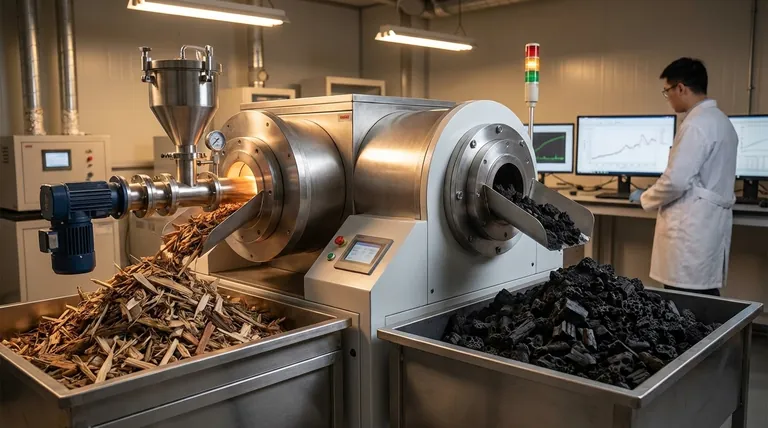
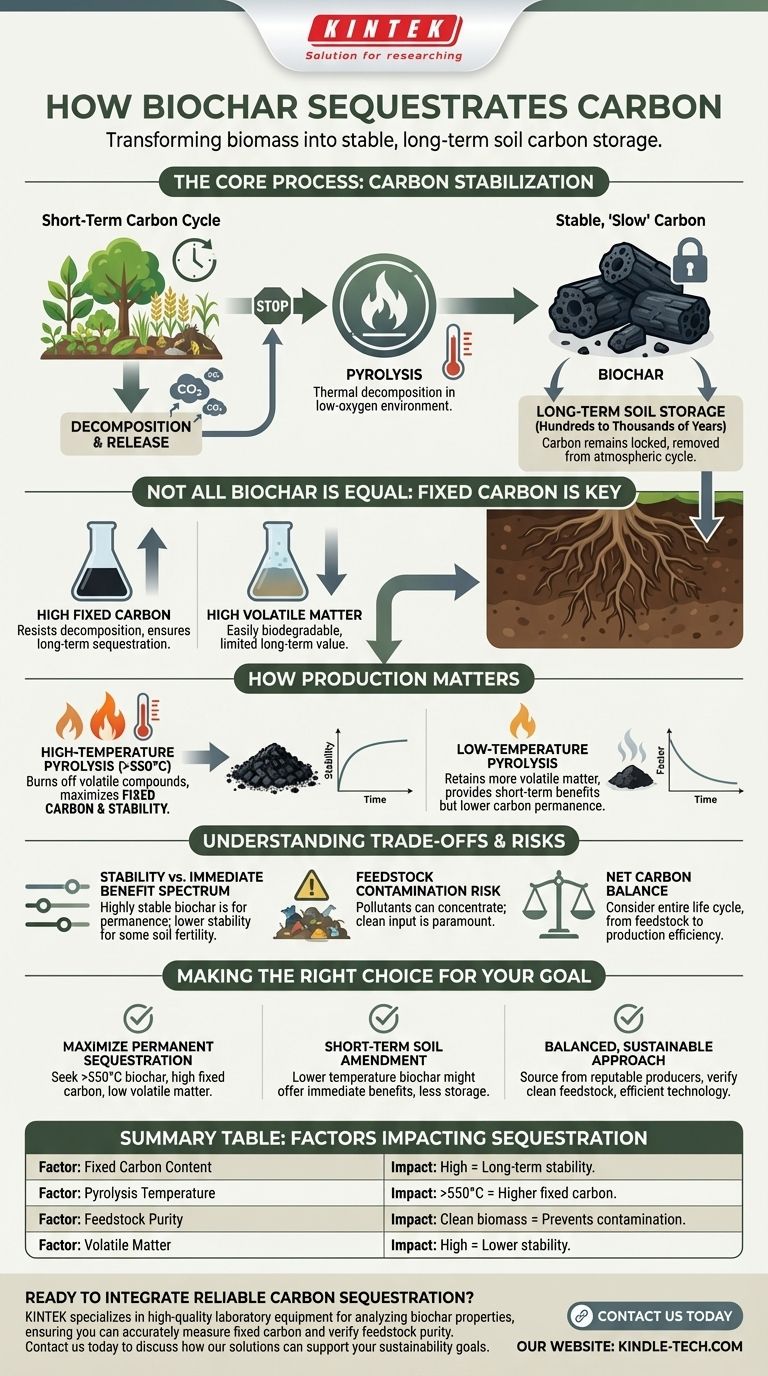
At its core, biochar sequesters carbon by transforming plant biomass, which would otherwise decompose and release its carbon, into a highly stable, charcoal-like substance. This process, called pyrolysis, creates a form of carbon that can remain locked in the soil for hundreds or even thousands of years, effectively removing it from the atmospheric cycle.
Biochar's value for carbon sequestration is not inherent; it is determined by its stability. The key is producing biochar with a high percentage of fixed carbon, as this is the component that resists decomposition and ensures long-term storage in the soil.

The Fundamental Principle: Carbon Stabilization
The entire concept of biochar sequestration rests on converting "fast" carbon into "slow" carbon. Plants are part of a rapid carbon cycle, absorbing CO2 but releasing it back upon decay.
From Unstable to Stable Carbon
When plants, wood, or other organic materials decompose, microbes break them down, releasing most of their stored carbon back into the atmosphere as CO2. This is part of the natural, short-term carbon cycle.
Biochar interrupts this cycle. By heating the biomass in a low-oxygen environment, it fundamentally alters the carbon's chemical structure, making it incredibly resistant to microbial decomposition.
The Pyrolysis Process
This conversion happens through pyrolysis—the thermal decomposition of materials at elevated temperatures in the absence of oxygen.
Instead of combusting and releasing carbon, the process drives off water and volatile compounds, leaving behind a carbon-rich, porous solid. This is biochar.
Not All Biochar Is Created Equal
The effectiveness of biochar as a carbon sink depends entirely on its quality, which is dictated by the production process and the original material (feedstock).
Fixed Carbon vs. Volatile Matter
A critical distinction is between fixed carbon and volatile matter. Fixed carbon is the stable, pure carbon backbone that forms the durable structure of biochar. This is the portion responsible for long-term sequestration.
Conversely, volatile matter consists of less stable, more easily biodegradable carbon compounds. As noted in soil studies, biochar with a high amount of volatile matter can be quickly mineralized by soil microbes, defeating the purpose of long-term storage.
How Production Conditions Matter
The temperature of pyrolysis is the primary lever controlling this ratio. Higher production temperatures (typically >550°C) burn off more volatile compounds, resulting in a biochar with higher fixed carbon content and greater stability.
Lower-temperature pyrolysis produces biochar with more volatile matter. While these compounds may offer some short-term benefits for soil microbes, they do not contribute to long-term carbon removal.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While maximizing fixed carbon is ideal for sequestration, it's important to recognize the associated trade-offs. There is no single "best" biochar, only the best biochar for a specific goal.
The Stability vs. Soil Benefit Spectrum
Highly stable, high-temperature biochar is excellent for carbon permanence but may have fewer immediately available sites for nutrient exchange or microbial colonization.
Lower-temperature biochars, with their higher volatile content, can sometimes provide more immediate benefits to soil fertility but at the cost of long-term carbon stability. The carbon sequestration value is significantly lower.
The Risk of Feedstock Contamination
The quality of the input material is paramount. If the biomass feedstock is contaminated with heavy metals, plastics, or other pollutants, these contaminants can become concentrated in the final biochar product, posing a risk to soil and water health.
Net Carbon Balance
A true accounting of sequestration must consider the entire life cycle. This includes the energy used to collect feedstock, the emissions from the pyrolysis unit itself, and transportation. Modern, efficient pyrolysis systems are designed to capture and use the volatile gases as energy, creating a nearly carbon-neutral or even carbon-negative production process.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To apply this knowledge, you must first define your primary objective. Different goals demand different types of biochar.
- If your primary focus is maximizing permanent carbon sequestration: Seek out biochar produced at high temperatures (>550°C) with a certified high fixed carbon content and low volatile matter.
- If your primary focus is short-term soil fertility and amendment: A lower-temperature biochar might provide some benefits, but you must acknowledge its limited value for long-term carbon storage.
- If your primary focus is a balanced, sustainable approach: Source biochar from reputable producers who provide a full analysis of its properties, verify a clean feedstock, and use modern, energy-efficient pyrolysis technology.
Ultimately, understanding the properties of biochar empowers you to choose a product that reliably achieves your specific environmental or agricultural goal.
Summary Table:
| Factor | Impact on Carbon Sequestration |
|---|---|
| Fixed Carbon Content | High = Long-term stability and sequestration |
| Pyrolysis Temperature | >550°C = Higher fixed carbon, greater stability |
| Feedstock Purity | Clean biomass = Prevents soil contamination |
| Volatile Matter | High = Lower stability, faster decomposition |
Ready to integrate reliable carbon sequestration into your operations?
Choosing the right biochar is critical for achieving verifiable, long-term carbon removal. KINTEK specializes in providing high-quality laboratory equipment and consumables for analyzing biochar properties, ensuring you can accurately measure fixed carbon content and verify feedstock purity.
Contact us today using the form below to discuss how our solutions can support your sustainability goals, from research and development to quality assurance.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace for Activated Carbon Regeneration
- Electric Rotary Kiln Pyrolysis Furnace Plant Machine Calciner Small Rotary Kiln Rotating Furnace
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace Biomass Pyrolysis Plant
- Electric Rotary Kiln Continuous Working Small Rotary Furnace Heating Pyrolysis Plant
People Also Ask
- How do high-temperature reaction furnaces control in-situ MMCs? Master Material Precision and Structural Integrity
- What are the process advantages of using a rotary tube furnace for WS2 powder? Achieve Superior Material Crystallinity
- At what temperature is conventional pyrolysis done? Unlock the Right Temperature for Your Desired Product
- What are the equipment requirements for loading platinum (Pt) onto composite supports? Precise Stirring for High Dispersion
- How is a high-temperature calcination furnace utilized in BZY20 Sol-gel? Achieve Pure Cubic Perovskite Phases



















