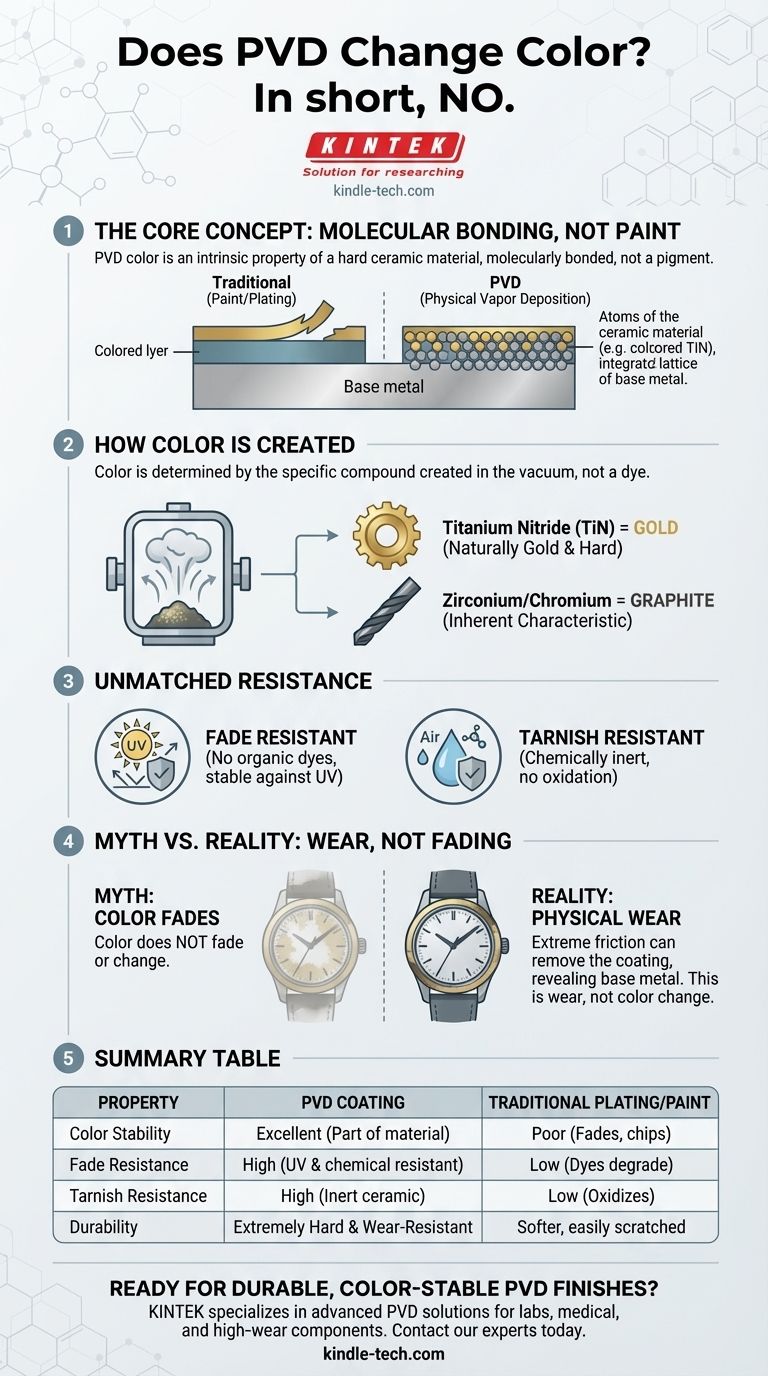
In short, no. Under normal circumstances, a PVD coating does not change color, fade, or tarnish. The color you see is an intrinsic property of an extremely hard ceramic material that is molecularly bonded to the base metal, making it exceptionally stable over time.
The core reason people worry about colored metal is their experience with paints that fade or plating that wears off. PVD is fundamentally different. Its color comes from the very structure of the durable, wear-resistant layer itself, not from pigments or dyes that can degrade.

What Exactly is a PVD Coating?
To understand why the color is so stable, you must understand that PVD is not a liquid coating. It is a highly technical vacuum deposition process that creates a thin film with superior properties.
It's Not Paint or Plating
Traditional methods like painting apply a layer of pigment on top of a surface. Electroplating deposits a thin layer of metal, like gold or chrome, which can wear away or flake off.
PVD (Physical Vapor Deposition) is a process where a solid material is vaporized in a vacuum and deposited onto the surface of a part. This creates a metal-ceramic layer that is molecularly bonded to the substrate.
How the Color is Created
The color of a PVD finish is not a dye. It is determined by the specific compound created during the process.
For example, a "gold" PVD finish is often Titanium Nitride, a ceramic that is naturally gold in color and incredibly hard. A "graphite" finish might be created using Zirconium or Chromium. The color is an inherent characteristic of this new, ultra-hard surface.
How PVD Color Holds Up Over Time
Because the color is integral to the ceramic layer, it resists the most common causes of discoloration that affect other finishes.
Unmatched Resistance to Fading
Since there are no organic dyes or pigments, a PVD coating is highly resistant to fading from UV light or sun exposure. Its color will remain consistent for years.
Superior Resistance to Tarnishing
The ceramic layer created by the PVD process is chemically inert and non-reactive. This means it will not oxidize or tarnish when exposed to air, moisture, or common chemicals, which is why it's a favored finish for watches, jewelry, and bathroom fixtures.
Understanding the Trade-offs: When PVD Can "Change"
While PVD is incredibly durable, it is not indestructible. It's critical to distinguish between color fading and physical wear.
The Myth of Fading vs. The Reality of Wear
A PVD coating will not fade, but with extreme and persistent friction or abrasion, the coating itself can eventually be worn away. If this happens, you are not seeing a color change—you are seeing the base metal underneath as the coating has been physically removed in that area.
This level of wear requires significant abuse, far beyond what would be seen in typical daily use for products like watches or faucets.
The Need for Special Removal
The durability of a PVD coating is proven by the fact that it cannot be removed easily.
As the references note, specialized industrial "de-coating" processes are required to strip the PVD layer without damaging the underlying product. This underscores its permanence under any normal condition.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
PVD is a premium finish chosen for its exceptional durability and color stability. Deciding if it's right for you depends entirely on your priority.
- If your primary focus is long-term color stability for a daily-use item (like a watch, ring, or faucet): PVD is one of the most reliable and colorfast finishing options you can choose.
- If your primary focus is protecting a component from extreme industrial abrasion (like a drill bit): The PVD coating provides a sacrificial layer of hardness that will eventually wear away, but its purpose is to dramatically extend the tool's life.
By choosing a PVD-coated product, you are investing in a finish engineered for superior durability and lasting color.
Summary Table:
| Property | PVD Coating | Traditional Plating/Paint |
|---|---|---|
| Color Stability | Excellent (color is part of the material) | Poor (can fade, chip, or wear) |
| Fade Resistance | High (resistant to UV light and chemicals) | Low (dyes and pigments can degrade) |
| Tarnish Resistance | High (chemically inert ceramic layer) | Low (can oxidize and tarnish) |
| Durability | Extremely hard and wear-resistant | Softer, can be easily scratched or worn away |
Ready to integrate durable, color-stable PVD finishes into your products?
At KINTEK, we specialize in advanced PVD coating solutions for laboratory equipment, medical devices, and high-wear components. Our expertise ensures your products benefit from a finish that combines lasting beauty with superior protection.
Contact our experts today to discuss how PVD coating can enhance your product's performance and longevity.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom CVD Diamond Coating for Lab Applications
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition RF PECVD
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine for Lamination and Heating
- Vacuum Dental Porcelain Sintering Furnace
- Molybdenum Disilicide (MoSi2) Thermal Elements Electric Furnace Heating Element
People Also Ask
- What is diamond coating film? A Thin Layer of Diamond for Extreme Performance
- What are diamond coated films? Enhance Materials with Super-Hard, Transparent Layers
- Is diamond coating permanent? The Truth About Its Long-Lasting Durability
- What is the process of CVD diamond coating? Grow a Superior, Chemically-Bonded Diamond Layer
- How long does diamond coating last? Maximize Lifespan with the Right Coating for Your Application



















