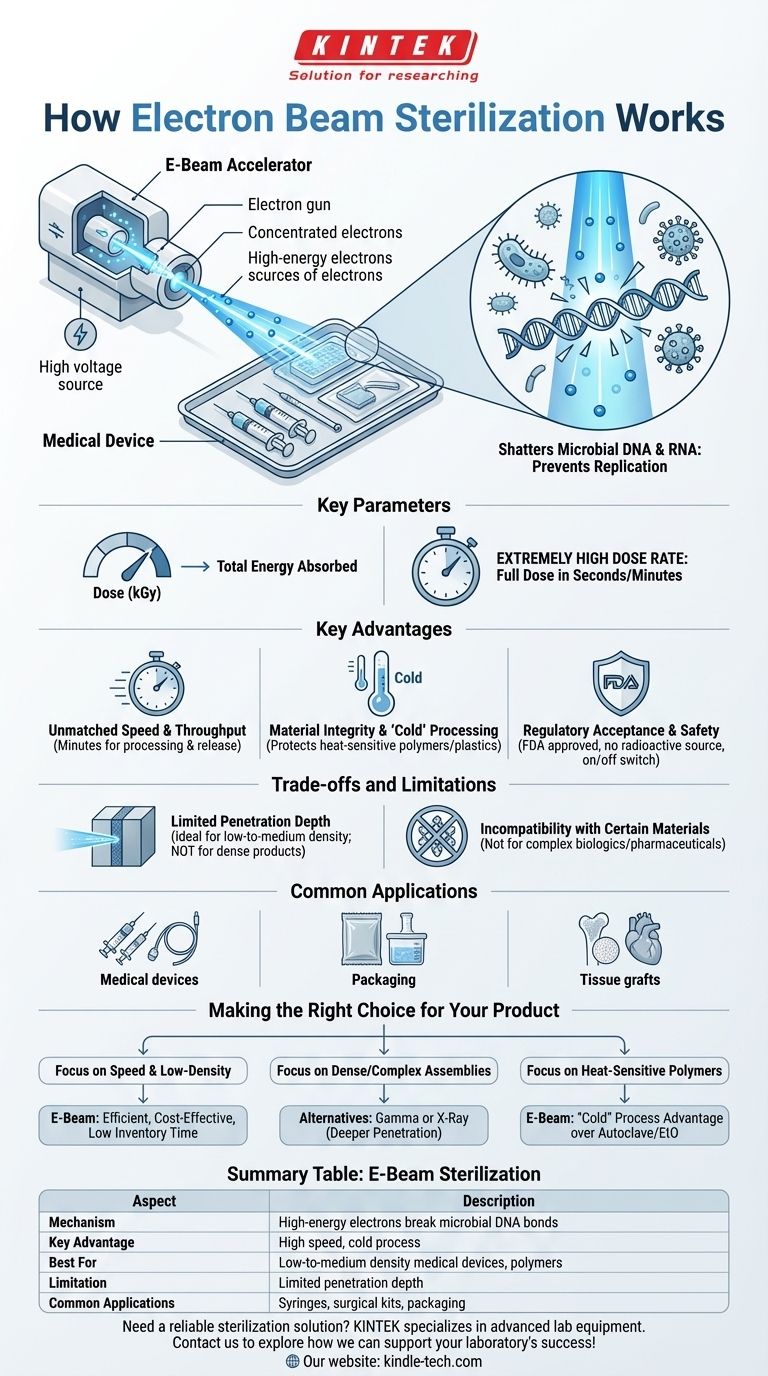
In essence, electron beam (e-beam) sterilization works by using a concentrated, high-energy stream of electrons to break the chemical bonds within the DNA of microorganisms. This damage renders bacteria, viruses, and other pathogens unable to reproduce, effectively sterilizing the product without using high heat or harsh chemicals. It is a form of ionizing radiation that offers a fast, safe, and highly effective method for sterilizing a wide range of products.
The core takeaway is that e-beam sterilization is a high-speed, "cold" process ideal for sterilizing low-to-medium density medical devices and materials. Its primary trade-off is a limited penetration depth compared to other radiation methods like gamma.

The Core Mechanism: How Electrons Achieve Sterility
Electron beam sterilization relies on a controlled and precise application of energy. The process can be broken down into two fundamental stages: generating the beam and its impact on microbial life.
Generating the Beam
An e-beam accelerator generates a powerful stream of electrons. These electrons are then accelerated to near the speed of light using high voltage, focusing them into a narrow, high-energy beam.
This concentrated beam is then scanned across the target product, much like a beam in an old cathode-ray tube television, ensuring the entire surface and a certain depth of the product receives the prescribed energy dose.
The Impact on Microorganisms
The true sterilizing action occurs when these high-energy electrons penetrate the product and collide with the molecules inside any present microorganisms.
This energy transfer primarily targets and shatters the DNA and RNA chains of the microbes. Without intact genetic material, the cells can no longer function or replicate, making them inert and non-hazardous. This direct molecular damage is what guarantees sterility.
Key Parameters: Dose and Dose Rate
The effectiveness of the process is governed by the radiation dose, measured in kiloGrays (kGy), which is the total amount of energy absorbed by the product.
E-beam technology is known for its extremely high dose rate. It can deliver a full, sterilizing dose in a matter of seconds or minutes, a significant advantage over other methods that may take hours.
Key Advantages of E-Beam Sterilization
The high-speed and targeted nature of e-beam technology provides several distinct benefits, making it a preferred choice for many modern applications.
Unmatched Speed and Throughput
The most significant advantage is processing speed. Because the sterilizing dose is delivered in minutes, products can be processed, verified, and released almost immediately, drastically reducing quarantine times and improving supply chain efficiency.
Material Integrity and "Cold" Processing
E-beam is effectively a "cold" process, as it causes a minimal temperature increase in the product. This is critical for protecting the integrity of heat-sensitive materials like polymers, plastics, and hydrogels, preventing the degradation that can occur with heat-based sterilization.
Regulatory Acceptance and Safety
The process is well-established, internationally accepted, and approved by the FDA. Unlike gamma sterilization, e-beam facilities do not require a persistent radioactive source (like Cobalt-60), which simplifies safety, handling, and security logistics. The system can be switched off completely.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
While powerful, e-beam technology is not a universal solution. Understanding its limitations is critical for proper application.
The Penetration Depth Constraint
The most significant trade-off is limited penetration. Electrons lose energy quickly as they pass through material. This makes e-beam ideal for low-to-medium density products in their final packaging but less suitable for very dense products or large, fully loaded pallets where the beam cannot reach the center.
Incompatibility with Certain Materials
Although gentle on many polymers, the high-energy radiation can be damaging to sensitive biological materials. E-beam is generally not recommended for complex biologics or certain pharmaceuticals where the radiation could damage the active molecules.
Product Configuration and Geometry
The product's shape and density must allow for uniform exposure to the beam. Complex devices with hidden internal surfaces or very dense components may experience a "shadowing" effect, where some areas do not receive the required sterilizing dose.
Common Applications: Where E-Beam Excels
E-beam is the method of choice when speed and material compatibility are paramount.
Medical Devices and Labware
This is the primary market for e-beam. It is exceptionally well-suited for single-use medical devices, including syringes, surgical kits, tubing, plastic labware, and wound dressings.
Pharmaceuticals and Packaging
The method is used to sterilize powders and can effectively penetrate sealed foil packaging and containers. It ensures the sterility of the final packaged product without compromising the container itself.
Tissue-Based Products
E-beam can be used for specific sterilized tissue materials such as bone grafts, cardiovascular valves, and aortic tissue, where its speed and low heat transfer are beneficial.
Making the Right Choice for Your Product
Selecting the correct sterilization method requires balancing product needs with process capabilities.
- If your primary focus is speed and high throughput for low-density products: E-beam is an exceptionally efficient and cost-effective choice that minimizes inventory holding time.
- If your primary focus is sterilizing dense, fully-loaded pallets or complex assemblies: You will likely need to consider alternatives like X-ray or gamma radiation, which offer deeper penetration.
- If your primary focus is preserving heat-sensitive polymers and plastics: E-beam's "cold" process provides a clear advantage over methods like autoclave (steam) or ethylene oxide (which also involves heat cycles).
Ultimately, a deep understanding of your product's material composition and density is the key to leveraging the right sterilization technology.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | E-Beam Sterilization |
|---|---|
| Mechanism | High-energy electrons break microbial DNA bonds |
| Key Advantage | High speed (seconds/minutes), cold process |
| Best For | Low-to-medium density medical devices, polymers, labware |
| Limitation | Limited penetration depth |
| Common Applications | Syringes, surgical kits, packaging, tissue grafts |
Need a reliable sterilization solution for your lab equipment? KINTEK specializes in providing advanced lab equipment and consumables tailored to your sterilization and research needs. Whether you're processing medical devices or sensitive materials, our expertise ensures efficiency and material integrity. Contact us today to explore how we can support your laboratory's success!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- VHP Sterilization Equipment Hydrogen Peroxide H2O2 Space Sterilizer
- Laboratory High Pressure Horizontal Autoclave Steam Sterilizer for Lab Use
- Desktop Fast Laboratory Autoclave Sterilizer 35L 50L 90L for Lab Use
- Electron Beam Evaporation Coating Oxygen-Free Copper Crucible and Evaporation Boat
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition PECVD Equipment Tube Furnace Machine
People Also Ask
- What are environmental impacts of biomass? Balancing Sustainability with Potential Harm
- What is the difference between oxidizing and reducing environments? Key Insights for Chemical Reactions
- What extreme conditions does a laboratory autoclave simulate? Testing Wear Resistance of Nuclear Fuel Cladding
- What is the standard time for sterilization? Optimize Your Process for Safety and Efficiency
- Are there any specific types of contamination that an autoclave cannot remove? Understanding the Limits of Steam


















