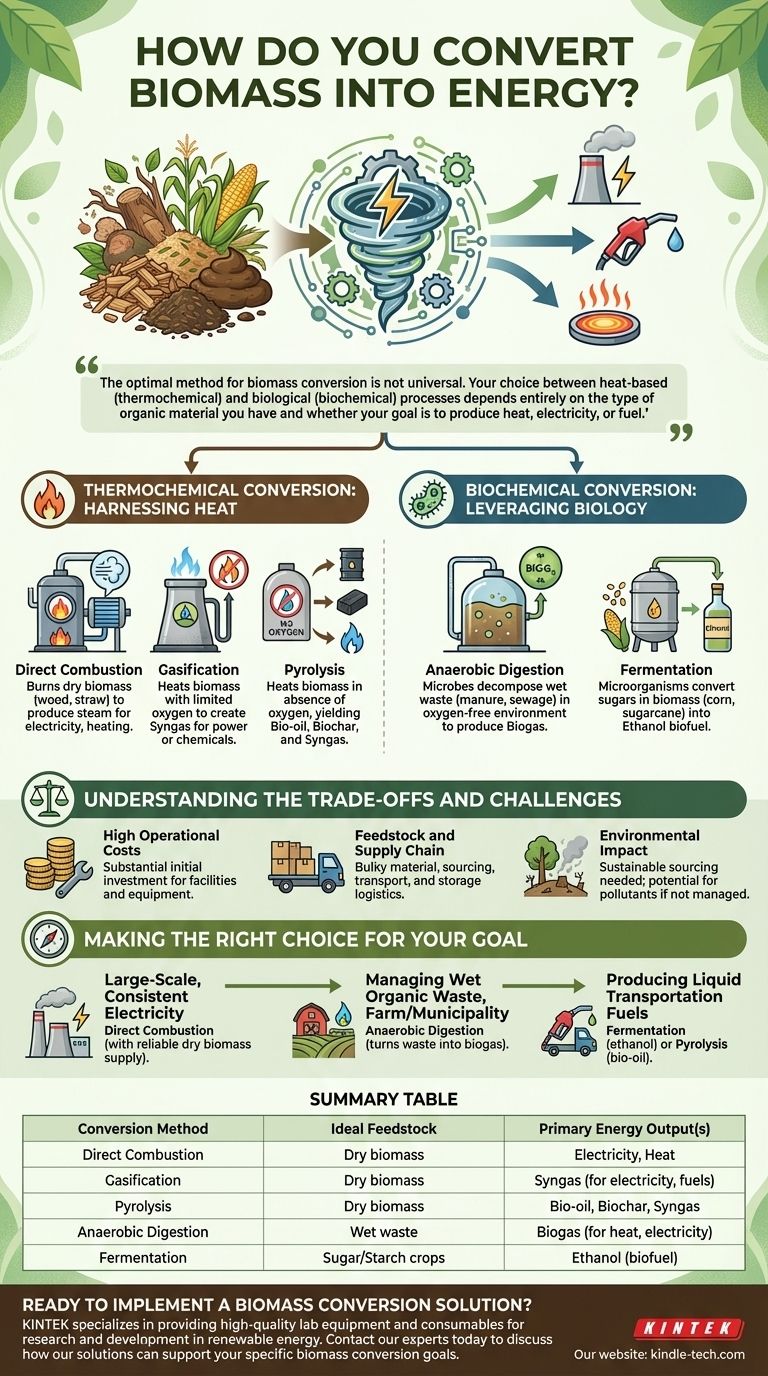
At its core, converting biomass into energy involves transforming organic matter into a usable form of power. This is primarily accomplished through two distinct categories of processes: thermochemical methods, which use heat to break down materials, and biochemical methods, which use microorganisms to decompose them.
The optimal method for biomass conversion is not universal. Your choice between heat-based (thermochemical) and biological (biochemical) processes depends entirely on the type of organic material you have and whether your goal is to produce heat, electricity, or fuel.

Thermochemical Conversion: Harnessing Heat
Thermochemical conversion uses high temperatures to convert biomass into energy. These methods are generally best suited for dry biomass like wood, straw, or other agricultural residues.
Direct Combustion
Direct combustion is the most straightforward and common method. It involves burning biomass in a boiler to produce high-pressure steam.
This steam then drives a turbine connected to a generator to produce electricity, or it can be used directly for industrial processes or heating.
Gasification
Gasification involves heating biomass with a limited amount of oxygen. This process doesn't burn the material completely but instead converts it into a flammable gas mixture called syngas.
This syngas is a flexible fuel that can be burned to generate electricity or further processed into liquid fuels and chemicals.
Pyrolysis
Pyrolysis is the process of heating biomass in the complete absence of oxygen.
This decomposition yields three key products: a liquid called bio-oil (which can be refined into fuel), a solid residue called biochar (a valuable soil amendment), and syngas.
Biochemical Conversion: Leveraging Biology
Biochemical processes use enzymes, bacteria, and other microorganisms to break down biomass. These methods are ideal for converting wet organic materials, such as sewage, animal manure, and food processing waste.
Anaerobic Digestion
This process uses microorganisms in an oxygen-free environment to decompose wet organic matter.
The primary output is biogas, which is mostly methane. This biogas can be captured and burned to generate localized heat and electricity, making it an excellent solution for farms and wastewater treatment plants.
Fermentation
Fermentation uses microorganisms (like yeast) to convert the carbohydrates and sugars in certain biomass crops (such as corn, sugarcane, or switchgrass) into alcohol.
The most common product is ethanol, a biofuel that is blended with gasoline to power vehicles.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Challenges
While biomass is a renewable resource, its conversion to energy is not without significant challenges that require careful consideration.
High Operational Costs
The initial investment for building a biomass energy facility can be substantial. Construction, production equipment, and ongoing maintenance contribute to high costs that can be a barrier to entry.
Feedstock and Supply Chain
Biomass is often bulky, has a lower energy density than fossil fuels, and may be geographically dispersed. Sourcing, collecting, transporting, and storing the raw material efficiently is a major logistical and financial challenge.
Environmental Impact
If not managed sustainably, sourcing biomass can lead to deforestation or competition for land that would otherwise be used for food production. Furthermore, direct combustion can release air pollutants like nitrogen oxides and particulates if not properly controlled.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the correct conversion technology is critical for a successful biomass project. Your decision should be guided by your available resources and ultimate energy goal.
- If your primary focus is large-scale, consistent electricity: Direct combustion is the most established and powerful method, assuming a reliable supply of dry biomass like wood chips or agricultural pellets.
- If your primary focus is managing wet organic waste: Anaerobic digestion is the ideal solution, as it effectively turns a waste stream from a farm, municipality, or food processor into valuable biogas.
- If your primary focus is producing liquid transportation fuels: Fermentation (for ethanol) or pyrolysis (for bio-oil) are the designated pathways, though they require specific types of feedstocks and often complex refining processes.
By understanding these distinct conversion pathways, you can strategically align your biomass resources with your specific energy objectives.
Summary Table:
| Conversion Method | Ideal Feedstock | Primary Energy Output(s) |
|---|---|---|
| Direct Combustion | Dry biomass (wood chips, straw) | Electricity, Heat |
| Gasification | Dry biomass | Syngas (for electricity, fuels) |
| Pyrolysis | Dry biomass | Bio-oil, Biochar, Syngas |
| Anaerobic Digestion | Wet waste (manure, sewage) | Biogas (for heat, electricity) |
| Fermentation | Sugar/Starch crops (corn, sugarcane) | Ethanol (biofuel) |
Ready to implement a biomass conversion solution in your lab or facility?
KINTEK specializes in providing high-quality lab equipment and consumables for research and development in renewable energy. Whether you are optimizing pyrolysis processes, analyzing bio-oil, or testing biogas yields, we have the reliable equipment you need to advance your biomass energy projects.
Contact our experts today to discuss how our solutions can support your specific biomass conversion goals and help you achieve efficient, sustainable energy production.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace Biomass Pyrolysis Plant
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Electric Rotary Kiln Continuous Working Small Rotary Furnace Heating Pyrolysis Plant
- Customizable High Pressure Reactors for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
- High Pressure Laboratory Autoclave Reactor for Hydrothermal Synthesis
People Also Ask
- Can you distill CBD? Master the Art of High-Purity CBD Refinement
- What is the role of a laboratory ultra-low temperature freezer in stainless steel corrosion studies? Ensure Data Integrity
- How do incubators keep a constant temperature? Precision Control for Reliable Cell Culture
- What are the physical properties of pyrolysis? Unlocking the Complex Nature of Pyrolysis Oil
- Are biofuels cheaper to produce? Unpacking the True Cost vs. Fossil Fuels
- What can I use instead of rotavap? Find the Perfect Solvent Removal Tool for Your Lab
- How profitable is biochar? Unlock Revenue from Waste, Energy, and Carbon Credits
- How many types of hardening techniques are there? A Multi-Layered Security Strategy Explained



















