In practice, pyrolysis is a powerful tool for reducing overall greenhouse gas emissions. Rather than contributing to the problem, it transforms materials that would otherwise release harmful gases—like landfill waste or atmospheric methane—into stable carbon and valuable, lower-emission fuels. The process itself is not a direct source of emissions when operated correctly.
The climate benefit of pyrolysis comes from what it prevents. It should be viewed as a GHG mitigation strategy that diverts high-emission pathways (like decomposition or fossil fuel use) toward a more controlled, value-added outcome.

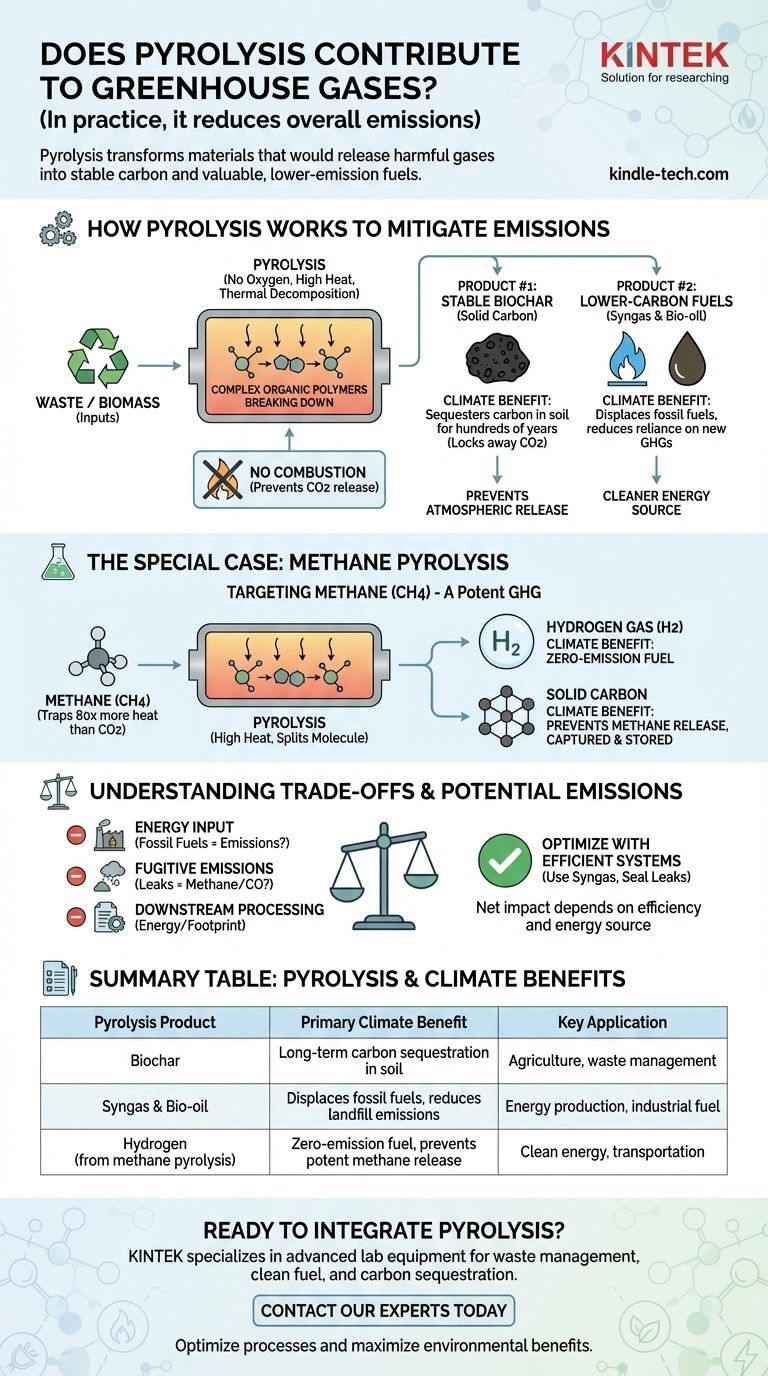
How Pyrolysis Works to Mitigate Emissions
Pyrolysis is a process of thermal decomposition, meaning it uses high heat to break down materials. The critical factor is that this occurs in an environment with little to no oxygen.
The Core Mechanism: Preventing Combustion
By heating organic materials without oxygen, pyrolysis avoids combustion (burning).
Combustion reacts carbon with oxygen to create and release carbon dioxide (CO2). Pyrolysis, instead, breaks complex organic polymers into simpler, more valuable components.
Product #1: Stable Biochar for Carbon Sequestration
A primary output of pyrolyzing biomass (like wood chips or agricultural waste) is biochar, a stable, solid form of carbon similar to charcoal.
When biomass decomposes naturally, its carbon is released back into the atmosphere as CO2 or methane. By converting it to biochar and adding it to soil, that carbon is sequestered, or locked away, for hundreds or even thousands of years.
Product #2: Lower-Carbon Fuels
Pyrolysis also produces syngas (a mix of hydrogen and carbon monoxide) and bio-oil.
These products can be refined and used as fuel, displacing the need for traditional fossil fuels. This provides a dual benefit: it avoids the emissions from landfill decomposition and reduces our reliance on a major source of new greenhouse gases.
The Special Case: Methane Pyrolysis
Beyond managing waste, pyrolysis can be used to directly target and break down existing greenhouse gases, most notably methane (CH4).
Targeting a Potent Greenhouse Gas
Methane is a far more potent greenhouse gas than CO2, trapping over 80 times more heat in its first 20 years in the atmosphere. It accounts for a significant portion of global emissions.
"Splitting" Methane into Hydrogen and Solid Carbon
Methane pyrolysis uses high temperatures to split the CH4 molecule into two valuable, clean outputs: hydrogen gas (H2) and solid carbon.
This process creates a zero-emission fuel (hydrogen) while simultaneously preventing methane from entering the atmosphere. The captured solid carbon can then be stored or used in industrial applications.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Potential Emissions
While the core process is beneficial, a full lifecycle analysis reveals areas where emissions can occur. A well-designed system is engineered to minimize these factors.
The Energy Input Requirement
Pyrolysis is an energy-intensive process that requires high temperatures. The source of this energy is critical.
If the heat is generated by burning fossil fuels, those emissions must be counted against the overall benefit of the system. The most sustainable pyrolysis operations use a portion of the syngas they produce to power themselves, creating a more circular system.
Fugitive Emissions
A pyrolysis system must be properly sealed. Any leaks can release fugitive emissions, which could include methane or carbon monoxide from the syngas. Modern engineering focuses heavily on preventing these leaks to ensure both safety and environmental integrity.
Downstream Processing
The bio-oil and syngas created during pyrolysis often require upgrading or cleaning before they can be used as high-grade fuels. These downstream processes can consume additional energy and have their own environmental footprint.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To determine if a pyrolysis application is truly beneficial, you must analyze its entire lifecycle in the context of a specific goal.
- If your primary focus is waste management: Pyrolysis is highly effective at diverting organic waste from landfills, which directly prevents the release of methane.
- If your primary focus is producing clean fuel: Methane pyrolysis offers a direct path to creating "turquoise" hydrogen fuel while sequestering carbon, but the energy source for the reactor is a key variable.
- If your primary focus is carbon sequestration: The production of stable biochar from biomass is one of pyrolysis's most significant and durable climate benefits, effectively locking carbon out of the atmosphere.
Ultimately, the net climate impact of a pyrolysis system hinges on its efficiency, the source of its energy, and what specific emissions it is designed to prevent.
Summary Table:
| Pyrolysis Product | Primary Climate Benefit | Key Application |
|---|---|---|
| Biochar | Long-term carbon sequestration in soil | Agriculture, waste management |
| Syngas & Bio-oil | Displaces fossil fuels, reduces landfill emissions | Energy production, industrial fuel |
| Hydrogen (from methane pyrolysis) | Zero-emission fuel, prevents potent methane release | Clean energy, transportation |
Ready to integrate pyrolysis into your sustainability strategy? KINTEK specializes in advanced lab equipment and consumables for pyrolysis research and development. Whether you're focused on waste management, clean fuel production, or carbon sequestration, our solutions help you optimize processes and maximize environmental benefits. Contact our experts today to explore how our equipment can support your net-zero goals.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace for Activated Carbon Regeneration
- Rotary Tube Furnace Split Multi Heating Zone Rotating Tube Furnace
- Laboratory Vacuum Tilt Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Laboratory Rapid Thermal Processing (RTP) Quartz Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- Why are high temperatures required when sintering stainless steels? Unlock Pure, High-Density Results
- What is the difference between pyrolysis combustion and gasification? A Guide to Thermal Conversion Technologies
- What is the range of pyrolysis? Master Temperature Control for Optimal Bio-Product Yields
- What are the main types of biomass conversion processes? Unlock the Best Pathway for Your Energy Needs
- At what temperature is conventional pyrolysis done? Unlock the Right Temperature for Your Desired Product



















