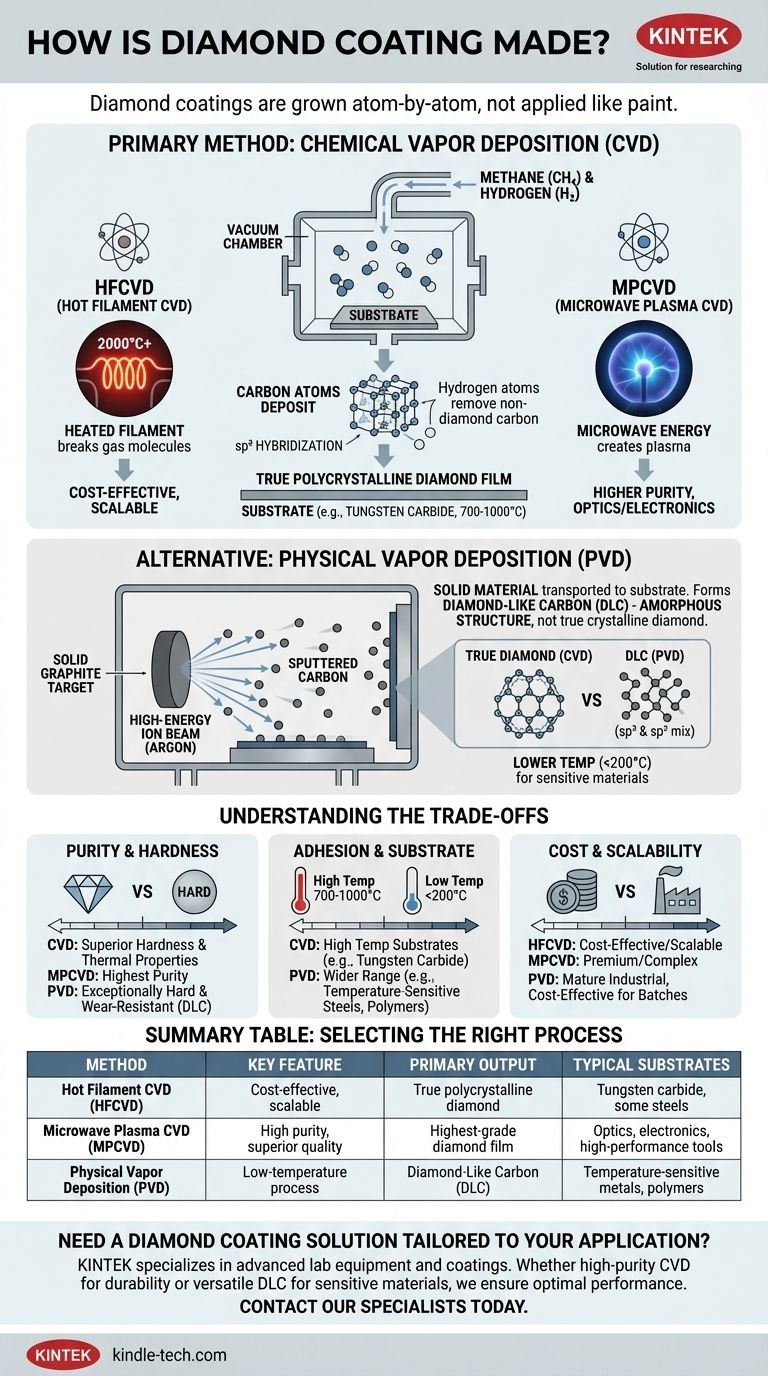
Diamond coatings are not applied like paint or plating; they are grown atom-by-atom directly onto a surface in highly controlled environments. The most prevalent method is Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD), a process that involves introducing carbon-rich gases (like methane) into a vacuum chamber and energizing them to break apart, allowing carbon atoms to arrange themselves into a crystalline diamond film on a substrate. A secondary family of techniques, Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD), is also used, though it often produces Diamond-Like Carbon (DLC), which has different properties than true diamond.
The method used to create a diamond coating is not just a manufacturing detail—it fundamentally dictates the coating's properties, from its purity and hardness to its cost and suitable applications. Choosing the right process is as important as choosing the coating itself.
The Primary Method: Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD)
Chemical Vapor Deposition is the workhorse for creating genuine, polycrystalline diamond films. It builds a coating from the bottom up using a chemical reaction in a gaseous state.
The Core Principle of CVD
Think of CVD like steam condensing on a cold mirror, but on a precise, atomic level. A carbon-containing gas (typically methane) mixed with hydrogen is fed into a low-pressure chamber containing the object to be coated, known as the substrate. Energy is then introduced to create a plasma, which breaks the gas molecules apart into reactive atomic carbon and hydrogen.
The atomic carbon then settles, or deposits, onto the hotter substrate surface. Under carefully controlled conditions, these carbon atoms link together in the strong tetrahedral bond structure (sp³ hybridization) that defines a true diamond crystal. The atomic hydrogen plays a critical role by selectively etching away any non-diamond carbon (sp² hybridization, like graphite) that may form, ensuring a pure diamond film grows.
Method 1: Hot Filament CVD (HFCVD)
This is one of the most common and cost-effective CVD methods. A tungsten filament, similar to the one in an old incandescent light bulb, is heated to over 2000°C.
The extreme heat from the filament provides the energy to break down the methane and hydrogen gases, initiating the deposition process. It's relatively simple and can be scaled to coat large surface areas.
Method 2: Microwave Plasma CVD (MPCVD)
This method uses microwave energy to create a dense, stable plasma ball inside the chamber. The substrate is placed directly within this highly energetic plasma.
MPCVD is a cleaner process than HFCVD because there is no filament to degrade and potentially contaminate the film. This allows for the growth of higher-purity, lower-stress diamond films with exceptional quality, making it the standard for high-performance applications like optics and electronics.
An Alternative: Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD)
PVD techniques operate on a different principle. Instead of building a film from a gas, they start with a solid material and transport it onto the substrate.
The PVD Process
In the context of carbon coatings, the PVD process typically involves placing a solid graphite target into a vacuum chamber. A high-energy beam of ions (often argon) is fired at the target, physically knocking carbon atoms off its surface.
This "sputtered" carbon material travels through the vacuum and deposits as a thin film onto the substrate. Think of it as a form of microscopic spray painting with individual atoms.
The Critical Distinction: Diamond vs. Diamond-Like Carbon (DLC)
It is crucial to understand that PVD processes rarely produce a true, crystalline polycrystalline diamond coating. Instead, they typically create Diamond-Like Carbon (DLC).
DLC is an amorphous material, meaning its atoms have no long-range crystal structure. It's a mixture of diamond-type (sp³) and graphite-type (sp²) bonds, often with hydrogen incorporated into the structure. While DLC is extremely hard and very slick (low friction), it does not possess the same thermal conductivity, optical transparency, or ultimate hardness of a true CVD diamond film.
Understanding the Trade-offs
The choice between these methods comes down to a balance of required performance, material compatibility, and cost.
Purity and Hardness
CVD produces true polycrystalline diamond, which is intrinsically harder and has superior thermal and optical properties. MPCVD offers the highest purity and quality.
PVD produces DLC, which is exceptionally hard and wear-resistant for many applications but is not as hard as pure diamond.
Adhesion and Substrate Material
CVD processes require very high substrate temperatures (700-1000°C), limiting their use to materials that can withstand the heat, like tungsten carbide, silicon nitride, and certain steels.
PVD is a lower-temperature process (often below 200°C), making it suitable for a much wider range of materials, including temperature-sensitive hardened steels, aluminum alloys, and even some polymers.
Cost and Scalability
HFCVD is generally the most cost-effective CVD method and scales well for coating large, simple geometries like cutting tool inserts.
MPCVD equipment is more complex and expensive, making it the premium choice for applications where ultimate performance justifies the cost. PVD is a mature industrial technology that can be very cost-effective for coating large batches of components.
Selecting the Right Process for Your Application
Choosing the correct coating starts with understanding the manufacturing process behind it.
- If your primary focus is maximum hardness and thermal conductivity: Choose Microwave Plasma CVD (MPCVD) for the highest purity polycrystalline diamond film.
- If your primary focus is coating wear-resistant tools on a budget: Consider Hot Filament CVD (HFCVD) as a cost-effective solution for true diamond coatings on compatible substrates.
- If your primary focus is lubricity and wear resistance on temperature-sensitive materials: A PVD-based Diamond-Like Carbon (DLC) coating is your most practical and versatile choice.
Understanding these fundamental production methods empowers you to look beyond marketing claims and select a coating based on the specific engineering performance you require.
Summary Table:
| Method | Key Feature | Primary Output | Typical Substrates |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hot Filament CVD (HFCVD) | Cost-effective, scalable | True polycrystalline diamond | Tungsten carbide, some steels |
| Microwave Plasma CVD (MPCVD) | High purity, superior quality | Highest-grade diamond film | Optics, electronics, high-performance tools |
| Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD) | Low-temperature process | Diamond-Like Carbon (DLC) | Temperature-sensitive metals, polymers |
Need a diamond coating solution tailored to your application? At KINTEK, we specialize in advanced lab equipment and consumables for cutting-edge material coatings. Whether you require high-purity CVD diamond for extreme durability or versatile DLC coatings for sensitive materials, our expertise ensures optimal performance and cost-efficiency. Contact our specialists today to discuss how our solutions can enhance your laboratory's capabilities!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition PECVD Equipment Tube Furnace Machine
- HFCVD Machine System Equipment for Drawing Die Nano-Diamond Coating
- Laboratory CVD Boron Doped Diamond Materials
- 915MHz MPCVD Diamond Machine Microwave Plasma Chemical Vapor Deposition System Reactor
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine for Lamination and Heating
People Also Ask
- What are the applications of physical vapor deposition method? Unlock Superior Thin-Film Performance
- What is a sputtering tool? A Guide to Precision Thin Film Deposition
- What conditions are needed to make artificial diamonds? A Guide to HPHT and CVD Methods
- What are the steps involved in CVD? Master the 6 Stages of Thin Film Deposition
- What are the types of thin film? A Guide to PVD vs. CVD Deposition Methods
- What equipment is needed for chemical vapor deposition? A Guide to the Essential CVD System Components
- What are the disadvantages of CVD? High Costs, Safety Risks, and Process Complexities
- On which factor properties of thin film varies? Master the Deposition Process for Optimal Performance



















