In essence, the CVD process grows a diamond atom by atom inside a specialized reactor. A small, thin diamond "seed" is placed in a vacuum chamber, which is then heated to extreme temperatures and filled with a carbon-rich gas. This gas is energized into a plasma, which breaks it down and frees the carbon atoms to attach to the seed, slowly building up a new, larger diamond crystal over several weeks.
The Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) method is not about simulating the immense pressure found deep within the Earth. Instead, it is a feat of materials science that uses precise control over a low-pressure, high-temperature environment to coax carbon atoms into arranging themselves into a perfect diamond lattice.
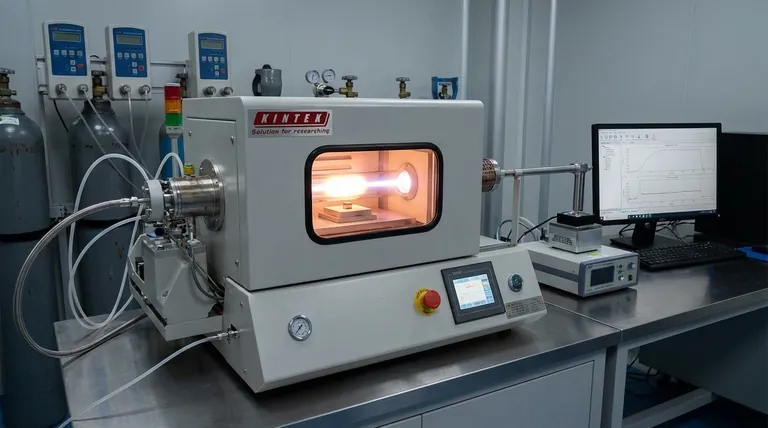

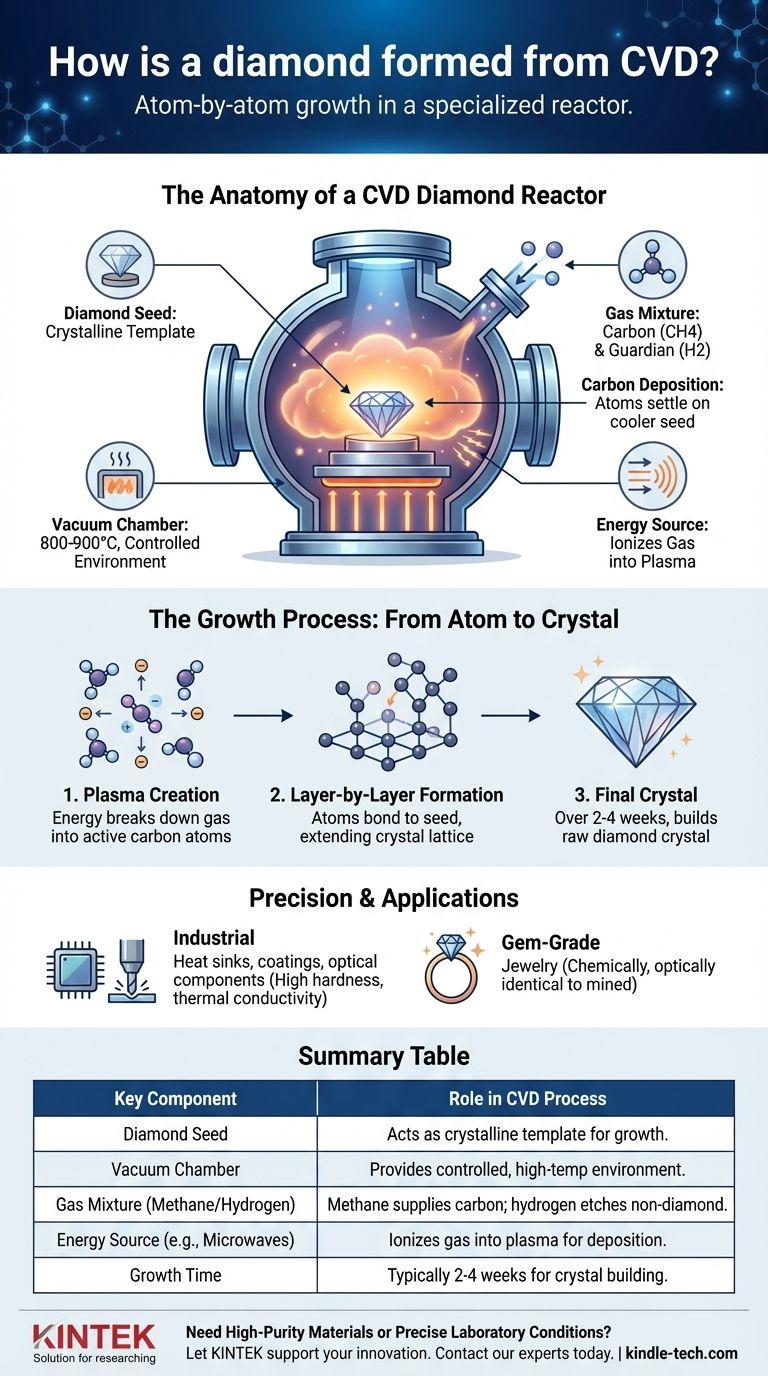
The Anatomy of a CVD Diamond Reactor
To understand how a CVD diamond is formed, you must first understand its four critical components: the seed, the chamber, the gas, and the energy source. Each plays a specific, interdependent role in the final outcome.
The Seed: The Blueprint for Growth
The process begins with a substrate, or diamond seed. This is typically a very thin, laser-cut slice from another high-quality diamond.
This seed is not just a starting point; it is the crystalline template. The new diamond will grow on top of this seed, perfectly mimicking its atomic structure. Meticulous cleaning of the seed is essential to prevent any imperfections.
The Chamber: A Controlled Vacuum Environment
The seed is placed inside a sealed vacuum chamber. The vacuum is critical because it removes all other atmospheric gases and contaminants that could interfere with the diamond's growth and purity.
Once sealed, the chamber is heated to between 800°C and 900°C (around 1,500°F). This high temperature provides the necessary energy for the chemical reactions to occur.
The Gas Mixture: Carbon and Its Guardian
A carefully calibrated mixture of gases is introduced into the chamber. The two primary components are a carbon source and hydrogen.
The most common carbon source is methane (CH4), a gas rich in the carbon atoms needed to build the diamond.
Hydrogen gas (H2) plays an equally crucial role. It acts as a "guardian" by selectively etching away any non-diamond carbon (like graphite) that may try to form. This ensures only the strong, desired diamond crystal structure is allowed to grow. The typical ratio is about 99% hydrogen to 1% methane.
The Catalyst: Creating Carbon Plasma
The gases are then energized, usually with microwaves, a hot filament, or a laser. This intense energy ionizes the gas into a plasma, stripping electrons from the atoms and breaking down the stable methane molecules.
This step releases pure, individual carbon atoms that are now chemically active and ready to bond.
The Growth Process: From Atom to Crystal
With the environment perfectly prepared, the diamond begins to form layer by layer in a highly controlled, methodical process.
Carbon Deposition
The freed carbon atoms are naturally drawn to and settle upon the slightly cooler surface of the diamond seed.
Layer-by-Layer Formation
Because the carbon atoms are depositing onto a diamond seed, they are forced to bond according to its existing crystal lattice. The diamond grows atom by atom, layer by layer, extending the original structure.
This process continues for two to four weeks, gradually building the raw diamond crystal. The final size of the diamond depends on the time it is allowed to grow.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Controls
The quality of a CVD diamond is not a matter of chance; it is a direct result of meticulous engineering and control over the growth environment.
Precision Is Everything
The final clarity, color, and purity of the diamond are determined by precise management of the process parameters. This includes the gas flow rate, the exact methane-to-hydrogen ratio, the chamber pressure, and the temperature stability. Any deviation can alter the final product.
Industrial vs. Gem-Grade Applications
This high level of control allows for the creation of diamonds for specific purposes. Because of their exceptional hardness, low friction, and high thermal conductivity, CVD diamonds are used as heat sinks in advanced electronics, coatings for cutting tools, and durable optical components.
The same process, when optimized for clarity and color, is used to grow the gem-quality diamonds used in jewelry. The resulting stone is chemically, physically, and optically identical to a mined diamond.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Understanding the CVD process empowers you to see the material for what it is: a triumph of controlled science.
- If your primary focus is technology and industry: CVD is a method for engineering a material with superior properties, allowing for the creation of high-performance components that would otherwise be impossible or uneconomical.
- If your primary focus is jewelry: The CVD process produces a real diamond whose quality and beauty are a testament to scientific precision, not its geological origin.
- If your primary focus is scientific understanding: CVD demonstrates how we can manipulate fundamental atomic processes to construct one of nature's most extreme materials from the ground up.
Ultimately, the CVD method reveals that these are not imitations, but diamonds engineered for a modern world.
Summary Table:
| Key Component | Role in CVD Process |
|---|---|
| Diamond Seed | Acts as a crystalline template for new diamond growth. |
| Vacuum Chamber | Provides a controlled, high-temperature (800-900°C) environment. |
| Gas Mixture (Methane/Hydrogen) | Methane supplies carbon; hydrogen etches away non-diamond carbon. |
| Energy Source (e.g., Microwaves) | Ionizes gas into a plasma, freeing carbon atoms for deposition. |
| Growth Time | Typically 2-4 weeks to build the diamond crystal layer by layer. |
Need High-Purity Materials or Precise Laboratory Conditions?
The controlled science behind CVD diamonds mirrors the precision we deliver at KINTEK. Whether you are developing advanced materials, require high-performance components, or need reliable lab equipment for sensitive processes, our expertise is your advantage.
Let KINTEK support your innovation. Contact our experts today to discuss how our laboratory solutions can help you achieve unparalleled quality and control in your work.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Customer Made Versatile CVD Tube Furnace Chemical Vapor Deposition Chamber System Equipment
- Cylindrical Resonator MPCVD Machine System Reactor for Microwave Plasma Chemical Vapor Deposition and Lab Diamond Growth
- Split Chamber CVD Tube Furnace with Vacuum Station Chemical Vapor Deposition System Equipment Machine
- 1200℃ Split Tube Furnace with Quartz Tube Laboratory Tubular Furnace
- Vertical Laboratory Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is a CVD tube furnace? A Complete Guide to Thin-Film Deposition
- Why are carbon nanotubes important in industry? Unlocking Next-Generation Material Performance
- What is the floating catalyst method? A Guide to High-Yield CNT Production
- What are the main advantages of Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD)? Achieve Precision Coating for Complex Geometries
- What are the advantages of industrial CVD for solid boriding? Superior Process Control and Material Integrity



















