To be precise, XRF analysis depth is not a single value. It is a highly variable range, typically from a few micrometers (µm) to several millimeters (mm), that is fundamentally determined by the density of the sample being analyzed and the energy of the X-rays involved. For dense materials like metals, the depth is extremely shallow, while for low-density materials like polymers, it can be significantly deeper.
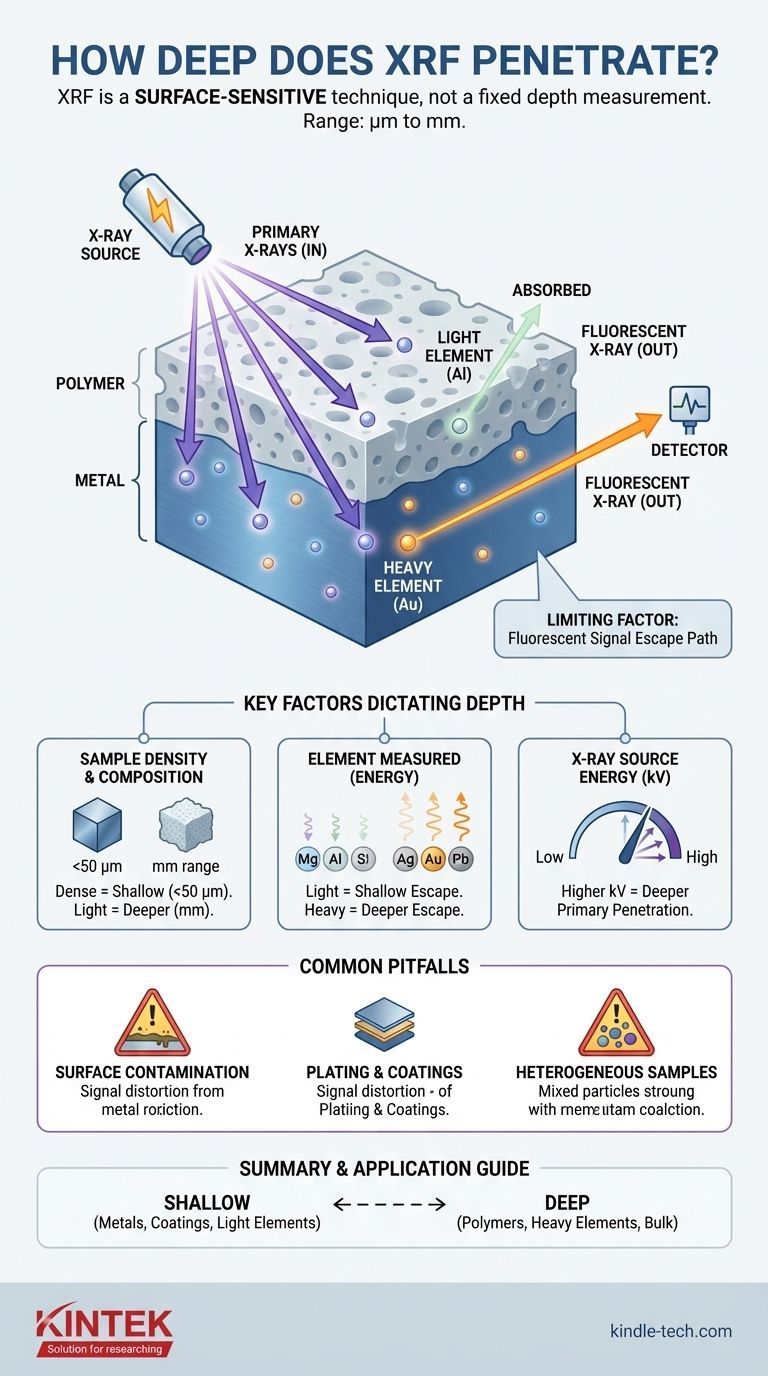
The most critical concept to understand is that X-Ray Fluorescence (XRF) is fundamentally a surface-sensitive analytical technique. The penetration depth is not a fixed setting on the instrument; it is the result of a physical interaction between the X-ray beam and the specific material you are measuring.
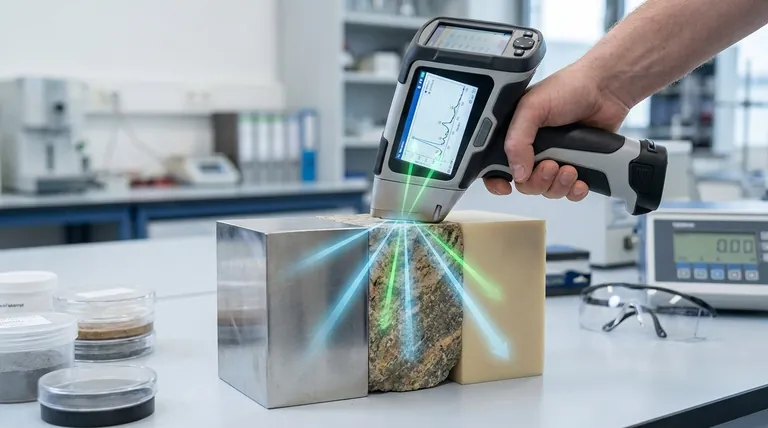

The Two-Part Journey of an X-ray
To grasp why analysis depth varies so much, you must understand that the process has two distinct stages: the X-ray going in and the fluorescent signal coming out. The "analysis depth" is limited by whichever of these two paths is shorter.
Primary X-ray Penetration (The "In" Path)
The process begins when the instrument fires primary X-rays into your sample. How deep these initial X-rays travel depends on their energy and the sample's composition.
Higher-energy X-rays penetrate deeper, while denser samples absorb X-rays more readily, leading to shallower penetration.
Fluorescent X-ray Escape (The "Out" Path)
Once a primary X-ray strikes an atom deep within the sample, that atom emits its own secondary, characteristic X-ray. This is the "fluorescent" signal the detector measures.
However, this fluorescent X-ray must travel back out of the sample to be detected. This escape path is often the true limiting factor for analysis depth.
Defining "True" Analysis Depth
The true analysis depth is the maximum depth from which a fluorescent X-ray can successfully escape the sample and reach the detector.
If the atom is too deep, its fluorescent signal will be absorbed by the surrounding material before it can ever escape. This is especially true for lighter elements.
Key Factors That Dictate Penetration Depth
Three variables work together to determine the final analysis depth for any given measurement. Understanding them gives you control over the interpretation of your results.
Sample Matrix Density and Composition
This is the single most important factor. A dense, high-atomic-number (high-Z) matrix absorbs X-rays much more effectively than a light, low-Z matrix.
Think of it like shining a light through water. It's easy to see through clear water (low density) but impossible to see through thick mud (high density).
- Metals & Alloys: Extremely shallow penetration, typically <50 micrometers.
- Polymers & Plastics: Deeper penetration, often in the range of several millimeters.
- Soils & Minerals: Intermediate penetration, varying based on composition.
The Element Being Measured
The energy of the fluorescent X-ray is unique to each element. Lighter elements (e.g., Magnesium, Aluminum, Silicon) emit very low-energy fluorescent X-rays.
These low-energy signals are easily absorbed by the surrounding sample matrix and can only escape from very close to the surface (a few micrometers). Heavier elements (e.g., Gold, Lead, Silver) emit high-energy X-rays that can escape from much deeper within the sample.
X-ray Source Energy (kV)
The voltage setting on the X-ray tube (measured in kilovolts, or kV) determines the maximum energy of the primary X-rays being sent into the sample.
A higher kV setting generates more powerful X-rays that penetrate deeper, allowing you to excite atoms further from the surface. However, this does not change the fundamental limitation of the fluorescent X-ray's ability to escape.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Common Pitfalls
Treating XRF as a bulk analysis technique without considering its surface sensitivity is the most common source of significant error.
The Surface Contamination Risk
Because the analysis depth is so shallow, especially in metals, any contamination on the surface will heavily influence the results.
Dirt, oil, corrosion, or an oxidation layer can be the primary material the instrument analyzes, leading to a completely inaccurate reading of the underlying bulk material.
The Plating and Coating Fallacy
XRF is excellent for measuring the thickness of coatings and platings precisely because it is a surface technique.
However, this also means that if your goal is to identify a substrate material, even a very thin coating can completely block the signal from the material underneath. The instrument will report the composition of the plating, not the base metal.
Misinterpreting Heterogeneous Samples
If a sample is not uniform in composition (e.g., a mineral ore, a mixed plastic flake), the XRF result is only an average of the small spot being measured. This result is heavily weighted toward the composition of the surface layer and may not be representative of the object as a whole.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Use your understanding of XRF's surface sensitivity to guide your measurement strategy and interpret your data accurately.
- If your primary focus is analyzing coatings or platings: XRF is an ideal tool, as its shallow analysis depth is a distinct advantage for this purpose.
- If your primary focus is the bulk composition of a dense metal: You must ensure the surface is clean, prepared, and truly representative of the material you wish to measure.
- If your primary focus is analyzing low-density materials like polymers or soil: You can achieve deeper analysis, but remember that the results for lighter elements (Mg, Al, Si) will always come from the near-surface region.
- If your primary focus is a sample that is not uniform: Consider preparing the sample (e.g., by grinding and pressing it into a pellet) or taking multiple measurements across the surface to get a more representative average.
Ultimately, understanding that XRF provides a surface-weighted analysis is the key to using this powerful technology effectively and with confidence.
Summary Table:
| Factor | Effect on Penetration Depth | Typical Depth Range |
|---|---|---|
| Sample Density | Higher density = shallower depth | Metals: <50 µm |
| Element Energy | Lighter elements = shallower depth | Light Elements (Mg, Al): A few µm |
| X-ray Source (kV) | Higher kV = deeper primary penetration | Varies with application |
Need precise elemental analysis for your materials? Understanding the exact penetration depth of XRF is crucial for accurate results. KINTEK specializes in high-performance lab equipment, including XRF analyzers, to meet your specific laboratory needs—from coating thickness measurement to bulk composition analysis. Let our experts help you choose the right tool for confident, surface-sensitive measurements. Contact us today to discuss your application!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Test Sieves and Sieving Machines
- Custom PTFE Teflon Parts Manufacturer for PTFE Tweezers
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Pulse Vacuum Lifting Sterilizer
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Vertical Pressure Steam Sterilizer for Liquid Crystal Display Automatic Type
- Benchtop Laboratory Freeze Dryer for Lab Use
People Also Ask
- What are the factors affecting sieving performance and efficiency? Optimize Your Particle Separation Process
- What is the function of sieving equipment in CuAlMn alloys? Master Pore Size Precision
- What are the specifications for test sieves? A Guide to ASTM & ISO Standards for Accurate Particle Analysis
- How is a vibratory sieve shaker used in the particle size analysis of mechanically alloyed powders? Expert Guide
- What is the primary function of a mechanical sieve shaker for biomass analysis? Optimize Particle Size Distribution



















