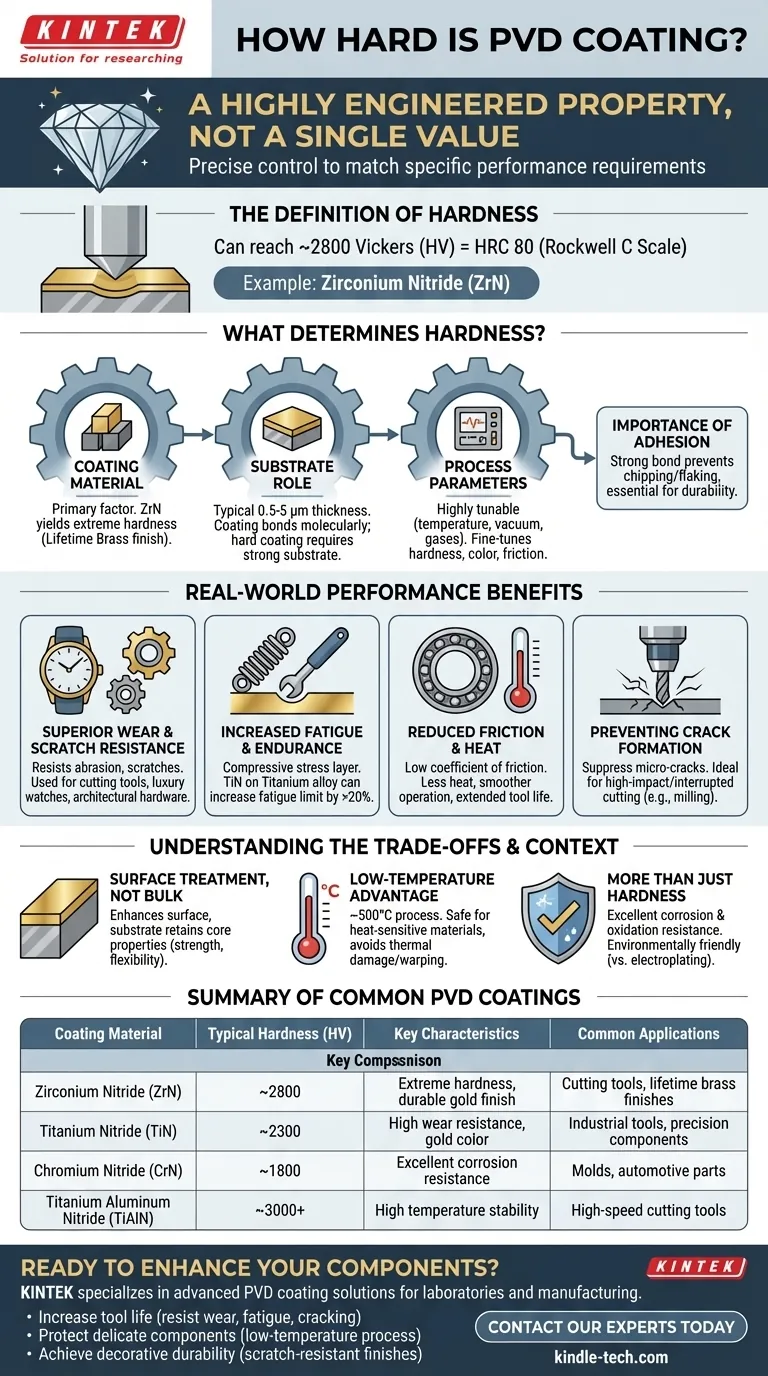
To be precise, a PVD coating like Zirconium Nitride (ZrN) can reach a hardness of 2800 Vickers, which is equivalent to HRC 80 on the Rockwell scale. However, the hardness of a PVD coating is not a single value; it is a highly engineered property that varies significantly based on the specific coating material used and the process parameters applied.
The key takeaway is that Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD) does not have one standard hardness. Instead, it is a sophisticated surface treatment process that creates an extremely hard, thin ceramic layer on a substrate, with the final hardness being precisely controlled to match the application's specific performance requirements.

What Determines the Hardness of a PVD Coating?
The final hardness and performance of a PVD coating are the result of a controlled interplay between the chosen material, the underlying substrate, and the deposition process itself.
The Coating Material
The type of ceramic or composite material deposited is the primary factor in determining potential hardness. Different materials yield different properties. For example, Zirconium Nitride (ZrN) is known for its extreme hardness and is often used for a durable "Lifetime Brass" finish.
The Role of the Substrate
A PVD coating is only a few microns thick (typically 0.5 to 5 μm). Its performance is fundamentally linked to the base material, or substrate, it is applied to. The coating molecularly bonds to the substrate, enhancing its surface properties. A hard coating on a strong, stable substrate will perform exceptionally well.
Control Over Process Parameters
The PVD process is highly tunable. Technicians can adjust factors like temperature, vacuum pressure, and the specific gases used in the chamber. These adjustments allow for fine-tuning the coating's final characteristics, including its hardness, color, and friction coefficient.
The Importance of Adhesion
A hard coating is only effective if it remains bonded to the substrate. The PVD process is designed to create high adhesion, ensuring the thin, hard layer does not chip or flake off under stress. This strong bond is what allows the coating to significantly increase the durability of the original part.
How Hardness Translates to Real-World Performance
The exceptional hardness of PVD coatings provides tangible benefits beyond just a number on a specification sheet. It directly improves the function and lifespan of the coated item.
Superior Wear and Scratch Resistance
The most direct benefit of high surface hardness is resistance to abrasion, scratches, and general wear. This is why PVD is used for everything from cutting tools and architectural hardware to luxury watches.
Increased Fatigue and Endurance
By creating a compressive stress layer on the surface, PVD coatings can significantly improve a material's fatigue life. For example, a Titanium Nitride (TiN) coating applied to a titanium alloy can increase its fatigue limit by over 20%.
Reduced Friction and Heat
Many PVD coatings have a very low coefficient of friction. For moving parts or cutting tools, this means less heat generation and smoother operation, which extends tool life and improves performance.
Preventing Crack Formation
The compressive stress inherent in the PVD process helps suppress the formation and expansion of micro-cracks on the surface. This makes PVD-coated tools particularly well-suited for high-impact or interrupted cutting operations like milling.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Context
While incredibly effective, it is crucial to understand what PVD is and what it is not.
It's a Surface Treatment, Not a Bulk Material
PVD enhances the surface of an object. A PVD-coated steel part is still a steel part at its core; it does not become a solid piece of ceramic. The coating imparts hardness and wear resistance to the surface while the substrate retains its original properties like strength and flexibility.
A Low-Temperature Advantage
PVD is a relatively low-temperature process, typically operating around 500°C. This is a significant advantage over other methods like Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD), as it allows for coating heat-sensitive materials without the risk of thermal damage or warping.
More Than Just Hardness
While hardness is a primary feature, PVD also provides excellent corrosion and oxidation resistance. Furthermore, it is an environmentally friendly process compared to traditional electroplating.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the right PVD coating depends entirely on your end goal.
- If your primary focus is extreme durability for industrial tools: A coating like TiN or ZrN should be specified, with the process optimized for maximum hardness and adhesion to withstand intense cutting forces.
- If your primary focus is a decorative finish with high scratch resistance: PVD offers a vast palette of stable, durable colors like black, blue, and brass that are far superior to paint or anodizing for items like jewelry, fixtures, or architectural components.
- If your primary focus is treating heat-sensitive or precision parts: The low-temperature nature of PVD makes it the ideal choice to add a hard surface without compromising the integrity of the underlying material.
Ultimately, PVD is best understood as a precise engineering solution that creates a functionally superior surface on an existing material.
Summary Table:
| Coating Material | Typical Hardness (HV) | Key Characteristics | Common Applications |
|---|---|---|---|
| Zirconium Nitride (ZrN) | ~2800 | Extreme hardness, durable gold finish | Cutting tools, lifetime brass finishes |
| Titanium Nitride (TiN) | ~2300 | High wear resistance, gold color | Industrial tools, precision components |
| Chromium Nitride (CrN) | ~1800 | Excellent corrosion resistance | Molds, automotive parts |
| Titanium Aluminum Nitride (TiAlN) | ~3000+ | High temperature stability | High-speed cutting tools |
Ready to enhance your components with a precisely engineered PVD coating?
At KINTEK, we specialize in advanced PVD coating solutions for laboratories and manufacturing. Our expertise ensures your parts achieve superior hardness, wear resistance, and longevity—tailored to your specific application needs.
We help you:
- Increase tool life with coatings that resist wear, fatigue, and cracking.
- Protect delicate components using our low-temperature process that avoids thermal damage.
- Achieve decorative durability with scratch-resistant finishes for consumer goods and architectural parts.
Let’s discuss how our PVD coatings can solve your surface challenges. Contact our experts today for a customized solution!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 915MHz MPCVD Diamond Machine Microwave Plasma Chemical Vapor Deposition System Reactor
- HFCVD Machine System Equipment for Drawing Die Nano-Diamond Coating
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine for Lamination and Heating
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Pulse Vacuum Lifting Sterilizer
- CVD Diamond Cutting Tool Blanks for Precision Machining
People Also Ask
- How difficult is it to grow a diamond? The Immense Challenge of Atomic-Level Precision
- What is the microwave plasma method? A Guide to High-Purity Material Synthesis
- What is MPCVD? Unlock Atom-by-Atom Precision for High-Purity Materials
- What is microwave plasma CVD? A Guide to High-Purity Diamond and Material Synthesis
- What is MPCVD method? A Guide to High-Purity Diamond Synthesis



















