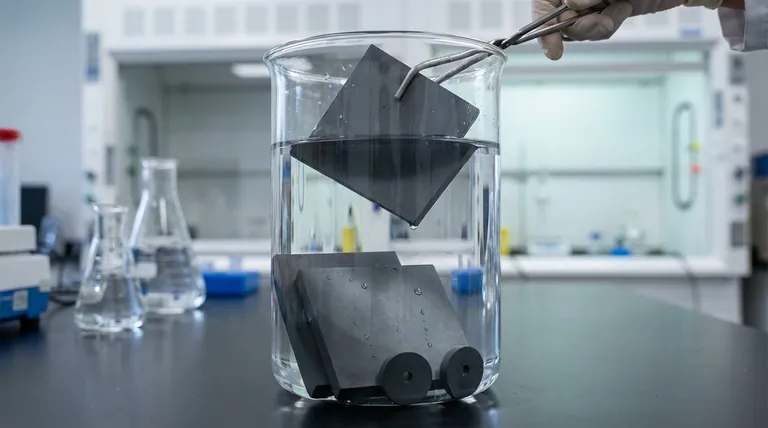
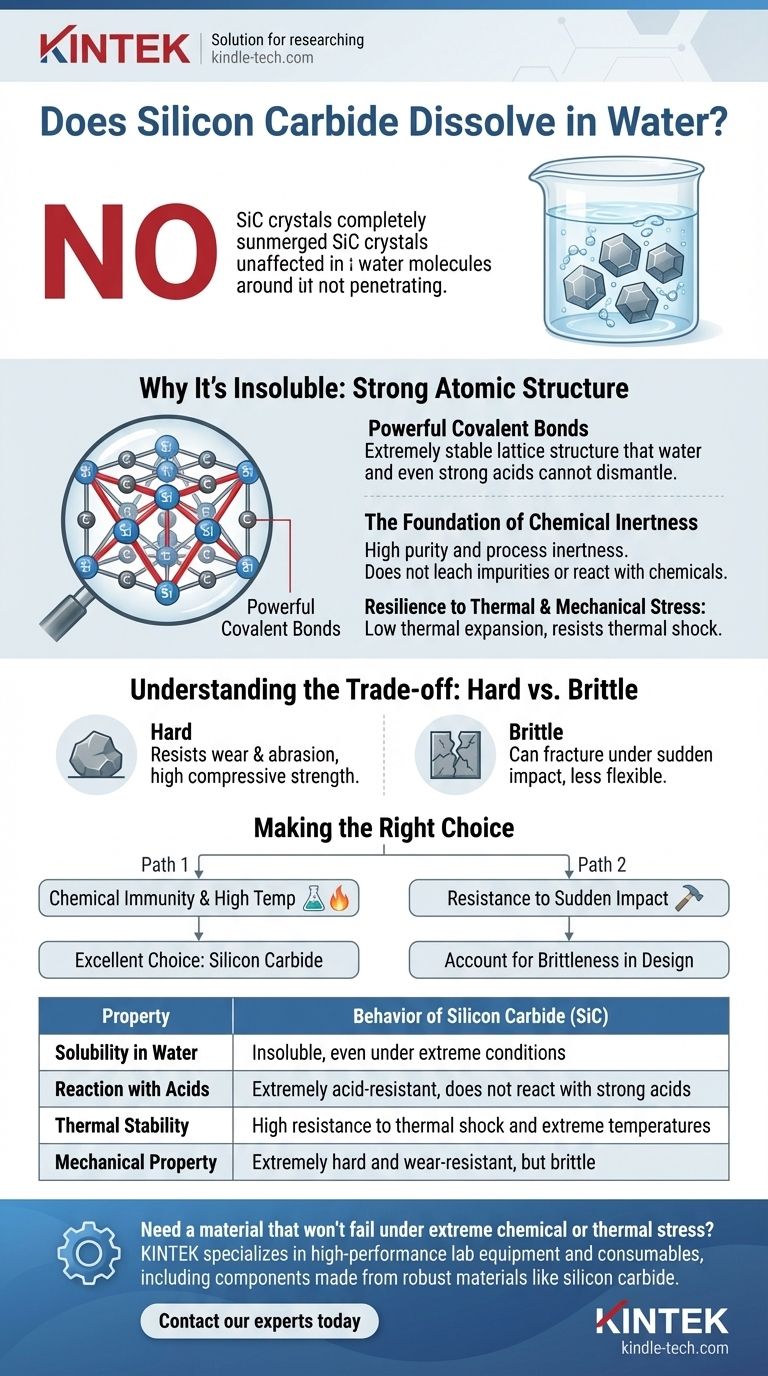
No, silicon carbide (SiC) does not dissolve in water. It is an exceptionally stable and chemically inert material, meaning it does not react with or break down in water, even under extreme conditions. This remarkable chemical resistance is a cornerstone of why it is valued in so many advanced industrial and high-tech applications.
The core reason for silicon carbide's insolubility is its powerful atomic structure. The extremely strong covalent bonds between silicon and carbon atoms create a highly stable lattice that water and even strong acids cannot easily dismantle.

The Foundation of SiC's Chemical Inertness
The inability of silicon carbide to dissolve in water is not a trivial characteristic; it is a direct result of its fundamental atomic makeup. This inherent stability makes it a material of choice for the most demanding environments.
An Exceptionally Strong Atomic Bond
Silicon carbide is a ceramic material defined by a crystal lattice of silicon and carbon atoms. These atoms are held together by powerful covalent bonds.
This bonding creates a rigid and tightly interlocked structure. Breaking these bonds requires a significant amount of energy, far more than water molecules can provide.
Why Water and Acids Fail to Dissolve It
Water is an excellent solvent for ionic compounds (like table salt) because its polar molecules can pull the ions apart. However, it is ineffective against materials with strong, non-polar covalent networks.
The provided technical data reinforces this, noting that SiC is "extremely acid-resistant and do not react with strong acids." If it can withstand potent acids, neutral water poses no threat to its structural integrity.
Key Properties Demonstrating SiC's Stability
Different forms of silicon carbide all exhibit this fundamental inertness, which is why they are trusted in critical components across various industries.
High Purity and Process Inertness
Advanced forms like Chemical Vapor Deposited (CVD) silicon carbide are valued for being "theoretically dense, intrinsically pure" and having a "high degree of chemical and process inertness."
This means the material does not leach impurities or react with chemicals used in sensitive processes, such as semiconductor manufacturing.
Resilience to Thermal and Mechanical Stress
Silicon carbide's stability extends beyond chemical resistance. It has a small expansion coefficient and good resistance to thermal shock.
This means it maintains its form and integrity even when subjected to rapid temperature changes, a condition where lesser materials would crack or degrade.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Hardness vs. Brittleness
While chemically robust, silicon carbide's properties present a key engineering trade-off. Understanding this is critical for its proper application.
Hard but Brittle
The same strong covalent bonds that provide chemical resistance also make SiC extremely hard. This hardness allows it to resist wear and abrasion effectively.
However, this rigidity also means it is brittle. While it can withstand immense compressive force, it can fracture under a sharp, sudden impact rather than bending or deforming.
Porosity in Certain Grades
Some grades, like recrystallized silicon carbide, are noted to have "high porosity." While the SiC material itself will not dissolve, this porosity means fluids can potentially seep into the structure.
Engineers must consider this factor in applications where fluid penetration, rather than chemical reaction, could be a concern.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Your decision to use silicon carbide should be based on a clear understanding of its exceptional strengths and its primary limitation.
- If your primary focus is chemical immunity and high-temperature performance: Silicon carbide is an outstanding choice, offering complete stability in water, acids, and extreme heat.
- If your primary focus is resistance to sudden impact or fracture: You must account for SiC's inherent brittleness in your design, potentially by reinforcing it or using it in applications where compressive strength is the dominant need.
Ultimately, you can select silicon carbide with full confidence in its unwavering chemical stability.
Summary Table:
| Property | Behavior of Silicon Carbide (SiC) |
|---|---|
| Solubility in Water | Insoluble, even under extreme conditions |
| Reaction with Acids | Extremely acid-resistant, does not react with strong acids |
| Thermal Stability | High resistance to thermal shock and extreme temperatures |
| Mechanical Property | Extremely hard and wear-resistant, but brittle |
Need a material that won't fail under extreme chemical or thermal stress?
KINTEK specializes in high-performance lab equipment and consumables, including components made from robust materials like silicon carbide. Whether you're in semiconductor manufacturing, metallurgy, or advanced materials research, our products are designed to provide the chemical inertness and thermal stability your laboratory demands.
Contact our experts today to discuss how our solutions can enhance the reliability and efficiency of your processes.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Silicon Carbide (SIC) Ceramic Sheet Wear-Resistant Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics
- Silicon Carbide SiC Thermal Heating Elements for Electric Furnace
- Precision Machined Silicon Nitride (SiN) Ceramic Sheet for Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics
- Conductive Boron Nitride BN Ceramics Composite for Advanced Applications
- High Purity Zinc Foil for Battery Lab Applications
People Also Ask
- What is the temperature resistance of silicon carbide? Withstands Extreme Heat Up to 1500°C
- Is silicon carbide heat resistant? Unlock Superior Performance in Extreme Temperatures
- What are the properties of SiC? Unlock High-Temperature, High-Frequency Performance
- What is the strongest ceramics? Silicon Carbide Leads in Hardness & Thermal Strength
- Which is harder silicon carbide or tungsten carbide? Discover the Key to Material Selection



















