To prevent a crucible from cracking, you must heat it slowly and uniformly to avoid thermal shock. Rapid temperature changes cause different parts of the material to expand at different rates, creating internal stress that leads to fractures. This is especially true if the crucible has absorbed any moisture, which can turn to steam and violently break the material from within.
The core principle is simple: brittle ceramic materials cannot tolerate sudden, uneven temperature changes. Your primary goal is to manage the rate of heating and cooling to ensure the entire crucible changes temperature as gradually and uniformly as possible.

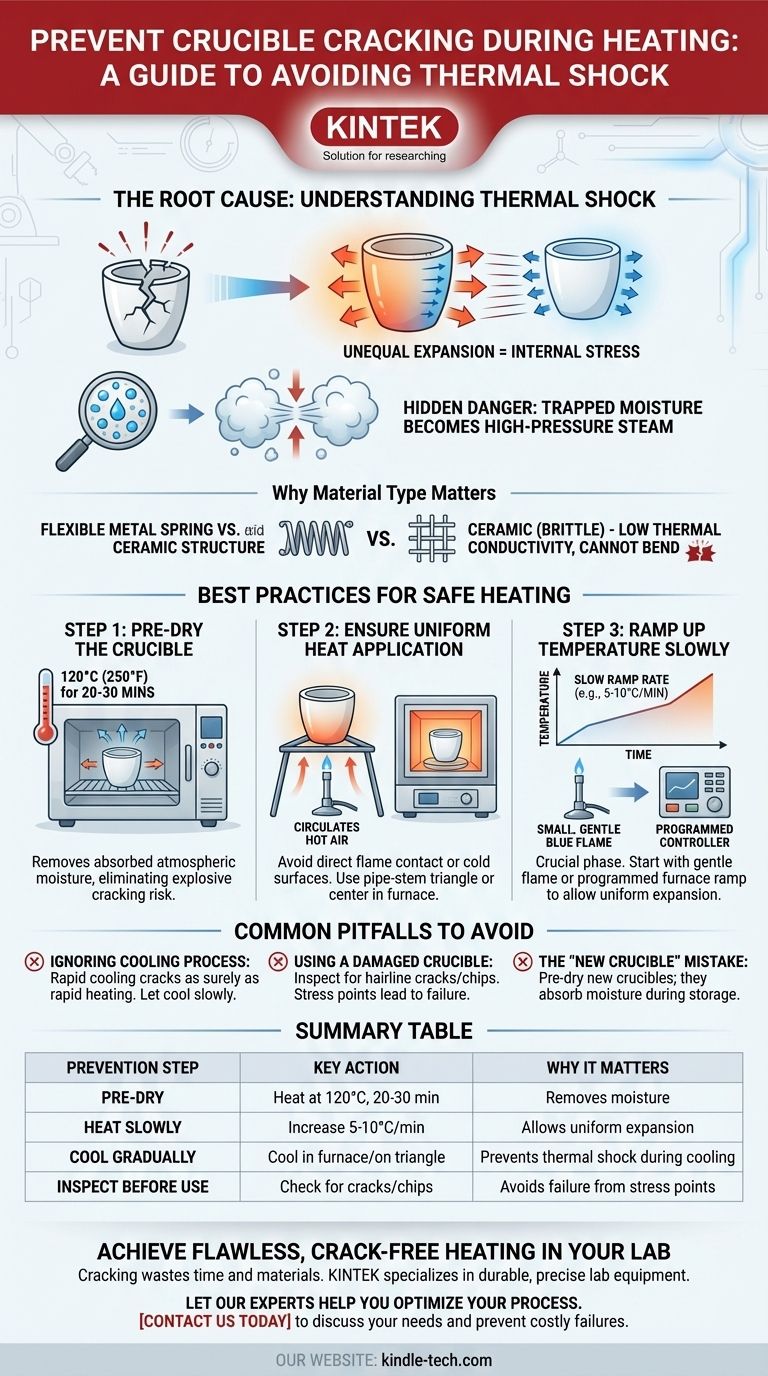
The Root Cause: Understanding Thermal Shock
Thermal shock is the single greatest threat to the integrity of a crucible. Understanding why it happens is the key to preventing it.
What Creates the Stress?
When one part of the crucible gets hot, it expands. If another part remains cool, it does not expand. This difference in size creates immense internal tension within the rigid, brittle structure of the ceramic. Once that tension exceeds the material's strength, it cracks.
The Hidden Danger of Moisture
Crucibles, especially those made of porcelain or clay, are porous and can absorb moisture from the air. When heated rapidly, this trapped water turns into high-pressure steam inside the material's microscopic pores. This internal pressure effectively blows the crucible apart from the inside, causing it to crack or even shatter.
Why Material Type Matters
Materials like porcelain, alumina, or zirconia are chosen for their high-temperature resistance, not their flexibility. Unlike metal, they have low thermal conductivity (heat moves through them slowly) and do not bend or stretch to accommodate stress. This makes them inherently vulnerable to cracking from uneven heating.
Best Practices for Safe Heating
Following a methodical heating procedure is not about being overly cautious; it's about respecting the physical limitations of the material.
Step 1: Always Pre-Dry the Crucible
Before any high-temperature use, gently pre-heat the crucible in a drying oven at around 120°C (250°F) for at least 20-30 minutes. This critical first step safely removes any absorbed atmospheric moisture, eliminating the primary cause of explosive cracking.
Step 2: Ensure Uniform Heat Application
Never place a crucible directly on a cold surface or concentrate a powerful flame on a single spot.
- Use a pipe-stem triangle to support the crucible over a flame. This allows hot air to circulate and heat the bottom and lower sides evenly.
- If using a furnace, ensure the crucible is placed in the center, away from direct contact with colder elements or walls.
Step 3: Ramp Up the Temperature Slowly
The most crucial phase is the initial temperature increase.
- With a Bunsen burner, start with a small, gentle, blue flame, warming the entire base of the crucible. Only after the entire piece is warm should you gradually increase the flame's intensity.
- With a muffle furnace, use a programmed controller to increase the temperature slowly. A ramp rate of 5-10°C per minute is a safe starting point for most applications.
Common Pitfalls to Avoid
Simple mistakes are often the cause of repeated failures. Being aware of these common errors can save you time, money, and materials.
Ignoring the Cooling Process
Thermal shock works both ways. Placing a red-hot crucible onto a cold lab bench or into a cool desiccator will crack it just as surely as rapid heating. Allow the crucible to cool slowly inside the furnace or on the triangle until it is safe to touch.
Using a Damaged Crucible
Before every use, inspect your crucible for hairline cracks, chips, or defects. Even a microscopic fracture creates a stress point. When heated, this tiny flaw will inevitably grow and lead to a complete failure of the crucible. Never use damaged equipment.
The "New Crucible" Mistake
Do not assume a brand-new crucible is ready for high heat. New crucibles have been sitting in storage, potentially for months, and have likely absorbed moisture. They must be pre-dried just like any other crucible.
How to Apply This to Your Process
Your specific heating protocol will depend on your equipment and objective.
- If your primary focus is simple drying or ashing with a Bunsen burner: Begin with a gentle "brushing" flame across the crucible's base and slowly increase its size over several minutes, ensuring the entire bottom is heated before applying intense heat.
- If your primary focus is high-temperature melting in a furnace: Program a slow ramp-up rate (e.g., 200°C/hour) to the target temperature and include a slow cooling ramp in your program as well.
- If your primary focus is safety and repeatability: Always pre-dry your crucible in an oven before it goes into a high-temperature environment, regardless of the heat source you plan to use.
Treating your crucible with an understanding of its material properties is the definitive way to ensure safe, repeatable, and successful results.
Summary Table:
| Prevention Step | Key Action | Why It Matters |
|---|---|---|
| Pre-Dry | Heat at 120°C (250°F) for 20-30 min | Removes moisture to prevent steam pressure cracks |
| Heat Slowly | Increase temperature at 5-10°C/min | Allows uniform expansion, reducing internal stress |
| Cool Gradually | Let cool inside furnace or on a triangle | Prevents thermal shock during the cooling phase |
| Inspect Before Use | Check for hairline cracks or chips | Avoids failure from existing stress points |
Achieve flawless, crack-free heating in your lab.
Cracking crucibles wastes time, money, and materials. KINTEK specializes in high-performance lab equipment and consumables designed for durability and precise thermal control. Our crucibles and furnaces are engineered to withstand rigorous use, but proper handling is key.
Let our experts help you optimize your process for maximum safety and repeatability.
Contact us today to discuss your specific laboratory needs and discover how KINTEK's solutions can enhance your results and prevent costly equipment failures.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Arc-Shaped Alumina Ceramic Crucible High Temperature Resistant for Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics
- Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics Alumina Al2O3 Crucible With Lid Cylindrical Laboratory Crucible
- Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics Alumina Crucibles (Al2O3) for Thermal Analysis TGA DTA
- Alumina Al2O3 Ceramic Crucible Semicircle Boat with Lid for Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics
- Engineering Advanced Fine Alumina Al2O3 Ceramic Crucible for Laboratory Muffle Furnace
People Also Ask
- Why are high-purity alumina crucibles selected for microwave red mud treatment? Ensure Purity and Energy Efficiency
- What are the functions of a high-purity graphite crucible in the FFC Cambridge process? Optimize Your Alloy Production
- What is a crucible porcelain? Choosing the Right High-Temperature Lab Vessel
- What is the efficiency of a crucible furnace? A Guide to Thermal Performance & Trade-offs
- Why do my crucibles keep breaking? Prevent Thermal Shock and Extend Crucible Life
- Does crucible size matter? Optimize Your Melt for Efficiency, Quality, and Safety
- What is the best crucible for melting copper? Choose Silicon Carbide or Clay Graphite for Optimal Performance
- What temperature can a crucible withstand? A Guide to Material Selection for Safe Melting



















