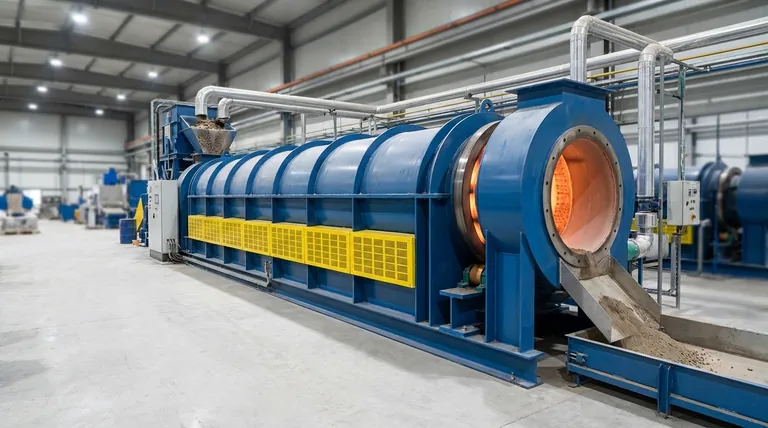
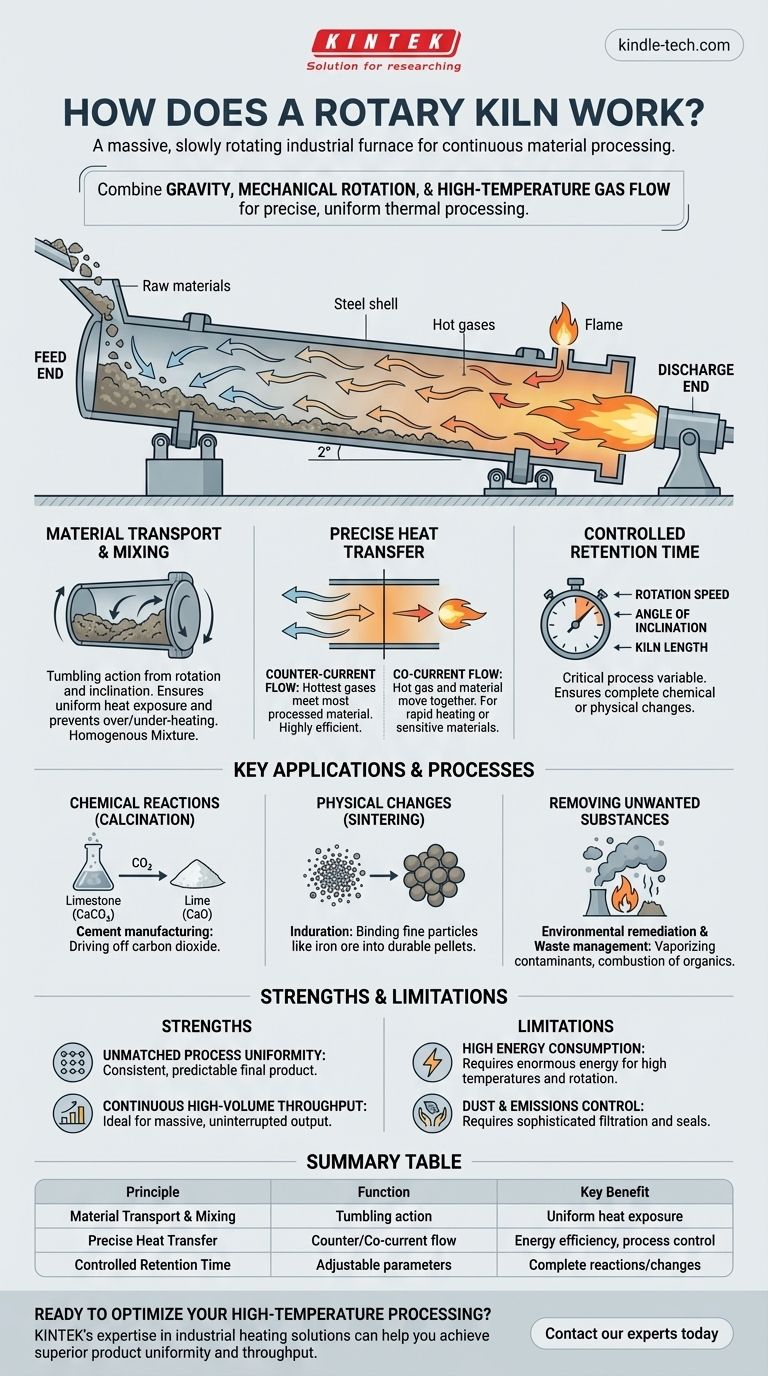
In essence, a rotary kiln is a massive, slowly rotating industrial furnace designed for continuous material processing. It consists of a long, hollow cylinder inclined at a slight angle. As the cylinder turns, raw material fed into the higher end tumbles and mixes as it gradually moves down toward the lower end, ensuring every particle is evenly exposed to the extremely high temperatures generated within.
The core principle of a rotary kiln is its ability to combine three simple forces—gravity, mechanical rotation, and high-temperature gas flow—to achieve precise, uniform, and continuous thermal processing of solid materials on an industrial scale.

The Core Principles of Operation
A rotary kiln's effectiveness comes from the elegant interplay of a few key physical principles. Understanding these is crucial to understanding why it's a cornerstone of heavy industry.
H3: Material Transport and Mixing
The entire system is built around controlled movement. The kiln is mounted on a slight angle, typically 1-4 degrees from the horizontal.
This inclination ensures that gravity constantly pulls material from the feed end toward the discharge end.
Simultaneously, the slow rotation of the cylinder continuously lifts the material up the side before it tumbles back down. This tumbling action is the key to ensuring a homogenous mixture and preventing any part of the material from being over- or under-heated.
H3: Precise Heat Transfer
Heat is applied via hot gases that flow through the length of the kiln. This can be achieved in two primary ways.
Counter-current flow is most common, where hot gases are introduced at the lower discharge end and flow up against the descending material. This is highly efficient, as the hottest gases meet the most processed material, and the coolest gases preheat the incoming raw material.
Co-current flow involves the hot gas and material moving in the same direction. This is used for specific processes where rapid heating is required or the material is sensitive to high initial temperatures.
The heat itself is often generated by a large burner or flame located inside the kiln at the discharge end.
H3: Controlled Retention Time
The amount of time material spends inside the kiln, known as retention time, is a critical process variable.
This is precisely controlled by adjusting three factors: the speed of rotation, the angle of inclination, and the length of the kiln. Slower rotation or a shallower angle increases the time the material is exposed to heat, ensuring a desired chemical reaction or physical change is fully completed.
Key Applications and Processes
Rotary kilns are not just furnaces; they are chemical reactors. Their design is optimized to facilitate specific transformations in the material being processed.
H3: Inducing Chemical Reactions (Calcination)
The most famous application is in cement manufacturing, where a kiln is used for calcination.
In this process, limestone (calcium carbonate) is heated to drive off carbon dioxide, producing lime (calcium oxide), a primary ingredient in cement. The kiln's ability to maintain a specific temperature profile is essential for this reaction.
H3: Driving Physical Changes (Sintering)
Kilns are used for sintering or induration, a process that changes a material's physical structure without melting it.
Fine particles, like iron ore dust, are heated until their surfaces begin to fuse. This binds them together into strong, durable pellets that are easier to handle and process in a blast furnace.
H3: Removing Unwanted Substances
In environmental applications, kilns excel at remediation. Thermal desorption uses heat to vaporize and remove contaminants like oil or mercury from soil.
For waste management, kilns function as highly efficient incinerators for the combustion of organic materials, ensuring complete and controlled destruction.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While incredibly powerful, the rotary kiln is a specialized tool with inherent benefits and limitations.
H3: Strength: Unmatched Process Uniformity
The constant tumbling and mixing action is a kiln's greatest advantage. It guarantees that every particle receives nearly identical exposure to heat, resulting in a highly consistent and predictable final product that is difficult to achieve in static furnaces.
H3: Strength: Continuous High-Volume Throughput
Unlike a batch furnace that must be loaded and unloaded, a rotary kiln operates continuously. This makes it the ideal solution for industries that require massive, uninterrupted output, such as cement and mineral processing.
H3: Limitation: High Energy Consumption
Heating a massive steel cylinder to over 1,400°C (2,550°F) and keeping it rotating requires an enormous amount of energy. This makes them expensive to operate and a significant factor in a plant's overall energy footprint.
H3: Limitation: Dust and Emissions Control
The combination of tumbling material and high-velocity gas flow inevitably creates dust. Modern rotary kiln systems require sophisticated seals, filters, and other air pollution control equipment to operate safely and meet environmental regulations.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The decision to use a rotary kiln is driven by the specific requirements of the thermal process.
- If your primary focus is high-volume manufacturing of a uniform product like cement or lime: The continuous operation and superior mixing of a rotary kiln are unparalleled.
- If your primary focus is driving a specific chemical reaction at a precise temperature: A kiln's ability to maintain a controlled temperature profile and retention time is essential for success.
- If your primary focus is agglomerating fine powders into durable pellets: The tumbling action is ideal for the sintering and induration processes required in mining and metallurgy.
Ultimately, a rotary kiln is an engineered solution for applying precise, uniform heat to solid materials on an immense industrial scale.
Summary Table:
| Principle | Function | Key Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Material Transport & Mixing | Tumbling action from rotation and inclination | Ensures uniform heat exposure for a consistent product |
| Precise Heat Transfer | Counter-current or co-current hot gas flow | Optimizes energy efficiency and process control |
| Controlled Retention Time | Adjusted via rotation speed, angle, and kiln length | Guarantees complete chemical reactions or physical changes |
Ready to optimize your high-temperature processing?
Whether your goal is calcination, sintering, or thermal desorption, KINTEK's expertise in industrial heating solutions can help you achieve superior product uniformity and throughput. Our team specializes in matching the right equipment to your specific material and production goals.
Contact our experts today to discuss how we can support your laboratory or industrial process needs.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Pyrolysis Furnace Plant Machine Calciner Small Rotary Kiln Rotating Furnace
- Electric Rotary Kiln Continuous Working Small Rotary Furnace Heating Pyrolysis Plant
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace for Activated Carbon Regeneration
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace Biomass Pyrolysis Plant
People Also Ask
- What is the difference between calcining and roasting? A Guide to High-Temperature Processing
- What are the zones in rotary kiln in cement production? Master the Core Process for High-Quality Clinker
- What is the purpose of a calciner? Boost Efficiency in High-Temperature Processing
- What is the principle of rotary kiln? Mastering Continuous Thermal Processing
- What are the industrial applications of pyrolysis? Transform Waste into Energy and Valuable Products



















