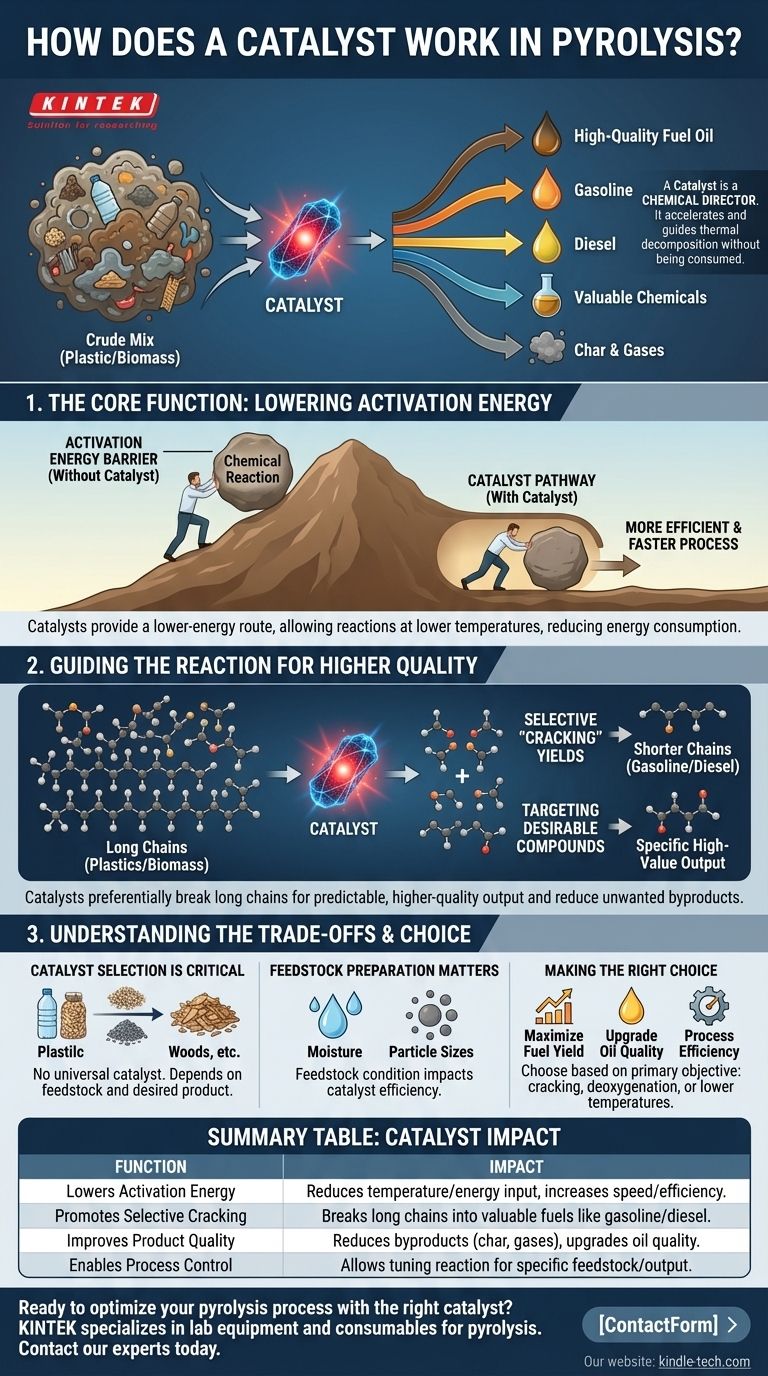
In short, a catalyst in pyrolysis acts as a chemical director. It is a substance that accelerates and guides the thermal decomposition of materials like plastic or biomass, promoting specific reactions that break down large, complex molecules into smaller, more valuable ones, such as those found in high-quality fuel oil. The catalyst achieves this without being consumed in the process itself.
The fundamental role of a catalyst is to lower the energy barrier for desired chemical reactions. This makes the pyrolysis process more efficient, faster, and allows for precise control over the final product, steering the outcome away from a crude mix of substances and towards valuable, upgradable fuels.
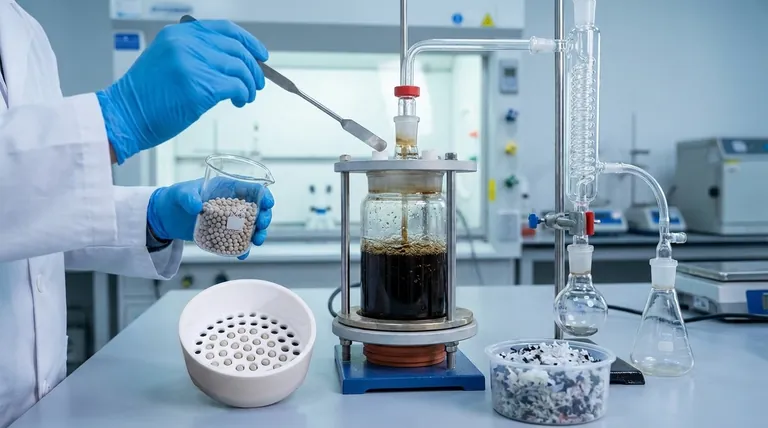

The Core Function: Lowering Activation Energy
Pyrolysis involves breaking strong chemical bonds, which requires a significant amount of energy. A catalyst fundamentally changes the energy equation of this process.
What is Activation Energy?
Think of a chemical reaction as pushing a boulder over a hill to get it to the valley on the other side. The height of that hill is the activation energy—the minimum energy required to get the reaction started.
How Catalysts Reduce This Barrier
A catalyst provides an entirely different route for the boulder—a lower pass or a tunnel through the hill. It creates an alternative pathway for the chemical reaction to follow, one that requires substantially less energy to initiate.
The Result: A More Efficient Process
By lowering the activation energy, the desired chemical reactions can occur at a faster rate and often at lower temperatures. This directly translates to reduced energy consumption and higher throughput for the entire pyrolysis system.
Guiding the Reaction for Higher Quality Output
Beyond just speeding things up, a catalyst's true power lies in its selectivity. It doesn't just break bonds randomly; it can be designed to target specific bonds to produce a predictable and higher-quality output.
Promoting Selective "Cracking"
The primary goal in fuel production is to "crack" the long, heavy hydrocarbon chains found in plastics or biomass into the shorter, lighter chains that make up gasoline and diesel. A well-chosen catalyst preferentially breaks these long chains while leaving smaller, more valuable molecules intact.
Targeting Desirable Compounds
Modern catalysts can be highly specialized or "tunable." For variable feedstocks like biomass, catalysts can be designed to favor reactions that yield specific high-value compounds, turning a basic decomposition process into a precise chemical manufacturing operation.
Reducing Unwanted Byproducts
Without a catalyst, pyrolysis can produce a significant amount of unwanted solid residue (char) and non-condensable gases. By directing the reaction pathways towards liquid fuel production, a catalyst inherently minimizes the formation of these less valuable byproducts.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Context
A catalyst is a powerful tool, but it is not a standalone solution. Its effectiveness is deeply interconnected with the entire pyrolysis system.
Catalyst Selection is Critical
There is no universal catalyst for pyrolysis. The choice depends entirely on the input material (the feedstock) and the desired final product. A catalyst that works wonders for turning plastics into diesel might be entirely ineffective for converting wood waste into bio-oil.
Feedstock Preparation Matters
The efficiency of any catalyst is influenced by the condition of the feedstock. Factors like moisture content and particle size must be carefully controlled. A catalyst cannot overcome the problems caused by poorly prepared input materials; it can only optimize the reaction of what it is given.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting and implementing a catalyst requires a clear understanding of your primary objective.
- If your primary focus is maximizing liquid fuel yield: You need a catalyst designed for efficient cracking of long-chain hydrocarbons, such as a zeolite-based catalyst.
- If your primary focus is upgrading oil quality: Choose a catalyst that promotes deoxygenation and the removal of impurities to create a product closer to a "drop-in" fuel.
- If your primary focus is process efficiency: The right catalyst can lower operating temperatures and reduce residence time, but this must be balanced with proper feedstock preparation to realize the full benefit.
Ultimately, a catalyst transforms pyrolysis from a brute-force thermal process into a refined and controllable engineering tool.
Summary Table:
| Function | Impact on Pyrolysis Process |
|---|---|
| Lowers Activation Energy | Reduces required temperature and energy input, increasing speed and efficiency. |
| Promotes Selective Cracking | Breaks long hydrocarbon chains into valuable fuels like gasoline/diesel. |
| Improves Product Quality | Reduces unwanted byproducts (char, gases) and upgrades oil quality. |
| Enables Process Control | Allows for tuning the reaction based on feedstock and desired output. |
Ready to optimize your pyrolysis process with the right catalyst?
KINTEK specializes in providing high-performance lab equipment and consumables for testing and scaling pyrolysis reactions. Our expertise helps you select the ideal catalyst for your specific feedstock—whether plastic, biomass, or other materials—to maximize fuel yield and quality.
Contact our experts today to discuss how we can enhance your pyrolysis efficiency and output.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Teflon Parts Manufacturer for PTFE Mesh F4 Sieve
- Custom PTFE Teflon Parts Manufacturer Adjustable Height Flower Basket
- Multifunctional Electrolytic Electrochemical Cell Water Bath Single Layer Double Layer
- Customizable CO2 Reduction Flow Cell for NRR ORR and CO2RR Research
- Custom PTFE Teflon Parts Manufacturer for PTFE Measuring Cylinder 10/50/100ml
People Also Ask
- How long is the calcination process? Optimize Your Process Time for Maximum Efficiency
- What are the disadvantages of rotary kiln incinerator? High Costs and Operational Complexities
- What is a calcining kiln? A Guide to Industrial Thermal Processing
- What is the most suitable temperature for burning of cement in rotary kiln? Achieve Perfect Clinker at 1450°C
- What is the refractory material of a rotary kiln? Choose the Right Lining for Efficiency & Durability
- What are the main parts of a rotary kiln? A Guide to Its Core Components and Functions
- What is the principle of a fluidized bed reactor? Achieve Superior Mixing and Heat Transfer
- How does the calcination process work? Master Thermal Decomposition for Material Purification



















