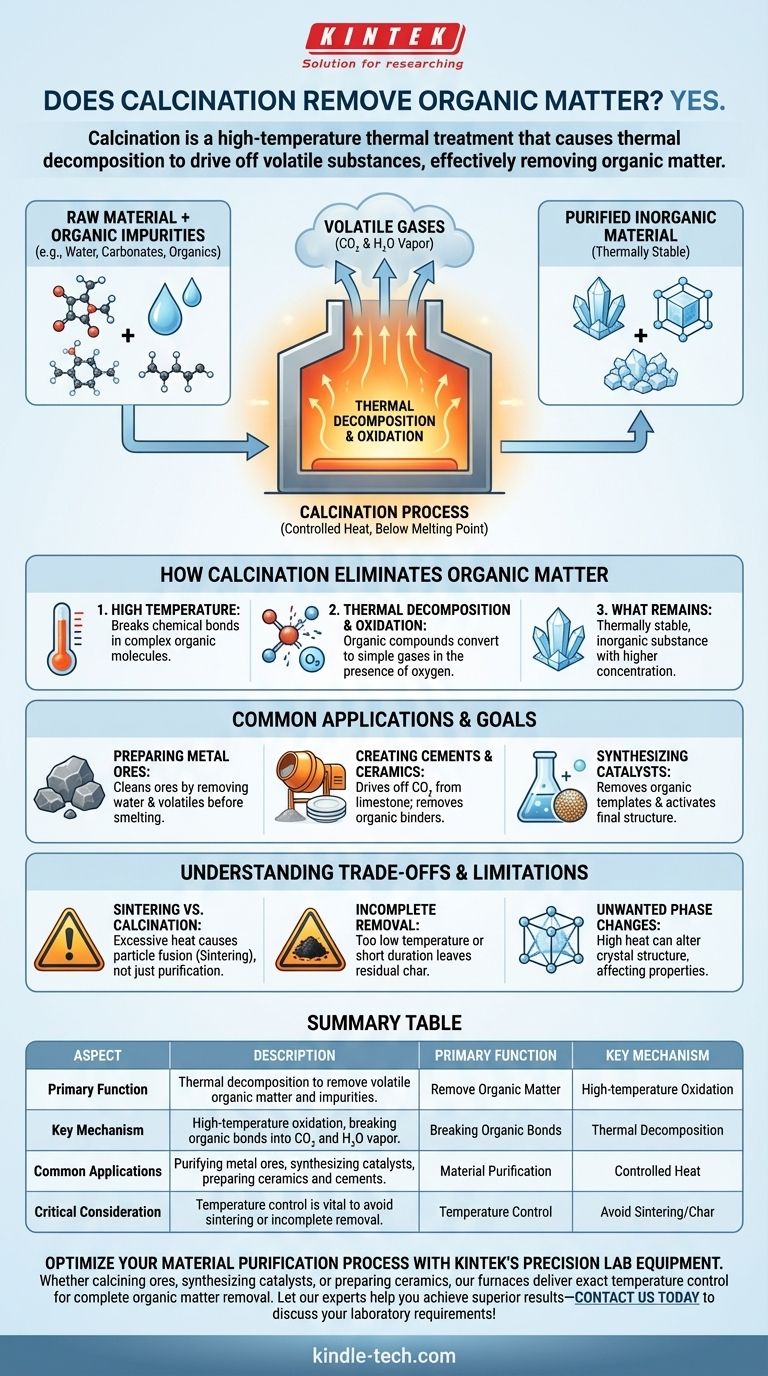
Yes, it does. Calcination is a high-temperature thermal treatment process specifically designed to cause thermal decomposition and drive off volatile substances from a solid. One of its primary and most effective applications is the complete removal of organic matter, along with other impurities like water or carbonates.
At its core, calcination is a purification and transformation tool. It uses controlled heat—below the material's melting point—to break down and eliminate volatile impurities like organic compounds, fundamentally altering the material's chemical composition and physical structure.

How Calcination Eliminates Organic Matter
Calcination is not merely heating; it is a precise process that leverages heat to induce specific chemical changes. The removal of organic matter is a direct result of this controlled thermal decomposition.
The Role of High Temperature
The energy supplied by high temperatures is the driving force behind the process. This thermal energy is sufficient to break the chemical bonds within complex organic molecules.
Thermal Decomposition and Oxidation
Once these bonds are broken, the organic compounds decompose into simpler, volatile substances. In the presence of oxygen, this becomes an oxidation reaction, converting the carbon and hydrogen in the organic matter primarily into carbon dioxide (CO2) and water (H2O) vapor, which then escape as gases.
What Remains After the Process
The final product is the thermally stable, inorganic material you intended to purify. By driving off the organic impurities, calcination leaves behind a substance with a higher concentration of the desired compound.
Common Applications and Goals
The ability to remove organic matter and other volatiles makes calcination a critical step in many industrial and laboratory processes.
Preparing Metal Ores
As noted in metallurgy, calcination is a foundational step. It cleans ores by removing water, carbonaceous materials, and other volatile impurities before the smelting process begins.
Creating Cements and Ceramics
In cement production, calcination of limestone (calcium carbonate) drives off carbon dioxide to produce lime (calcium oxide). In ceramics, it removes organic binders and plasticizers used during the shaping process, preparing the material for final firing (sintering).
Synthesizing Catalysts
Catalyst preparation often involves calcining a precursor material. This step removes unwanted organic templates or salts and activates the final catalyst structure.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
While powerful, calcination is a process that requires precise control. Misunderstanding its parameters can lead to undesirable outcomes.
Sintering vs. Calcination
The most common pitfall is applying excessive heat. If the temperature gets too close to the material's melting point, particles can begin to fuse together. This is a separate process called sintering, which aims to increase density and strength, not just purify. Confusing the two can ruin your intended outcome.
Incomplete Removal
If the temperature is too low or the heating duration is too short, the organic matter may not be fully removed. This can leave behind residual carbon or "char," which can be detrimental to the final product's properties.
Unwanted Phase Changes
The high temperatures involved can also alter the crystal structure of your material. While sometimes this is the goal, an unintended phase transformation can negatively impact the material's desired chemical or physical properties.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To use calcination effectively, you must align the process parameters with your specific objective.
- If your primary focus is purifying a mineral ore: Calcination is a standard and highly effective step to remove water and carbonaceous impurities before further processing.
- If your primary focus is preparing a ceramic or catalyst: You must carefully control the temperature ramp-up and final temperature to fully remove organic binders without causing premature sintering.
- If your primary focus is changing the chemical state (e.g., carbonate to oxide): The key is holding the material at a specific decomposition temperature long enough to ensure the chemical reaction goes to completion.
Mastering calcination means viewing it not as simple heating, but as a precise instrument for chemical and physical transformation.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Description |
|---|---|
| Primary Function | Thermal decomposition to remove volatile organic matter and impurities. |
| Key Mechanism | High-temperature oxidation, breaking organic bonds into CO₂ and H₂O vapor. |
| Common Applications | Purifying metal ores, synthesizing catalysts, preparing ceramics and cements. |
| Critical Consideration | Temperature control is vital to avoid sintering or incomplete removal. |
Optimize your material purification process with KINTEK's precision lab equipment. Whether you're calcining ores, synthesizing catalysts, or preparing ceramics, our furnaces deliver the exact temperature control and uniformity you need for complete organic matter removal. Let our experts help you achieve superior results—contact us today to discuss your specific laboratory requirements!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
People Also Ask
- What is commonly used during a dry ashing experiment? Essential Equipment for Accurate Ash Analysis
- What are 2 advantages of dry ashing? Achieve High-Throughput Sample Analysis with Safety
- What is the process of dry ashing of sample treatment? A Guide to High-Temperature Mineral Analysis
- How do you choose calcination temperature? A Guide to Optimizing Material Properties
- What are the advantages and disadvantages to using a dry ashing technique? A Guide to High-Temperature Sample Prep



















